CAN FD offers higher data throughput and greater flexibility in message length compared to the traditional CAN 2.0 protocol, making it ideal for modern automotive and industrial applications that demand faster, more efficient communication. Explore the rest of the article to understand how adopting CAN FD can enhance Your network performance and compatibility.
Table of Comparison
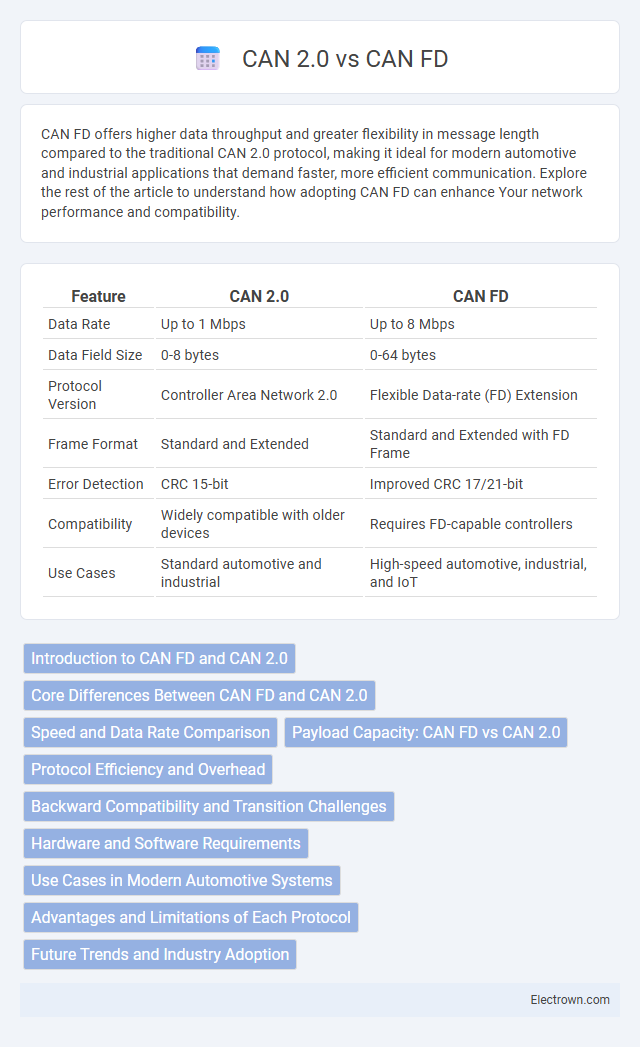
| Feature | CAN 2.0 | CAN FD |
|---|---|---|
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Mbps | Up to 8 Mbps |
| Data Field Size | 0-8 bytes | 0-64 bytes |
| Protocol Version | Controller Area Network 2.0 | Flexible Data-rate (FD) Extension |
| Frame Format | Standard and Extended | Standard and Extended with FD Frame |
| Error Detection | CRC 15-bit | Improved CRC 17/21-bit |
| Compatibility | Widely compatible with older devices | Requires FD-capable controllers |
| Use Cases | Standard automotive and industrial | High-speed automotive, industrial, and IoT |
Introduction to CAN FD and CAN 2.0
CAN FD (Controller Area Network Flexible Data-rate) extends the classic CAN 2.0 protocol by offering higher data transmission rates up to 8 Mbps and increased payload size of up to 64 bytes, compared to CAN 2.0's 1 Mbps and 8-byte limit. This advancement enables Your automotive or industrial network to handle more complex communication tasks with greater efficiency and speed. CAN FD maintains backward compatibility with CAN 2.0, ensuring seamless integration into existing CAN systems while providing enhanced performance.
Core Differences Between CAN FD and CAN 2.0
CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate) improves upon CAN 2.0 by increasing the maximum data payload from 8 bytes to 64 bytes per frame, enabling faster data transmission. The bit rate in CAN FD can dynamically switch between standard and higher speeds within the same message, optimizing communication efficiency. Your systems benefit from enhanced bandwidth and reliability by adopting CAN FD's flexible timing and extended frame format compared to CAN 2.0's fixed 1 Mbps rate and 8-byte payload limit.
Speed and Data Rate Comparison
CAN FD (Flexible Data-rate) significantly surpasses CAN 2.0 in speed, offering data rates up to 8 Mbps compared to CAN 2.0's maximum of 1 Mbps. CAN FD allows for longer data frames, increasing payload capacity from 8 bytes in CAN 2.0 to 64 bytes, enhancing data throughput and efficiency. This substantial improvement in data rate and frame size makes CAN FD ideal for modern automotive and industrial applications requiring faster communication and larger data transfers.
Payload Capacity: CAN FD vs CAN 2.0
CAN FD significantly increases payload capacity by allowing up to 64 bytes per frame compared to CAN 2.0's 8-byte limit, enhancing data throughput and communication efficiency. This expanded payload capacity supports complex applications in automotive and industrial systems that require larger data packets. You can achieve higher performance and system flexibility with CAN FD due to this improved data handling capability.
Protocol Efficiency and Overhead
CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate) enhances protocol efficiency by allowing larger data payloads up to 64 bytes compared to CAN 2.0's fixed 8-byte limit, reducing message overhead and increasing throughput. CAN FD supports faster bit rates during the data phase, significantly decreasing transmission time and bus load. This flexibility minimizes protocol overhead and improves bandwidth utilization in high-demand automotive and industrial networks.
Backward Compatibility and Transition Challenges
CAN FD maintains backward compatibility with CAN 2.0 by allowing controllers to communicate at traditional CAN 2.0 bit rates during a message's arbitration phase, ensuring seamless interaction with legacy systems. Transition challenges arise from differences in frame formats and data payload sizes, requiring updated hardware and software for full CAN FD support while still supporting older CAN 2.0 nodes. Network designers must carefully manage mixed networks to prevent communication errors and ensure reliable data transmission during the migration from CAN 2.0 to CAN FD.
Hardware and Software Requirements
CAN FD requires updated hardware compatible with flexible data rate and larger payloads up to 64 bytes, unlike CAN 2.0's fixed 8-byte limit and standard bit rate. Software for CAN FD must support extended frame formats and dynamic bit timing, while CAN 2.0 software is simpler, focusing on fixed 11-bit or 29-bit identifiers and consistent timing. Implementation of CAN FD demands careful integration of CAN transceivers, controllers, and protocol stacks to handle higher speeds and increased data throughput effectively.
Use Cases in Modern Automotive Systems
CAN FD offers higher data rates up to 8 Mbps and increased payload sizes, supporting advanced applications like autonomous driving and real-time sensor fusion that demand rapid and large data transfers. CAN 2.0 remains suitable for simpler control functions such as window regulation or door locking, where bandwidth requirements are lower. Your choice between CAN FD and CAN 2.0 should align with the complexity and data throughput needs of your automotive system.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Protocol
CAN FD offers higher data rates up to 8 Mbps and larger data payloads of up to 64 bytes, improving transmission efficiency over CAN 2.0, which supports only 1 Mbps and 8-byte payloads. CAN 2.0 provides widespread compatibility and proven reliability in legacy automotive and industrial applications but suffers from slower data transfer and limited message size. CAN FD enhances real-time data communication and system flexibility but requires updated hardware and software, potentially increasing implementation costs and complexity.
Future Trends and Industry Adoption
CAN FD offers a significant improvement over CAN 2.0 by supporting higher data rates up to 8 Mbps and larger payloads of up to 64 bytes, making it the preferred protocol for future automotive and industrial communication systems. Industry adoption is rapidly increasing as manufacturers prioritize CAN FD for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), electric vehicles, and industrial automation, driven by its enhanced performance and scalability. The trend toward integrating CAN FD with other automotive networks aligns with the growing demand for faster, more reliable in-vehicle data exchange and comprehensive diagnostics.
CAN FD vs CAN 2.0 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com