PID control provides precise and smooth regulation by continuously adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, effectively minimizing error over time. Bang-bang control, on the other hand, toggles output fully on or off with no intermediate states, offering simplicity but less accuracy; discover how these methods impact your system's performance by reading more.
Table of Comparison
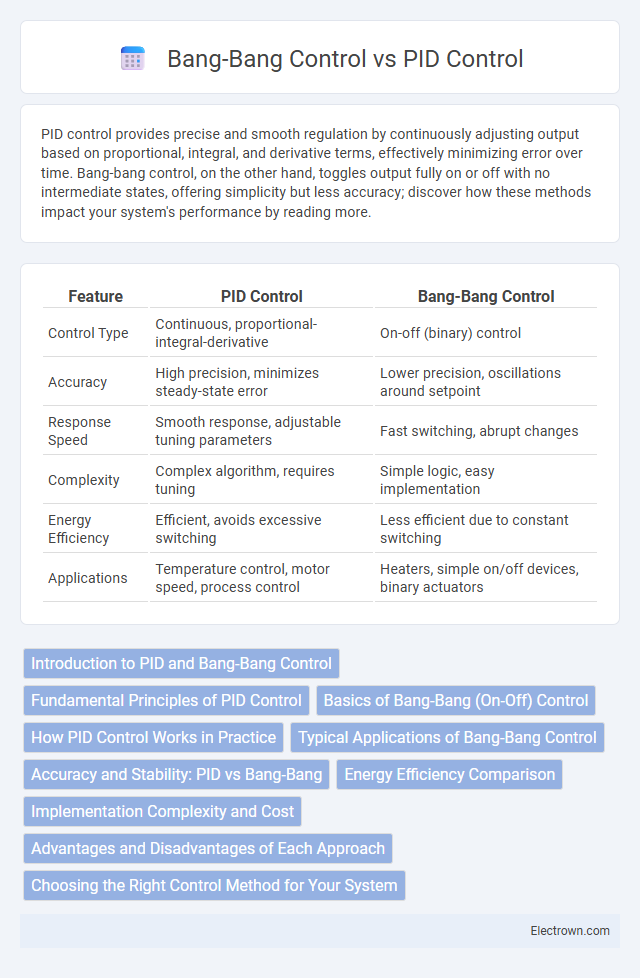
| Feature | PID Control | Bang-Bang Control |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Continuous, proportional-integral-derivative | On-off (binary) control |
| Accuracy | High precision, minimizes steady-state error | Lower precision, oscillations around setpoint |
| Response Speed | Smooth response, adjustable tuning parameters | Fast switching, abrupt changes |
| Complexity | Complex algorithm, requires tuning | Simple logic, easy implementation |
| Energy Efficiency | Efficient, avoids excessive switching | Less efficient due to constant switching |
| Applications | Temperature control, motor speed, process control | Heaters, simple on/off devices, binary actuators |
Introduction to PID and Bang-Bang Control
PID control continuously adjusts the control input based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize system error and ensure smooth, stable responses. Bang-Bang control operates by switching between two extreme states, fully on or fully off, offering simplicity and rapid response but often causing oscillations around the setpoint. While PID control is preferred for precision and stability in complex systems, Bang-Bang control is suitable for applications requiring straightforward implementation and quick toggling.
Fundamental Principles of PID Control
PID control operates by continuously calculating an error value as the difference between a desired setpoint and a measured process variable, leveraging proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize this error over time. The proportional component addresses present error, the integral sums past errors for eliminating steady-state offsets, and the derivative predicts future error trends to improve system stability. This combination enables precise and smooth control in dynamic systems, contrasting with the abrupt switching behavior of bang-bang control.
Basics of Bang-Bang (On-Off) Control
Bang-Bang control operates by switching the output fully on or off based on a preset threshold, creating a simple and cost-effective feedback mechanism. Unlike PID control, which continuously adjusts output proportionally to error, Bang-Bang control results in rapid toggling around the setpoint, leading to potential oscillations. This method is commonly used in thermostats and other systems where precise control is less critical and system response speed is prioritized.
How PID Control Works in Practice
PID control continuously adjusts the output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize the error between a desired setpoint and the actual process variable. The proportional term reacts to current error, the integral term accumulates past errors to eliminate steady-state offset, and the derivative term predicts future error trends for smoother response. This dynamic adjustment allows PID controllers to maintain precise control in systems like temperature regulation, motor speed, or fluid levels.
Typical Applications of Bang-Bang Control
Bang-bang control is commonly used in simple on/off systems such as thermostats, basic temperature controllers, and motor control where precise regulation is not critical. Its application includes heating systems, refrigerator compressors, and basic pneumatic valves, leveraging straightforward on/off switching for cost-effective and reliable operation. This control method is favored in scenarios requiring rapid decision-making and minimal hardware complexity without the need for smooth or continuous control adjustments.
Accuracy and Stability: PID vs Bang-Bang
PID control provides superior accuracy and stability by continuously adjusting the control output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, minimizing steady-state error and reducing oscillations. Bang-bang control, also known as on-off control, switches abruptly between fully on and off states, resulting in larger oscillations and less precise control. Consequently, PID is preferred in systems requiring smooth, stable responses, while bang-bang suits simpler applications with less demanding accuracy requirements.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
PID control provides superior energy efficiency compared to bang-bang control by continuously adjusting output to minimize error, reducing excessive power consumption and wear on components. Bang-bang control frequently switches between full-on and full-off states, causing high energy spikes and inefficient operation. Studies show PID controllers can reduce energy use by up to 30% in temperature regulation and motor control applications compared to bang-bang methods.
Implementation Complexity and Cost
PID control involves more complex algorithms requiring precise tuning of proportional, integral, and derivative parameters, leading to higher implementation complexity and cost due to the need for advanced microcontrollers or digital signal processors. Bang-bang control features a simpler on-off mechanism with minimal hardware and programming requirements, making it cost-effective and easier to implement in applications with less stringent control accuracy. You should consider PID control when precise, stable regulation is essential despite increased costs and complexity, whereas bang-bang suits low-budget, straightforward systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Approach
PID control offers precise regulation of system output by continuously adjusting control signals based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, minimizing steady-state error and improving stability. Its complexity requires careful tuning and computational resources, which can be challenging in systems with rapidly changing dynamics or noise sensitivity. Bang-bang control operates with simple on/off switches, providing fast response and ease of implementation but often causing oscillations, wear on mechanical components, and less accuracy in maintaining desired setpoints.
Choosing the Right Control Method for Your System
PID control offers precise and continuous adjustments ideal for systems requiring smooth and stable performance, while bang-bang control provides simple on/off action suited for applications where rapid switching is acceptable. Your choice depends on factors such as system complexity, desired accuracy, response speed, and tolerance for oscillations or overshoot. Evaluating these parameters ensures the best control method aligns with your system's operational needs and performance goals.
PID control vs bang-bang control Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com