USART offers synchronous and asynchronous communication modes, providing more flexibility compared to UART, which supports only asynchronous data transfer. Discover how these differences impact your communication system by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
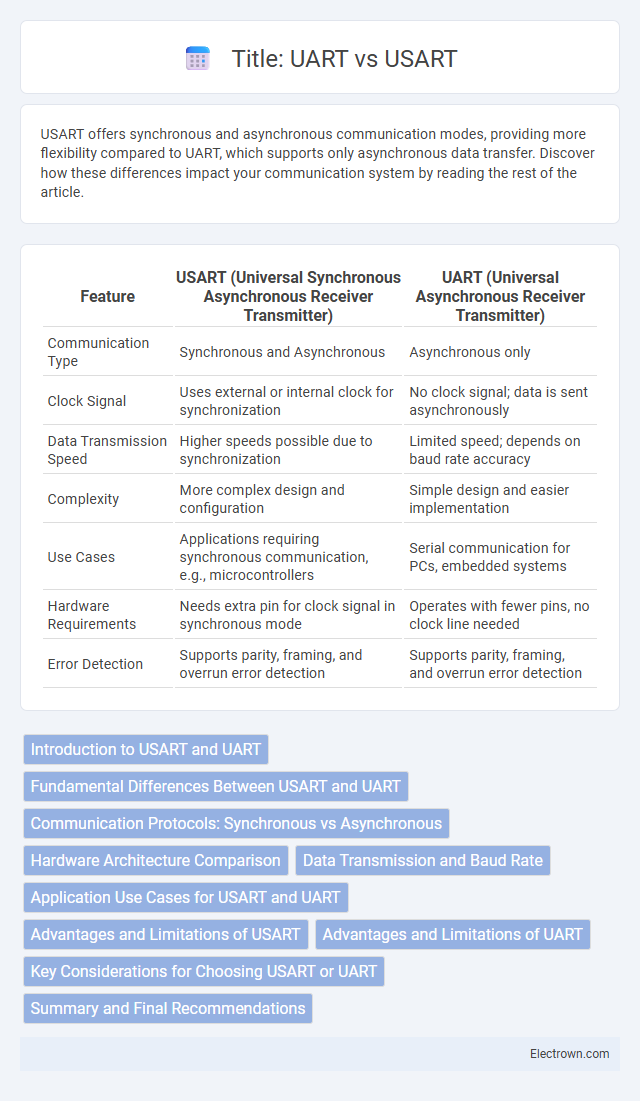
| Feature | USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) | UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Synchronous and Asynchronous | Asynchronous only |
| Clock Signal | Uses external or internal clock for synchronization | No clock signal; data is sent asynchronously |
| Data Transmission Speed | Higher speeds possible due to synchronization | Limited speed; depends on baud rate accuracy |
| Complexity | More complex design and configuration | Simple design and easier implementation |
| Use Cases | Applications requiring synchronous communication, e.g., microcontrollers | Serial communication for PCs, embedded systems |
| Hardware Requirements | Needs extra pin for clock signal in synchronous mode | Operates with fewer pins, no clock line needed |
| Error Detection | Supports parity, framing, and overrun error detection | Supports parity, framing, and overrun error detection |
Introduction to USART and UART
USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) and UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) are essential communication protocols used in serial data transmission. UART operates solely in asynchronous mode, transmitting data without a clock signal, while USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous communication, providing greater flexibility for various applications. Your choice depends on the requirement for clock synchronization and the speed of data transfer in embedded systems.
Fundamental Differences Between USART and UART
USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous communication modes, while UART operates solely in asynchronous mode. USART includes a clock line to synchronize data transfer, enabling better timing control, whereas UART relies on start and stop bits for synchronization. Understanding this fundamental difference helps optimize Your choice for applications requiring precise timing or simpler communication protocols.
Communication Protocols: Synchronous vs Asynchronous
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) operates using an asynchronous communication protocol, transmitting data without a shared clock signal, relying on start and stop bits for synchronization. USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) supports both synchronous and asynchronous communication, enabling data transfer with or without a shared clock, which allows for higher data rates and more reliable timing in synchronous mode. Synchronous protocols in USART improve performance by aligning transmitter and receiver clocks, whereas UART's asynchronous protocol offers simpler hardware implementation but may suffer from timing inaccuracies at higher speeds.
Hardware Architecture Comparison
USART features a versatile hardware architecture capable of both synchronous and asynchronous communication, incorporating clock generation and control logic, while UART is limited to asynchronous transmission with a simpler design lacking a clock signal. The USART module includes additional registers and configuration options, enabling precise timing control and mode selection, whereas UART relies on fixed baud rates and basic framing structures. Your choice depends on whether you require synchronous communication capabilities and flexible settings found in USART or the straightforward, minimal hardware of UART for asynchronous data exchange.
Data Transmission and Baud Rate
USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous data transmission, allowing for flexible communication settings, while UART operates strictly in asynchronous mode. Baud rate in USART can be finely tuned with clock signals to achieve higher accuracy, whereas UART relies on a fixed baud rate without clock synchronization, which may result in timing errors. Choosing between USART and UART depends on your application's need for precise baud rate control and data transmission mode.
Application Use Cases for USART and UART
USART is commonly used in applications requiring synchronous and asynchronous communication, such as microcontroller interfacing in embedded systems, GPS modules, and industrial automation where flexibility in data transmission modes is essential. UART is widely utilized in simpler, cost-effective serial communication scenarios like PC serial ports, Bluetooth modules, and GPS receivers, focusing primarily on asynchronous data transfer. Understanding your specific communication needs helps determine whether USART's versatility or UART's straightforward functionality best suits your project requirements.
Advantages and Limitations of USART
USART offers the advantage of supporting both synchronous and asynchronous communication, making it versatile for various serial data transmission applications. Its ability to synchronize data transfer with a clock signal enhances data integrity and speed compared to UART, which only supports asynchronous communication. However, the complexity and higher cost of USART modules limit their use in simpler, low-speed communication scenarios where UART is more practical.
Advantages and Limitations of UART
UART offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for short-distance, low-speed communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices without the need for a clock signal. Its limitations include susceptibility to noise, lower data transfer rates compared to synchronous protocols like USART, and reliance on precise timing synchronization, which can lead to data corruption in long-distance or high-speed applications. Despite these drawbacks, UART remains widely used in embedded systems due to its ease of implementation and minimal hardware requirements.
Key Considerations for Choosing USART or UART
Choosing between USART and UART depends on the required communication protocol and flexibility; USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous modes, while UART only supports asynchronous communication. Consider system clock availability and timing accuracy, as USART requires a clock signal in synchronous mode for precise data timing, making it suitable for high-speed or clocked interfaces. Power consumption and hardware complexity are also factors; UART offers simpler design and lower power needs, ideal for cost-sensitive or low-speed applications.
Summary and Final Recommendations
USART supports both synchronous and asynchronous communication, offering more flexibility compared to UART, which only handles asynchronous data transfer. For applications requiring precise timing and higher data rates, USART is the preferred choice, while UART is ideal for simpler, low-speed serial communication tasks. Your decision should align with the specific communication protocol needs and complexity of your embedded system.
USART vs UART Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com