SMB connectors offer a compact design and quick snap-on coupling ideal for high-frequency RF applications, while BNC connectors provide secure bayonet locking commonly used in video and radio frequency setups. Explore the rest of this article to understand which connector suits your specific needs best.
Table of Comparison
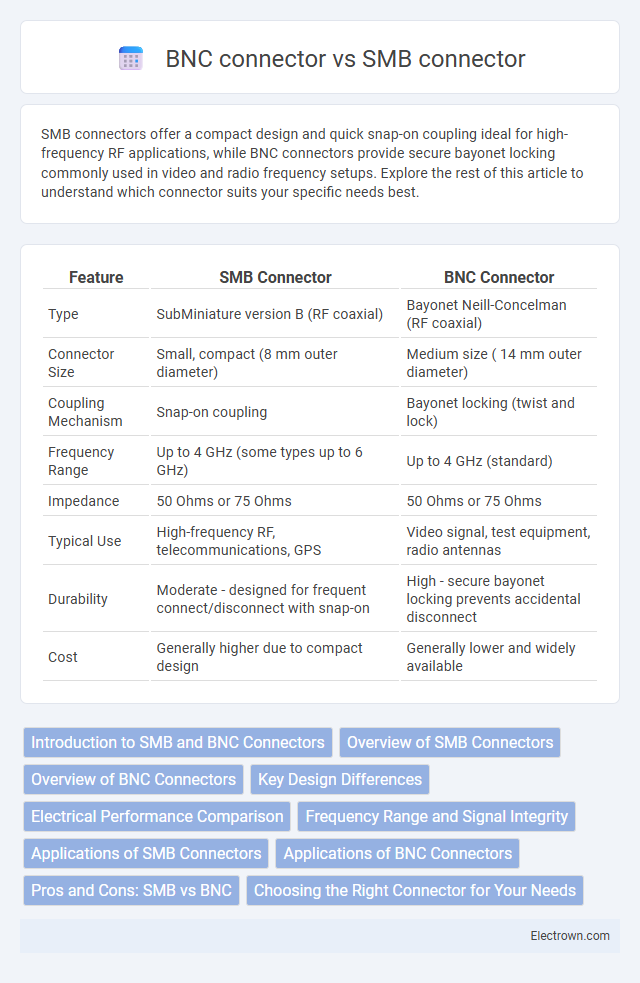
| Feature | SMB Connector | BNC Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Type | SubMiniature version B (RF coaxial) | Bayonet Neill-Concelman (RF coaxial) |
| Connector Size | Small, compact (8 mm outer diameter) | Medium size ( 14 mm outer diameter) |
| Coupling Mechanism | Snap-on coupling | Bayonet locking (twist and lock) |
| Frequency Range | Up to 4 GHz (some types up to 6 GHz) | Up to 4 GHz (standard) |
| Impedance | 50 Ohms or 75 Ohms | 50 Ohms or 75 Ohms |
| Typical Use | High-frequency RF, telecommunications, GPS | Video signal, test equipment, radio antennas |
| Durability | Moderate - designed for frequent connect/disconnect with snap-on | High - secure bayonet locking prevents accidental disconnect |
| Cost | Generally higher due to compact design | Generally lower and widely available |
Introduction to SMB and BNC Connectors
SMB connectors are compact RF connectors used for quick connect and disconnect applications in microwave systems, offering reliable performance up to 4 GHz. BNC connectors, larger in size, are widely used for radio, television, and networking applications with frequency support up to 4 GHz as well, known for their bayonet locking mechanism ensuring secure connections. Choosing the right connector depends on your specific size constraints and ease of use requirements in high-frequency signal transmission.
Overview of SMB Connectors
SMB connectors feature a compact, snap-on coupling mechanism designed for quick and reliable RF connections, commonly used in telecommunications and networking equipment. You benefit from their small size and excellent performance at frequencies up to 4 GHz, allowing for efficient signal transfer in confined spaces. SMB connectors outperform BNC connectors when size and ease of installation are critical, catering to applications requiring frequent connect and disconnect cycles.
Overview of BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are bayonet-style RF connectors commonly used for coaxial cable connections in radio, television, and other radio-frequency electronic equipment. They provide a secure and quick connect/disconnect mechanism, supporting frequencies up to 4 GHz with characteristic impedances of 50 or 75 ohms. Compared to SMB connectors, BNC connectors are typically larger, more durable, and preferred in applications requiring reliable, high-frequency signal integrity.
Key Design Differences
SMB connectors feature a snap-on coupling mechanism that allows for quick and easy connections, while BNC connectors use a bayonet-style locking system providing a secure and stable connection. The SMB connector's smaller size is ideal for compact devices, whereas BNC connectors are larger and typically used in professional broadcast and test equipment. Your choice depends on factors like space constraints, required connection security, and application-specific standards.
Electrical Performance Comparison
SMB connectors offer superior high-frequency performance with a typical operating range up to 4 GHz, while BNC connectors reliably function up to 2 GHz, making SMB more suitable for advanced RF applications. The SMB's smaller size and snap-on coupling provide lower signal loss and better impedance stability over a wider bandwidth compared to the bayonet coupling of BNC connectors. When optimizing Your system's electrical performance, choosing SMB connectors can minimize insertion loss and reflections in high-frequency signal transmission scenarios.
Frequency Range and Signal Integrity
SMB connectors typically support frequencies up to 4 GHz, making them suitable for moderate-frequency applications with good signal integrity due to their snap-on coupling mechanism. BNC connectors operate effectively up to 4 GHz as well but excel in maintaining signal integrity in RF and video applications because of their secure bayonet locking system. The choice between SMB and BNC connectors depends on the specific frequency requirements and the need for reliable, low-loss signal transmission.
Applications of SMB Connectors
SMB connectors are widely used in telecommunications, GPS systems, and Wi-Fi devices due to their compact size and reliable performance at high frequencies up to 4 GHz. Their snap-on coupling mechanism allows for quick and secure connections in tight spaces, making them ideal for portable and mobile communication equipment. In comparison, BNC connectors, known for their bayonet locking system, are predominantly utilized in video surveillance, audio, and test instrumentation applications requiring durable and stable RF connections.
Applications of BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are widely used in RF applications, including video signals, test equipment, and radio-frequency circuits, due to their reliable quick connect/disconnect design. They are common in CCTV systems, oscilloscopes, and amateur radio setups, supporting frequencies up to 4 GHz. Your choice of a BNC connector ensures stable performance in broadcasting, networking, and signal measurement environments.
Pros and Cons: SMB vs BNC
SMB connectors offer a compact design with quick snap-on coupling, making them ideal for limited-space applications and fast installation, while BNC connectors provide a robust bayonet locking mechanism ensuring a secure connection in environments prone to vibration. SMB connectors typically support higher frequency ranges up to 4 GHz, but their smaller size can result in slightly higher insertion loss compared to BNC connectors, which excel in durability and ease of mating at frequencies up to 2 GHz. Your choice between SMB and BNC connectors should consider factors like frequency requirements, mechanical stability, and installation speed to match the specific demands of your RF system.
Choosing the Right Connector for Your Needs
SMB connectors offer compact size and quick snap-on coupling ideal for space-constrained applications, while BNC connectors provide bayonet locking for secure, reliable connections commonly used in broadcasting and test equipment. Selecting the right connector depends on factors like space availability, frequency range, and required mechanical stability. For high-frequency signals up to 4 GHz in tight spaces, SMB connectors excel, whereas BNC connectors are preferred for ease of use and robustness in medium-frequency applications.
SMB connector vs BNC connector Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com