Optical transducers convert light signals into electrical signals or vice versa, enabling precise measurement in fiber optics and communication systems, while electrical transducers directly convert physical parameters into electrical signals for a wide range of applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how each transducer type can enhance your sensing and measurement solutions.
Table of Comparison
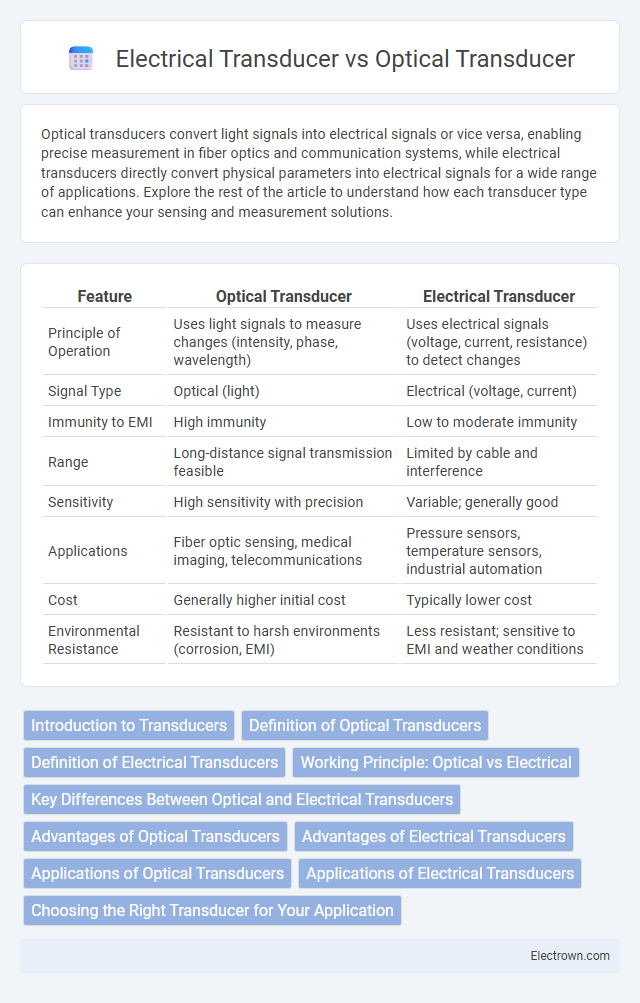
| Feature | Optical Transducer | Electrical Transducer |
|---|---|---|
| Principle of Operation | Uses light signals to measure changes (intensity, phase, wavelength) | Uses electrical signals (voltage, current, resistance) to detect changes |
| Signal Type | Optical (light) | Electrical (voltage, current) |
| Immunity to EMI | High immunity | Low to moderate immunity |
| Range | Long-distance signal transmission feasible | Limited by cable and interference |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity with precision | Variable; generally good |
| Applications | Fiber optic sensing, medical imaging, telecommunications | Pressure sensors, temperature sensors, industrial automation |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Typically lower cost |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to harsh environments (corrosion, EMI) | Less resistant; sensitive to EMI and weather conditions |
Introduction to Transducers
Transducers convert physical quantities into measurable signals, with optical transducers using light properties such as intensity or wavelength to detect changes, while electrical transducers rely on electrical signals like voltage or current variations. Optical transducers offer advantages in high sensitivity and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for precise measurements in harsh environments. Your choice between optical and electrical transducers depends on the application's accuracy requirements and environmental conditions.
Definition of Optical Transducers
Optical transducers convert light signals into electrical signals or vice versa, enabling precise measurement of physical parameters such as displacement, pressure, and temperature using variations in light intensity, phase, or wavelength. Unlike electrical transducers, which directly measure electrical quantities like voltage or current, optical transducers leverage the unique properties of light, offering benefits like high sensitivity, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and remote sensing capabilities. Your choice of an optical transducer is ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
Definition of Electrical Transducers
Electrical transducers are devices that convert physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, or displacement into electrical signals for measurement and control purposes. Unlike optical transducers, which rely on light signals to detect changes, electrical transducers use electrical properties like resistance, capacitance, or inductance to produce an output. Understanding the definition of electrical transducers helps you select the appropriate sensor technology for precise and reliable data acquisition in various applications.
Working Principle: Optical vs Electrical
Optical transducers convert physical parameters into modulated light signals using sensors like photodiodes or fiber optics, leveraging changes in light intensity, phase, or wavelength for measurement. Electrical transducers translate physical quantities directly into electrical signals such as voltage or current through components like piezoelectric sensors or resistive elements. Understanding the difference in working principles helps you select the optimal transducer type for precise, application-specific sensing needs.
Key Differences Between Optical and Electrical Transducers
Optical transducers convert physical quantities into modulated light signals using components like photodiodes and lasers, offering high sensitivity and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Electrical transducers transform physical parameters into electrical signals such as voltage or current, commonly utilizing sensors like strain gauges and thermocouples with easier interfacing in standard electronics. Your choice depends on application needs, with optical transducers favoring precision and noise resistance, while electrical transducers provide simpler, cost-effective integration.
Advantages of Optical Transducers
Optical transducers offer superior immunity to electromagnetic interference, ensuring accurate signal transmission in harsh industrial environments where electrical transducers may struggle. They provide higher sensitivity and precision, making them ideal for applications requiring exact measurements, especially in fiber optic sensing and telecommunications. Your choice of optical transducers enhances system reliability and allows for longer signal transmission distances without significant signal degradation.
Advantages of Electrical Transducers
Electrical transducers offer high accuracy, fast response times, and easy integration with electronic systems, making them ideal for precise measurements and control applications. They provide reliable signal output with minimal noise interference and are generally more cost-effective compared to optical transducers. Your choice of an electrical transducer ensures efficient conversion of physical stimuli into electrical signals suitable for real-time processing and automation.
Applications of Optical Transducers
Optical transducers are widely used in telecommunications for converting electrical signals into optical signals for high-speed data transmission over fiber optic cables. They find critical applications in medical imaging devices, such as endoscopes and optical coherence tomography systems, where precise light detection is essential. Your choice of an optical transducer can enhance accuracy and signal integrity in environments requiring minimal electromagnetic interference.
Applications of Electrical Transducers
Electrical transducers are widely used in industrial automation for converting physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and displacement into electrical signals for measurement and control systems. These transducers enable precise monitoring and feedback in manufacturing processes, automotive systems, and robotics, ensuring operational accuracy and safety. Your choice of electrical transducers can significantly enhance the efficiency of sensor networks and data acquisition systems in various engineering applications.
Choosing the Right Transducer for Your Application
Optical transducers offer high sensitivity and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for applications requiring precise measurements in noisy environments. Electrical transducers provide robust performance, ease of integration, and cost-effectiveness in standard industrial and consumer applications. Selecting the right transducer depends on factors like environmental conditions, signal transmission distance, and accuracy requirements, with optical transducers favored for long-distance or high-precision sensing and electrical transducers suited for general-purpose uses.
optical transducer vs electrical transducer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com