Strain gauges measure deformation by detecting changes in electrical resistance, offering precise strain data, while load cells convert force into an electrical signal for direct weight measurement in various applications. Discover the key differences and which device suits your needs by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
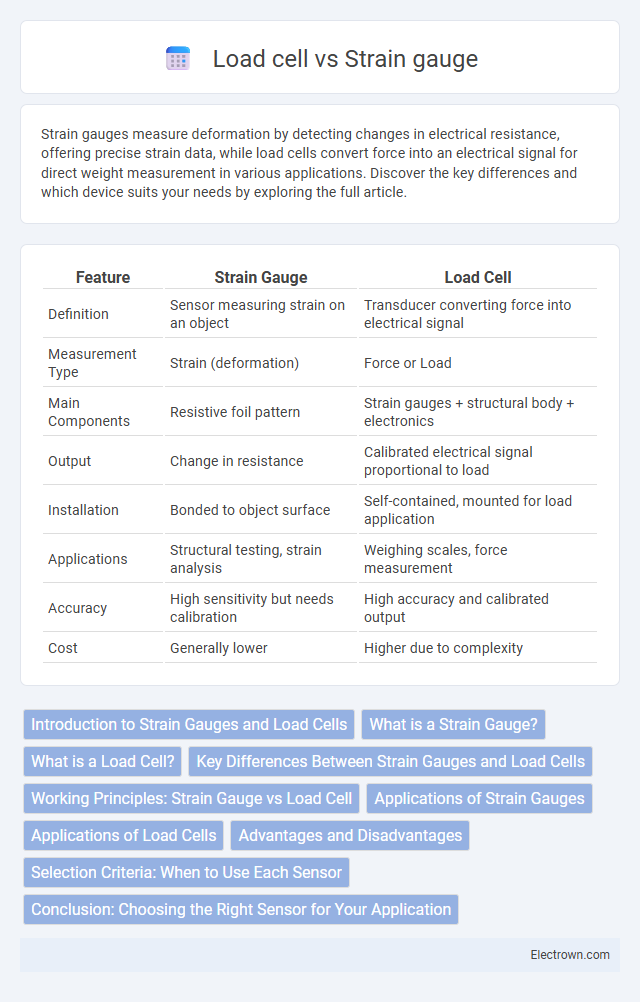
| Feature | Strain Gauge | Load Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sensor measuring strain on an object | Transducer converting force into electrical signal |
| Measurement Type | Strain (deformation) | Force or Load |
| Main Components | Resistive foil pattern | Strain gauges + structural body + electronics |
| Output | Change in resistance | Calibrated electrical signal proportional to load |
| Installation | Bonded to object surface | Self-contained, mounted for load application |
| Applications | Structural testing, strain analysis | Weighing scales, force measurement |
| Accuracy | High sensitivity but needs calibration | High accuracy and calibrated output |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to complexity |
Introduction to Strain Gauges and Load Cells
Strain gauges measure strain by detecting minute changes in electrical resistance when an object deforms, making them essential for precise stress analysis. Load cells incorporate strain gauges but provide direct force or weight measurements through a calibrated sensor system, offering robust output signals suitable for industrial applications. Both devices are critical in engineering fields for accurate load and stress monitoring, with load cells often preferred for their integrated data output and ease of use.
What is a Strain Gauge?
A strain gauge is a sensor used to measure the amount of strain or deformation on an object by converting mechanical displacement into an electrical signal. It consists of a thin, conductive foil pattern applied to a flexible backing, which changes resistance when stretched or compressed. Your ability to accurately detect stress or force in materials often relies on the precise function of strain gauges, which serve as fundamental components in load cells and other force measurement devices.
What is a Load Cell?
A load cell is a transducer that converts force or weight into an electrical signal, typically using strain gauges bonded to a metal body that deforms under load. The electrical resistance of the strain gauges changes proportionally to the applied force, allowing precise measurement of weight or tension. Load cells are essential components in industrial weighing systems, ensuring accurate and reliable force measurement across various applications.
Key Differences Between Strain Gauges and Load Cells
Strain gauges measure strain by detecting minute deformations in materials, while load cells convert force or load directly into an electrical signal for measurement. Load cells typically incorporate multiple strain gauges configured in a Wheatstone bridge to enhance accuracy and sensitivity. Your choice between strain gauges and load cells depends on whether you need raw strain data for material analysis or precise force measurement in industrial applications.
Working Principles: Strain Gauge vs Load Cell
Strain gauges operate on the principle of electrical resistance change when a material undergoes deformation, providing precise measurement of strain by detecting minute changes in resistance. Load cells, often incorporating strain gauges within their structure, measure force or load by converting mechanical deformation into an electrical signal, delivering accurate force quantification. While strain gauges alone detect strain, load cells integrate multiple strain gauges and mechanical components to measure comprehensive load values effectively.
Applications of Strain Gauges
Strain gauges are widely used in structural health monitoring, aerospace engineering, and mechanical testing due to their ability to measure minute deformations in materials. They provide precise data on stress, strain, and force in bridges, aircraft fuselages, and mechanical components, enabling preventive maintenance and safety improvements. Your choice of a strain gauge can enhance accuracy in applications requiring detailed material behavior analysis under load.
Applications of Load Cells
Load cells are extensively used in industrial weighing systems, including conveyor belt scales, tank and hopper weighing, and truck scales, providing precise force measurement crucial for process control and inventory management. In aerospace and automotive testing, load cells measure stress and load during component testing and crash simulations, ensuring safety and performance standards. Your manufacturing or quality assurance processes benefit from load cells' accuracy in material testing machines and robotic automation, optimizing product reliability and operational efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Strain gauges offer high sensitivity and precise measurement of strain, making them ideal for structural testing and material stress analysis, but they require careful installation and temperature compensation. Load cells provide direct force measurement with robust construction and ease of integration into industrial applications, yet they can be more expensive and bulky compared to strain gauges. Your choice depends on the need for accuracy, environment conditions, and budget considerations.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each Sensor
Strain gauges are ideal for applications requiring precise measurement of material deformation under stress, offering high sensitivity for small strain detection in structural monitoring or fatigue testing. Load cells suit scenarios demanding accurate force or weight measurement with built-in calibration and robustness, such as industrial weighing systems or force measurement in manufacturing processes. Your choice depends on whether the primary need is detailed strain analysis or consistent, direct force measurement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Selecting between a strain gauge and a load cell depends on your specific measurement needs, accuracy requirements, and environmental conditions. Strain gauges provide precise strain measurement for structural analysis, while load cells offer direct force or weight measurement with integrated electronics for industrial applications. Understanding your application's load range, sensitivity, and installation constraints ensures optimal sensor performance and reliable data.
Strain gauge vs Load cell Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com