Bench power supplies offer adjustable voltage and current with multiple output channels, ideal for general electronics testing and development, while laboratory power supplies provide higher precision, stability, and advanced features for scientific research and detailed experiments. Discover how choosing the right power supply can enhance Your work by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
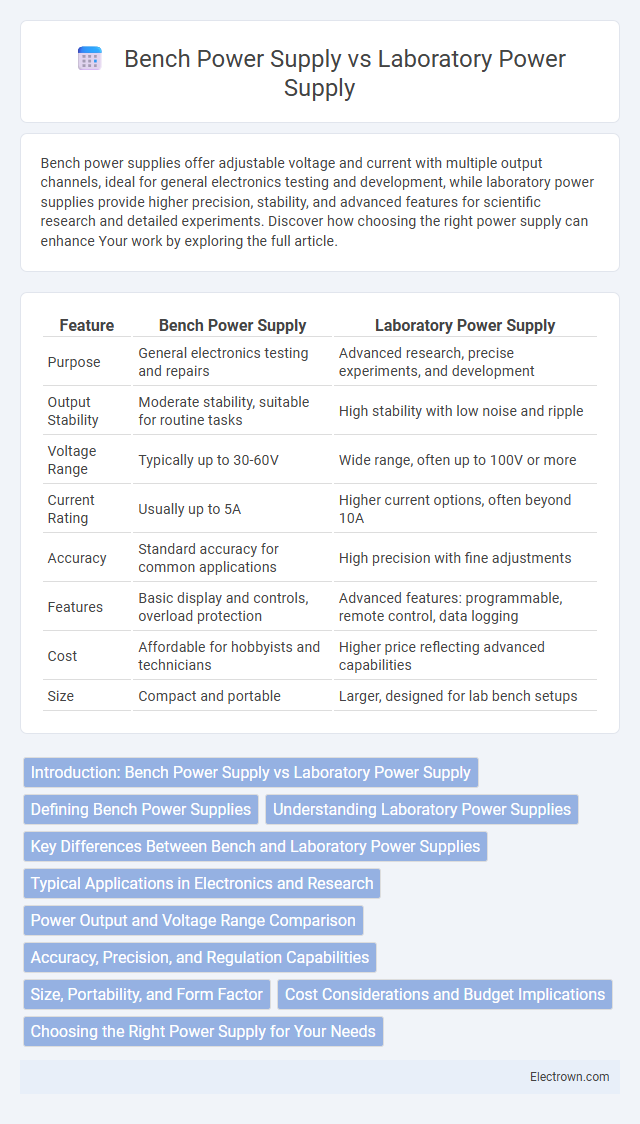
| Feature | Bench Power Supply | Laboratory Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | General electronics testing and repairs | Advanced research, precise experiments, and development |
| Output Stability | Moderate stability, suitable for routine tasks | High stability with low noise and ripple |
| Voltage Range | Typically up to 30-60V | Wide range, often up to 100V or more |
| Current Rating | Usually up to 5A | Higher current options, often beyond 10A |
| Accuracy | Standard accuracy for common applications | High precision with fine adjustments |
| Features | Basic display and controls, overload protection | Advanced features: programmable, remote control, data logging |
| Cost | Affordable for hobbyists and technicians | Higher price reflecting advanced capabilities |
| Size | Compact and portable | Larger, designed for lab bench setups |
Introduction: Bench Power Supply vs Laboratory Power Supply
Bench power supplies and laboratory power supplies both provide precise voltage and current outputs for testing and development purposes. Bench power supplies are typically designed for general electronics workstations, offering adjustable voltage, current limiting, and multiple channels for versatile applications. Laboratory power supplies generally feature higher accuracy, programmable functions, and stricter safety standards, making them ideal for research, development, and advanced testing environments.
Defining Bench Power Supplies
Bench power supplies are compact, portable units designed for providing adjustable DC voltage and current in electronics testing and development environments. Unlike laboratory power supplies, which often feature multiple channels and advanced functionality for complex experiments, bench power supplies prioritize ease of use and precise control for general-purpose solutions. Your choice depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as power range, stability, and additional features.
Understanding Laboratory Power Supplies
Laboratory power supplies offer precise voltage and current adjustments essential for accurate testing and experimentation, surpassing the capabilities of standard bench power supplies designed primarily for general electronics work. These devices provide stable output with minimal ripple and noise, ensuring reliable performance under varying load conditions critical in research and development settings. Advanced features such as programmable outputs, remote sensing, and multiple channel support distinguish laboratory power supplies as indispensable tools for scientific and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Bench and Laboratory Power Supplies
Bench power supplies typically offer fixed voltage and current settings suited for routine testing, while laboratory power supplies provide highly adjustable output ranges and enhanced precision for intricate experiments. Laboratory models often include advanced features such as programmable outputs, multiple channels, and digital displays, enabling detailed control and monitoring. The main distinction lies in versatility and accuracy, with laboratory power supplies designed for complex research applications compared to the simpler, general-purpose functionality of bench power supplies.
Typical Applications in Electronics and Research
Bench power supplies are commonly used in electronics repair, prototyping, and development where stable and adjustable voltage/current is required for testing circuits and components. Laboratory power supplies are designed for more precise and reliable performance in research environments, supporting advanced experiments and instrumentation with features like programmable output and multiple channels. Both types serve crucial roles in electronics and research but differ in complexity and application scope.
Power Output and Voltage Range Comparison
Bench power supplies typically offer higher power output and wider voltage ranges than standard laboratory power supplies, accommodating more demanding electronic testing applications. Laboratory power supplies often provide precise voltage control and stability within lower voltage and power limits, making them ideal for delicate experiments and low-power devices. Your choice should depend on whether you require high power capacity or finely tuned voltage regulation for your specific tasks.
Accuracy, Precision, and Regulation Capabilities
Bench power supplies typically offer high accuracy with voltage tolerances around +-0.5% and current tolerances near +-1%, making them suitable for general electronics tasks requiring reliable outputs. Laboratory power supplies enhance precision further, often reaching voltage accuracy within +-0.1% and current accuracy below +-0.5%, enabling more exacting experimental conditions. In terms of regulation capabilities, laboratory power supplies maintain stable voltage and current under varying load conditions with rapid transient response times, whereas benchtop models provide adequate but comparatively slower regulation suitable for less sensitive applications.
Size, Portability, and Form Factor
Bench power supplies typically feature a compact, box-like form factor designed for stationary use on workbenches, offering limited portability due to their weight and size. Laboratory power supplies tend to be larger with modular designs to accommodate diverse testing requirements, often sacrificing portability for enhanced functionality and stability. For Your needs, a bench power supply provides easier transportability for fieldwork, while laboratory units deliver expansive capabilities suited for fixed lab environments.
Cost Considerations and Budget Implications
Bench power supplies typically offer a more affordable solution for basic testing and prototyping, making them ideal for hobbyists and small-scale projects with limited budgets. Laboratory power supplies tend to have higher precision, advanced features, and better stability, which command a premium price suitable for professional research and development environments. Evaluating cost considerations involves balancing initial investment against long-term reliability, performance needs, and budget constraints.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
When choosing the right power supply for your needs, consider that bench power supplies offer adjustable voltage and current settings suitable for general electronics testing and prototyping. Laboratory power supplies typically provide higher precision, multiple channels, and advanced features necessary for complex research and development tasks. Your decision should balance the required output accuracy, stability, and the complexity of your projects.
bench power supply vs laboratory power supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com