Active probes feature built-in amplifiers that enhance signal integrity and reduce loading on the circuit, making them ideal for high-frequency and sensitive measurements; passive probes, on the other hand, are simpler and generally less expensive but can introduce more signal distortion and loading effects due to their direct connection. Understanding the differences between active and passive probes can help you select the right tool for accurate and reliable oscilloscope readings--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
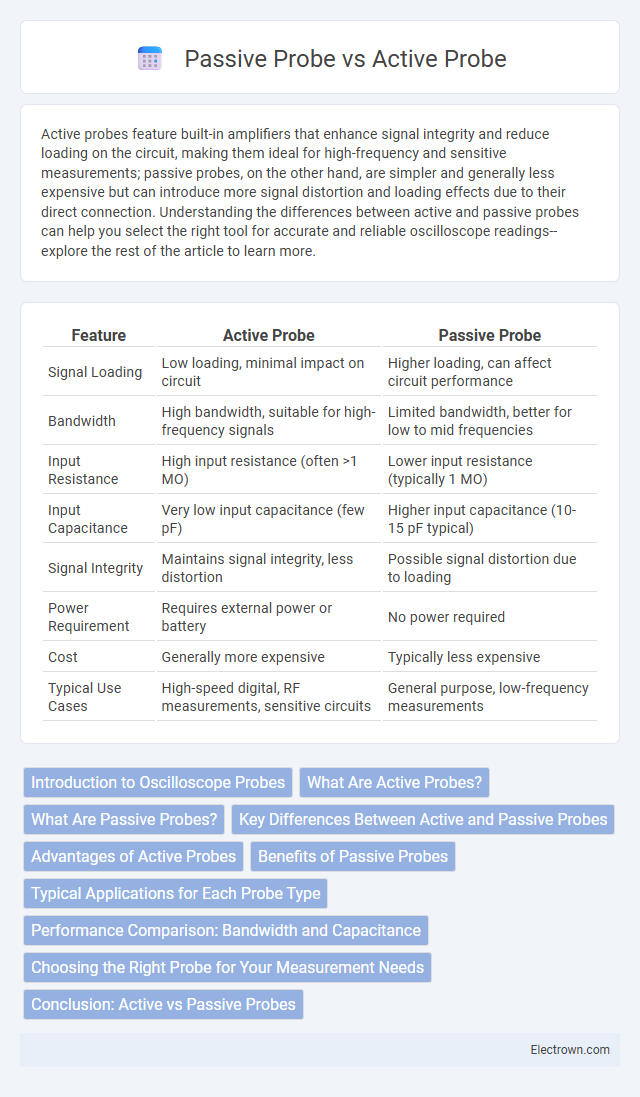
| Feature | Active Probe | Passive Probe |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Loading | Low loading, minimal impact on circuit | Higher loading, can affect circuit performance |
| Bandwidth | High bandwidth, suitable for high-frequency signals | Limited bandwidth, better for low to mid frequencies |
| Input Resistance | High input resistance (often >1 MO) | Lower input resistance (typically 1 MO) |
| Input Capacitance | Very low input capacitance (few pF) | Higher input capacitance (10-15 pF typical) |
| Signal Integrity | Maintains signal integrity, less distortion | Possible signal distortion due to loading |
| Power Requirement | Requires external power or battery | No power required |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Typically less expensive |
| Typical Use Cases | High-speed digital, RF measurements, sensitive circuits | General purpose, low-frequency measurements |
Introduction to Oscilloscope Probes
Oscilloscope probes are essential tools for accurate signal measurement, with active probes providing higher bandwidth and lower input capacitance ideal for high-speed circuits, while passive probes offer simplicity and durability for general-purpose testing. Active probes incorporate active components like transistors to amplify signals, minimizing distortion and loading effects on your circuit. Choosing the right probe ensures precise waveform capture and reliable data analysis during electronic testing.
What Are Active Probes?
Active probes contain built-in amplifiers and components that enhance signal integrity by reducing loading effects and improving bandwidth in high-frequency measurements. They are designed to accurately capture fast, low-amplitude signals with minimal distortion, making them ideal for testing complex electronic circuits and high-speed digital systems. Unlike passive probes, active probes require power and provide higher input impedance and better signal fidelity.
What Are Passive Probes?
Passive probes are measurement devices used in oscilloscopes that consist of only resistors and capacitors, lacking any active components like transistors or amplifiers. They offer high input impedance, typically around 1 MO, minimizing signal distortion and loading effects on the circuit under test. These probes are suitable for general-purpose signal measurement but may struggle with high-frequency or low-amplitude signals due to their limited bandwidth and signal attenuation.
Key Differences Between Active and Passive Probes
Active probes incorporate built-in amplifiers that provide higher input impedance and better signal integrity, making them ideal for high-frequency or low-amplitude signals. Passive probes rely on simple resistive dividers without amplification, resulting in lower input impedance and potential signal distortion at high frequencies. Your choice between active and passive probes depends on the signal characteristics and measurement accuracy required for your application.
Advantages of Active Probes
Active probes offer significant advantages in high-frequency and high-speed signal measurements due to their built-in amplification and low input capacitance, which minimize signal distortion and loading effects. These probes enable more accurate and precise readings of fast-changing signals, making them ideal for modern digital circuits and RF applications. Your measurements benefit from improved fidelity and enhanced bandwidth when using active probes compared to passive ones.
Benefits of Passive Probes
Passive probes offer benefits such as lower cost, simplicity, and broad frequency response suitable for general-purpose measurements. Their high input impedance and low loading effect minimize circuit disturbance, preserving signal integrity during testing. These probes are reliable for high-impedance circuits and provide accurate voltage measurements without requiring additional power.
Typical Applications for Each Probe Type
Active probes are typically used in high-frequency or high-speed digital circuit testing where signal integrity and minimal loading are crucial, such as in semiconductor device characterization and high-speed data communication analysis. Passive probes are commonly applied for general-purpose measurements in analog and digital circuits, including troubleshooting and signal monitoring in power electronics and microcontroller development. Your choice between active and passive probes should consider the application's frequency range, signal amplitude, and sensitivity requirements to ensure accurate and reliable measurements.
Performance Comparison: Bandwidth and Capacitance
Active probes typically offer higher bandwidth and lower input capacitance compared to passive probes, enabling more accurate signal measurements at high frequencies. Passive probes tend to have higher input capacitance, which can load the circuit and reduce measurement accuracy, especially in high-speed applications. Your choice of probe directly impacts the fidelity of signal capture, with active probes preferred for performance-critical, high-frequency environments.
Choosing the Right Probe for Your Measurement Needs
Selecting the right probe between active and passive types depends on factors like signal frequency, impedance, and measurement accuracy. Active probes offer higher input impedance and better performance for high-frequency and low-signal measurements, while passive probes are more durable and cost-effective for general-purpose testing. Understanding your specific requirements ensures optimal signal integrity and measurement precision.
Conclusion: Active vs Passive Probes
Active probes offer higher bandwidth and better signal integrity due to their built-in amplification and lower loading effect on the circuit. Passive probes are simpler, more durable, and less expensive but may introduce signal distortion and loading, limiting accuracy in high-frequency measurements. Your choice depends on the required measurement precision, frequency range, and budget constraints.
active probe vs passive probe Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com