Capacitive humidity sensors measure humidity by detecting changes in the dielectric constant of a polymer or ceramic layer, offering high accuracy and stability in varying environments, while resistive humidity sensors rely on changes in electrical resistance caused by moisture absorption, typically providing faster response times but potential susceptibility to contamination. Explore the rest of the article to understand which sensor type aligns best with your specific application needs.
Table of Comparison
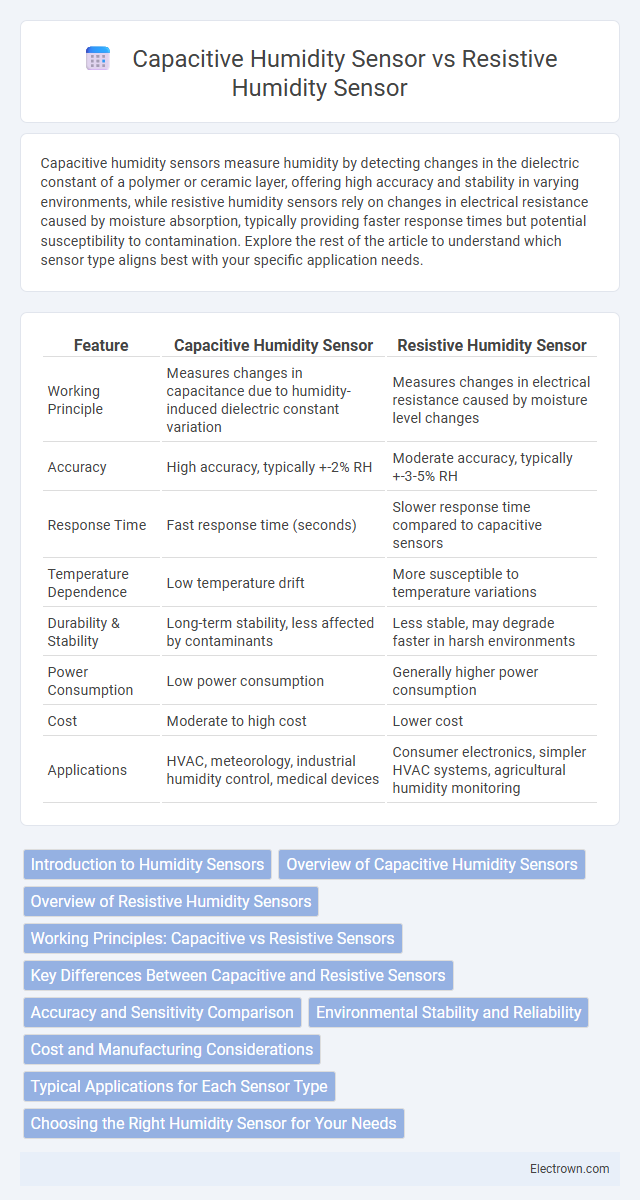
| Feature | Capacitive Humidity Sensor | Resistive Humidity Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Measures changes in capacitance due to humidity-induced dielectric constant variation | Measures changes in electrical resistance caused by moisture level changes |
| Accuracy | High accuracy, typically +-2% RH | Moderate accuracy, typically +-3-5% RH |
| Response Time | Fast response time (seconds) | Slower response time compared to capacitive sensors |
| Temperature Dependence | Low temperature drift | More susceptible to temperature variations |
| Durability & Stability | Long-term stability, less affected by contaminants | Less stable, may degrade faster in harsh environments |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption | Generally higher power consumption |
| Cost | Moderate to high cost | Lower cost |
| Applications | HVAC, meteorology, industrial humidity control, medical devices | Consumer electronics, simpler HVAC systems, agricultural humidity monitoring |
Introduction to Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors measure moisture levels in the air using different technologies. Capacitive humidity sensors detect changes in capacitance caused by water vapor, offering high accuracy and stability across a wide humidity range. Resistive humidity sensors measure changes in electrical resistance due to moisture, providing cost-effective and simple solutions for monitoring relative humidity in various environments.
Overview of Capacitive Humidity Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors detect changes in humidity by measuring the variation in electrical capacitance caused by the moisture content of the surrounding air. These sensors use a hygroscopic dielectric material between two conductive plates, which alters capacitance as relative humidity fluctuates. Your choice of a capacitive humidity sensor offers benefits such as high accuracy, stability, and fast response time in diverse environmental conditions.
Overview of Resistive Humidity Sensors
Resistive humidity sensors measure humidity by detecting changes in the electrical resistance of a hygroscopic conductive material exposed to moisture. These sensors are widely used in applications requiring cost-effective and straightforward humidity measurement, such as HVAC systems and industrial process control. Their key advantages include high sensitivity, fast response time, and the ability to operate effectively across a broad humidity range, although they can be less stable in highly variable temperature environments compared to capacitive sensors.
Working Principles: Capacitive vs Resistive Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors measure relative humidity by detecting changes in the dielectric constant of a polymer or metal-oxide film, which alters the sensor's capacitance as moisture levels fluctuate. Resistive humidity sensors operate by measuring the variation in electrical resistance of a hygroscopic conductive material, which changes as it absorbs or releases water vapor. Understanding these working principles helps you select the appropriate sensor for your application based on sensitivity, accuracy, and environmental conditions.
Key Differences Between Capacitive and Resistive Sensors
Capacitive humidity sensors measure changes in capacitance caused by variations in relative humidity, offering high accuracy and stability, while resistive humidity sensors detect changes in electrical resistance due to moisture levels, typically providing faster response times but lower precision. Capacitive sensors operate effectively in a wider temperature range and are less affected by contaminants, making them suitable for industrial applications, whereas resistive sensors are often more cost-effective and used in consumer electronics. The key differences lie in their sensing mechanisms, measurement accuracy, environmental durability, and application scope.
Accuracy and Sensitivity Comparison
Capacitive humidity sensors typically provide higher accuracy and better sensitivity over a wider humidity range compared to resistive sensors, due to their stable dielectric material response to moisture changes. Resistive humidity sensors may exhibit faster response times but often suffer from lower precision and greater drift caused by contamination or aging effects. Your choice depends on the required measurement accuracy and environmental stability, with capacitive sensors favored for applications demanding reliable long-term humidity monitoring.
Environmental Stability and Reliability
Capacitive humidity sensors offer superior environmental stability and long-term reliability due to their polymer dielectric layer, which maintains consistent performance across wide temperature ranges and varying humidity levels. Resistive humidity sensors, while cost-effective, tend to suffer from drift and reduced accuracy in harsh environmental conditions caused by contamination and electrode degradation. Your choice of sensor should consider the operating environment, with capacitive sensors providing more dependable and stable readings for applications requiring precise humidity control.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Capacitive humidity sensors generally incur higher manufacturing costs due to their complex multilayer structure and precision materials such as polymer dielectrics or metal oxides. Resistive humidity sensors offer a cost-effective alternative with simpler fabrication processes, typically utilizing conductive polymer or ceramic composites that reduce production expenses. Despite initial cost differences, capacitive sensors benefit from greater long-term stability and lower maintenance costs, which can influence overall cost-effectiveness depending on application requirements.
Typical Applications for Each Sensor Type
Capacitive humidity sensors are widely used in HVAC systems, weather monitoring, and industrial process control due to their high accuracy and stability in varying environmental conditions. Resistive humidity sensors are commonly applied in consumer electronics, automotive climate control, and portable devices where cost-effectiveness and quick response times are essential. Your choice depends on the need for precision or affordability in specific applications.
Choosing the Right Humidity Sensor for Your Needs
Selecting the right humidity sensor depends on application requirements such as accuracy, response time, and environmental conditions. Capacitive humidity sensors offer high accuracy, wide measurement range, and durability, making them suitable for HVAC systems, industrial monitoring, and weather stations. Resistive humidity sensors provide cost-effective solutions with faster response times, ideal for consumer electronics and simple humidity detection tasks.
Capacitive humidity sensor vs Resistive humidity sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com