Triodes and pentodes differ primarily in the number of internal electrodes, with triodes containing three and pentodes five, impacting their amplification and noise characteristics. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right vacuum tube for your audio or radio projects; continue reading to explore their specific applications and performance nuances.
Table of Comparison
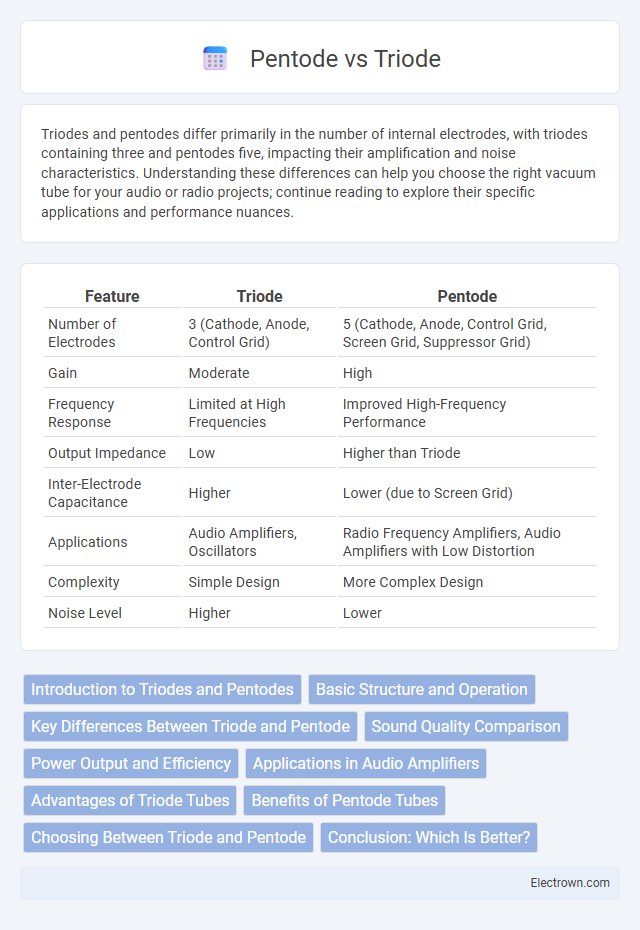
| Feature | Triode | Pentode |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Electrodes | 3 (Cathode, Anode, Control Grid) | 5 (Cathode, Anode, Control Grid, Screen Grid, Suppressor Grid) |
| Gain | Moderate | High |
| Frequency Response | Limited at High Frequencies | Improved High-Frequency Performance |
| Output Impedance | Low | Higher than Triode |
| Inter-Electrode Capacitance | Higher | Lower (due to Screen Grid) |
| Applications | Audio Amplifiers, Oscillators | Radio Frequency Amplifiers, Audio Amplifiers with Low Distortion |
| Complexity | Simple Design | More Complex Design |
| Noise Level | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Triodes and Pentodes
Triodes, key components in early electronic amplification, consist of three elements: the cathode, anode, and control grid, enabling signal modulation by controlling electron flow. Pentodes expand on this design by incorporating two additional grids, known as the screen and suppressor grids, to reduce distortion and improve gain. These differences in structure directly impact their performance in amplification circuits, with pentodes offering higher gain and better frequency response compared to triodes.
Basic Structure and Operation
A triode consists of three main elements: the cathode, anode, and control grid, where the control grid modulates the electron flow between the cathode and anode to amplify signals. A pentode incorporates two additional grids--a screen grid and a suppressor grid--that enhance gain and reduce capacitance and secondary emission, leading to improved performance over triodes. The pentode's complex structure allows for higher amplification and better frequency response, making it preferable in RF and audio amplification circuits.
Key Differences Between Triode and Pentode
Triode and pentode vacuum tubes differ primarily in their internal structure, with triodes containing three elements--cathode, anode, and control grid--while pentodes have five elements, adding a screen grid and suppressor grid to reduce capacitance and secondary emission. This structural difference results in pentodes offering higher gain, greater power output, and improved efficiency compared to triodes, which are known for their simplicity and lower distortion. Your choice between triode and pentode depends on whether you prioritize audio fidelity and warmth, typically associated with triodes, or higher amplification and power, attributes of pentodes.
Sound Quality Comparison
Triode amplifiers deliver warm, smooth sound with natural harmonic distortion, producing a richer and more musical tone favored by audiophiles seeking clarity and warmth. Pentode amplifiers provide higher gain and greater power output, resulting in louder sound but often introducing more distortion and a harsher tonal character compared to triodes. Your choice between triode and pentode technology significantly impacts sound quality, depending on whether you prioritize warmth and detail or power and volume.
Power Output and Efficiency
Pentodes typically deliver higher power output than triodes due to their additional grids, which improve electron control and amplify signals more effectively. Triodes exhibit greater efficiency in linear amplification with lower distortion, making them preferable for high-fidelity audio applications despite their lower power output. Pentodes offer better performance in power amplification stages, whereas triodes excel in efficiency and sound quality in low-power scenarios.
Applications in Audio Amplifiers
Triode tubes are favored in high-fidelity audio amplifiers for their warm, smooth sound characterized by low distortion and rich harmonic content. Pentode tubes deliver higher gain and greater power output, making them suitable for driving speakers in guitar amplifiers and high-power audio applications. Audiophiles often prefer triodes for preamplification and low-power stages, while pentodes are used in power amplifier stages due to their efficiency and versatility.
Advantages of Triode Tubes
Triode tubes offer superior linearity and lower distortion compared to pentode tubes, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio applications. They have simpler construction with fewer internal components, resulting in more stable operation and reduced noise levels. The lower output impedance of triodes facilitates better matching with audio transformers, enhancing overall sound quality.
Benefits of Pentode Tubes
Pentode tubes offer higher gain and improved amplification efficiency compared to triodes, making them ideal for applications requiring greater power output and reduced distortion. Their additional electrode, the screen grid, minimizes the capacitance between the anode and control grid, enhancing high-frequency performance and stability. Your audio or radio equipment benefits from clearer signal transmission and increased overall reliability when using pentode tubes.
Choosing Between Triode and Pentode
Choosing between triode and pentode depends on the desired audio performance and application. Triodes offer lower distortion and a warmer, more natural sound, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio equipment, while pentodes provide higher gain and greater efficiency, suitable for applications requiring more power and volume. Understanding the trade-offs between triode's simplicity and pentode's complexity helps audiophiles and engineers optimize amplifier design for specific sound characteristics.
Conclusion: Which Is Better?
Pentodes generally offer higher gain, better efficiency, and greater output power compared to triodes, making them ideal for applications requiring strong amplification and low distortion at high frequencies. Triodes provide simpler circuit designs with lower noise and more linear amplification, preferred in audio applications demanding warmth and clarity. The choice between triode and pentode depends on the specific performance criteria, with pentodes favored for power and triodes for audio fidelity.
Triode vs Pentode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com