UV LEDs emit ultraviolet light with shorter wavelengths ideal for applications like sterilization and curing, while Blue LEDs produce visible light commonly used in displays and indicators. Explore the detailed differences and advantages to understand which LED type best suits Your needs.
Table of Comparison
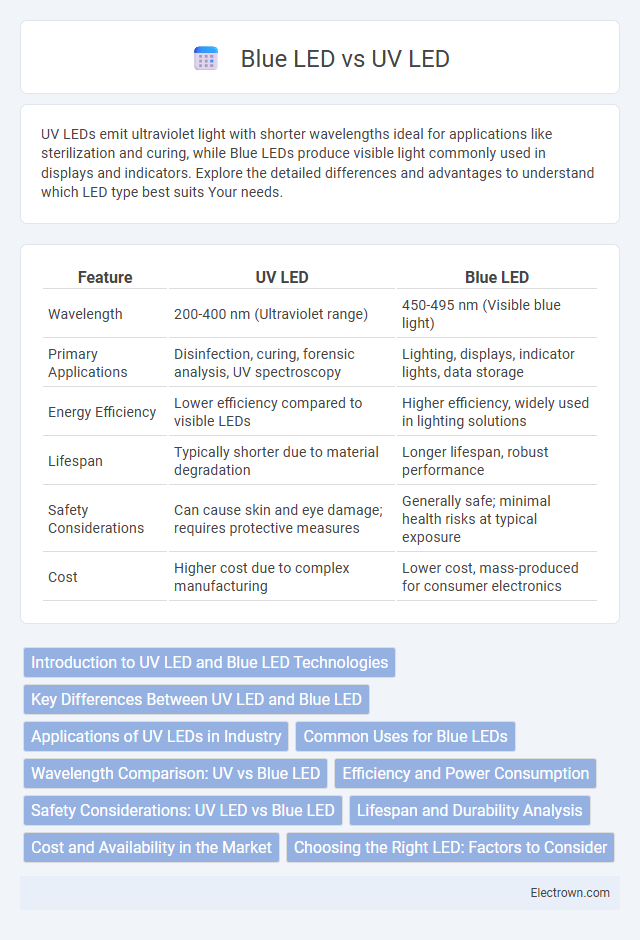
| Feature | UV LED | Blue LED |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 200-400 nm (Ultraviolet range) | 450-495 nm (Visible blue light) |
| Primary Applications | Disinfection, curing, forensic analysis, UV spectroscopy | Lighting, displays, indicator lights, data storage |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower efficiency compared to visible LEDs | Higher efficiency, widely used in lighting solutions |
| Lifespan | Typically shorter due to material degradation | Longer lifespan, robust performance |
| Safety Considerations | Can cause skin and eye damage; requires protective measures | Generally safe; minimal health risks at typical exposure |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing | Lower cost, mass-produced for consumer electronics |
Introduction to UV LED and Blue LED Technologies
UV LED technology emits ultraviolet light with wavelengths typically ranging from 200 to 400 nanometers, making it highly effective for sterilization, curing, and sensing applications. Blue LEDs operate at longer wavelengths, usually around 450 to 495 nanometers, and are commonly used in displays, lighting, and signaling due to their visible, high-intensity output. You can optimize your technology choice by understanding the distinct spectral properties and practical uses of UV versus blue LEDs.
Key Differences Between UV LED and Blue LED
UV LEDs emit light in the ultraviolet spectrum, typically ranging from 200 to 400 nanometers, while blue LEDs produce light in the visible spectrum around 450 to 495 nanometers. UV LEDs are widely used for sterilization, curing, and fluorescence applications due to their shorter wavelength and higher photon energy. Blue LEDs are primarily utilized in display technologies, general lighting, and optical storage because of their efficient visible light output and longer wavelength.
Applications of UV LEDs in Industry
UV LEDs are extensively used in industrial applications such as curing adhesives, inks, and coatings due to their efficient and rapid polymerization capabilities. They enable precise disinfection and sterilization processes in medical equipment manufacturing and water purification systems. The semiconductor industry utilizes UV LEDs for photolithography and phototherapy treatments benefit from their specific wavelength emissions.
Common Uses for Blue LEDs
Blue LEDs are widely used in electronic displays, indicator lights, and automotive lighting due to their high brightness and energy efficiency. They play a critical role in LED screens, including smartphones, TVs, and computer monitors, where they provide vibrant color and clarity. Your devices benefit from blue LEDs' ability to efficiently convert electricity into visible light, enhancing both performance and battery life.
Wavelength Comparison: UV vs Blue LED
UV LEDs emit wavelengths typically ranging from 200 to 400 nanometers, while blue LEDs operate within a narrower range of approximately 450 to 495 nanometers. The shorter wavelengths of UV LEDs enable applications such as sterilization and fluorescence excitation, contrasting with blue LEDs used primarily in lighting, displays, and indicators. The efficiency and material composition also differ significantly between UV and blue LEDs due to their distinct wavelength requirements.
Efficiency and Power Consumption
UV LEDs typically exhibit lower efficiency and higher power consumption compared to blue LEDs due to the challenges in generating ultraviolet light at shorter wavelengths. Blue LEDs, with mature technology and higher external quantum efficiency, often deliver more lumens per watt, making them ideal for applications prioritizing energy savings. When selecting a light source for your project, consider that blue LEDs provide superior power efficiency, while UV LEDs may consume more energy to achieve the same output.
Safety Considerations: UV LED vs Blue LED
UV LEDs emit ultraviolet light, which poses higher risks of skin and eye damage compared to blue LEDs, making protective measures crucial during use. Blue LEDs emit visible light, generally considered safer, but prolonged exposure can still cause retinal strain and potential photochemical damage. Proper shielding, limited exposure time, and protective eyewear are essential safety considerations for both UV and blue LED applications.
Lifespan and Durability Analysis
UV LEDs typically offer a longer lifespan, often exceeding 20,000 hours, due to their robust semiconductor materials designed to withstand higher energy emissions. Blue LEDs, while also durable with lifespans around 25,000 to 50,000 hours, are generally less resilient to heat and photodegradation compared to UV LEDs. The superior durability of UV LEDs makes them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance under harsh conditions such as sterilization and curing processes.
Cost and Availability in the Market
UV LEDs generally have higher costs due to specialized semiconductor materials and manufacturing processes, resulting in limited availability compared to blue LEDs. Blue LEDs benefit from mass production and widespread use in consumer electronics, driving down prices and ensuring greater market presence. The cost difference influences adoption rates, with blue LEDs dominating in price-sensitive applications while UV LEDs remain niche but essential for sterilization and curing technologies.
Choosing the Right LED: Factors to Consider
When choosing between UV LED and Blue LED, consider the wavelength requirements, as UV LEDs emit light typically between 100-400 nm, ideal for sterilization and curing applications, while Blue LEDs operate around 450-495 nm, suited for visible light tasks like displays and lighting. Evaluate energy efficiency and lifespan since Blue LEDs usually offer higher efficiency and longer durability compared to most UV LEDs. Your decision should align with the specific use case, ensuring the LED type matches the intended application for optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
UV LED vs Blue LED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com