Single facet lasers emit light from one surface, offering simpler design and lower costs but limited power output, while dual facet lasers utilize both surfaces to increase brightness and efficiency, ideal for high-performance applications. Discover how choosing between single and dual facet lasers can impact your project's success by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
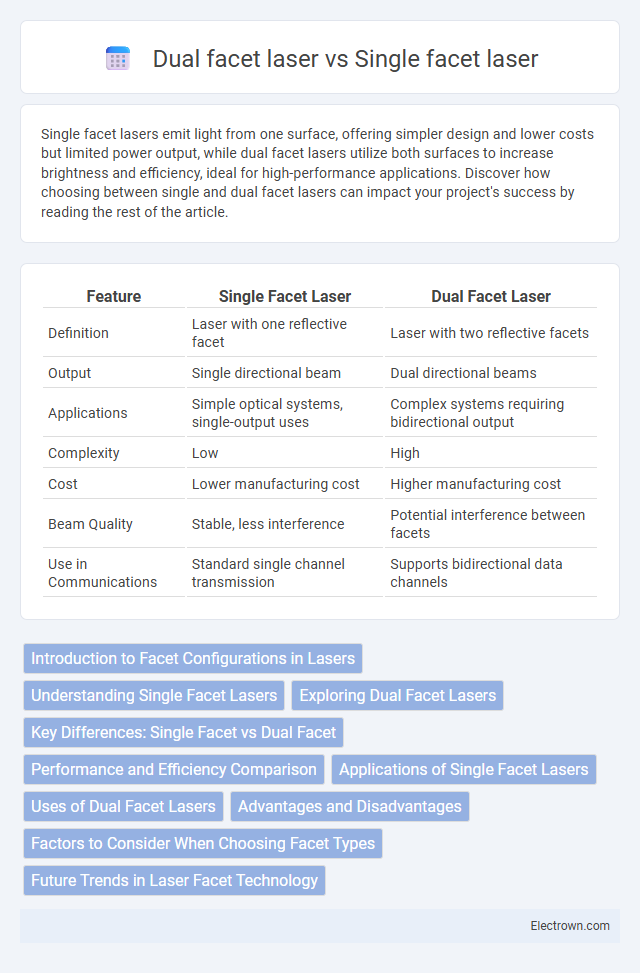
| Feature | Single Facet Laser | Dual Facet Laser |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Laser with one reflective facet | Laser with two reflective facets |
| Output | Single directional beam | Dual directional beams |
| Applications | Simple optical systems, single-output uses | Complex systems requiring bidirectional output |
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Beam Quality | Stable, less interference | Potential interference between facets |
| Use in Communications | Standard single channel transmission | Supports bidirectional data channels |
Introduction to Facet Configurations in Lasers
Single facet lasers feature a reflective coating on one end and an anti-reflective coating on the other, optimizing light emission through a single output face. Dual facet lasers have reflective coatings on both ends, enabling bidirectional light output or enhanced feedback control for improved laser stability and performance. Understanding these facet configurations helps you select the appropriate laser design for applications requiring specific emission characteristics and power levels.
Understanding Single Facet Lasers
Single facet lasers feature a single polished facet that acts as the output mirror, providing a straightforward design ideal for simple, cost-effective applications. These lasers typically offer stable performance but have limited feedback control compared to dual facet lasers, which possess two reflective facets for improved efficiency and coherence. Understanding single facet lasers helps you choose the right laser type based on your application's need for simplicity versus advanced optical feedback.
Exploring Dual Facet Lasers
Dual facet lasers offer enhanced performance by utilizing two emitting surfaces to improve output power and beam quality compared to single facet lasers. This design reduces thermal effects and allows for better heat dissipation, which increases the laser's efficiency and operational stability. If you require higher power and reliability in your applications, dual facet lasers provide a robust solution by delivering superior optical performance and durability.
Key Differences: Single Facet vs Dual Facet
Single facet lasers utilize one polished surface as the emission facet, resulting in simpler alignment but potential limitations in power output and beam quality. Dual facet lasers employ two polished facets, enhancing emission direction control and allowing higher power thresholds with improved beam characteristics. The key differences revolve around emission efficiency, thermal management, and application suitability in high-precision environments.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Single facet lasers typically offer high output power but suffer from lower beam quality due to unidirectional emission, limiting overall performance in precision applications. Dual facet lasers improve beam quality and stability by enabling bidirectional emission, resulting in enhanced efficiency and consistent optical output. Efficiency gains in dual facet designs stem from balanced thermal management and reduced optical losses, boosting performance in high-speed communication and sensing systems.
Applications of Single Facet Lasers
Single facet lasers are widely used in fiber optic communications due to their ability to provide stable, high-quality single-mode output suitable for long-distance data transmission. These lasers are also common in sensing applications and precision measurement systems because their single emitting facet enables reduced feedback and enhanced coherence. Their compact design and reliable performance make them ideal for integration into portable and industrial laser modules.
Uses of Dual Facet Lasers
Dual facet lasers are widely used in optical communication systems where simultaneous transmission and reception of signals are required, enhancing data throughput efficiency. These lasers offer advantages in sensing applications, such as LIDAR, by providing precise bidirectional measurements. Your optical network or sensor setup benefits from the compact design and integrated functionality of dual facet lasers, improving performance in complex signal processing tasks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Single facet lasers offer simplicity and cost efficiency due to their straightforward design, making them ideal for basic optical applications with moderate power needs. Dual facet lasers provide higher output power and improved beam quality through enhanced heat dissipation but come with increased complexity and production costs. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize budget-friendly solutions or advanced performance for demanding laser applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Facet Types
Choosing between single facet and dual facet lasers depends on factors such as power efficiency, beam quality, and thermal management. Single facet lasers typically offer simpler fabrication and alignment, while dual facet lasers provide higher output power and enhanced performance stability. Your application requirements, including desired wavelength stability and operational lifetime, play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate facet type.
Future Trends in Laser Facet Technology
Future trends in laser facet technology highlight advancements toward dual facet lasers, which offer enhanced performance including improved power output and beam quality compared to single facet designs. These innovations focus on integrating sophisticated coatings and thermal management techniques to extend device lifespan and efficiency. Your choice between single and dual facet lasers will increasingly depend on application-specific requirements, balancing cost and performance benefits as technology evolves.
Single facet vs Dual facet laser Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com