Laser marking produces a surface-level change on materials with high precision and minimal damage, ideal for barcodes or serial numbers, while laser engraving removes material to create deeper, tactile designs lasting longer on various surfaces. Explore the rest of the article to discover which laser technique best suits your project's needs.
Table of Comparison
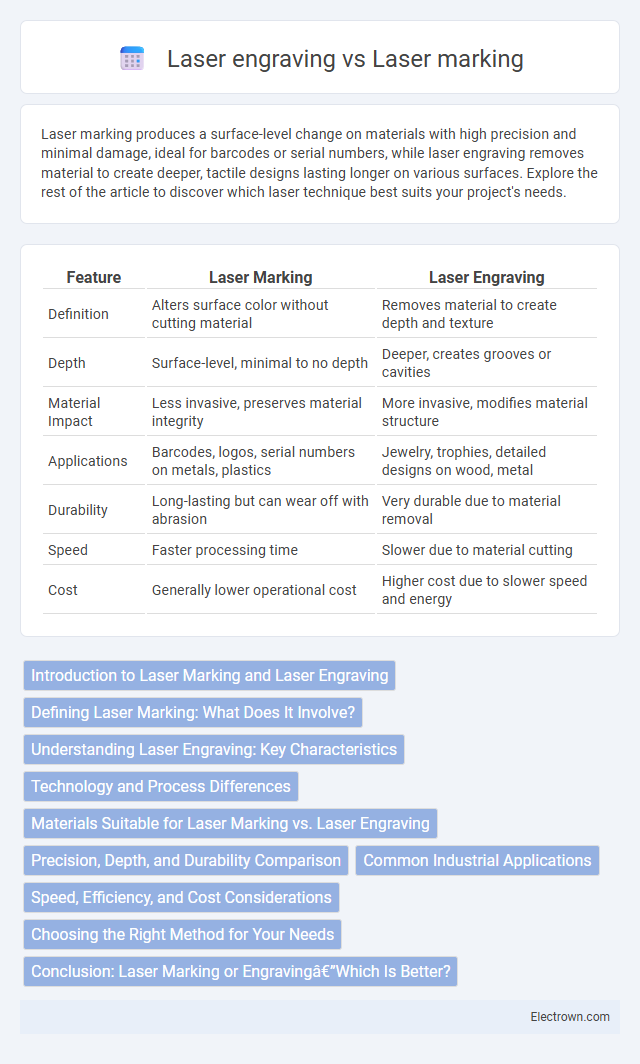
| Feature | Laser Marking | Laser Engraving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alters surface color without cutting material | Removes material to create depth and texture |
| Depth | Surface-level, minimal to no depth | Deeper, creates grooves or cavities |
| Material Impact | Less invasive, preserves material integrity | More invasive, modifies material structure |
| Applications | Barcodes, logos, serial numbers on metals, plastics | Jewelry, trophies, detailed designs on wood, metal |
| Durability | Long-lasting but can wear off with abrasion | Very durable due to material removal |
| Speed | Faster processing time | Slower due to material cutting |
| Cost | Generally lower operational cost | Higher cost due to slower speed and energy |
Introduction to Laser Marking and Laser Engraving
Laser marking involves altering the surface of a material to create high-contrast, permanent marks without removing material, ideal for barcodes, serial numbers, and logos on metals, plastics, and ceramics. Laser engraving removes a layer of the surface to produce deeper, tactile designs often used for decorative purposes and personalized items, effective on wood, glass, and acrylic. Choosing between laser marking and laser engraving depends on your application needs, surface type, and desired depth and permanence of the design.
Defining Laser Marking: What Does It Involve?
Laser marking involves using a concentrated laser beam to create precise, high-contrast marks on a material's surface without cutting deeply, ideal for barcodes, serial numbers, and logos. This process alters the surface's appearance through discoloration, oxidation, or foaming, ensuring durability and legibility without compromising structural integrity. You benefit from laser marking's efficiency and permanence for applications requiring clear, non-invasive identification.
Understanding Laser Engraving: Key Characteristics
Laser engraving uses high-powered lasers to remove material from a surface, creating deep, permanent marks that are ideal for durability and detail. This process alters the substrate beneath the top layer, ensuring your designs resist wear and fading over time. Unlike laser marking, which primarily changes the surface color without material removal, laser engraving produces tactile, textured results suitable for a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
Technology and Process Differences
Laser marking uses a lower power density laser to alter the surface color or create a contrast without removing material, often through oxidation or color change, making it ideal for fine details on metals and plastics. Laser engraving, by contrast, employs higher power to vaporize material, producing deeper, tactile grooves and more durable markings suitable for industrial applications. The engraving process typically requires more time and energy, but offers greater permanence and resistance to wear compared to marking.
Materials Suitable for Laser Marking vs. Laser Engraving
Laser marking works best on metals, plastics, ceramics, and coated materials, providing surface-level contrast without cutting into the substrate. Laser engraving suits a wider range of materials, including wood, leather, glass, and stone, as it removes layers to create deeper, more tactile designs. Your choice depends on the material's composition and the desired durability and depth of the mark or engraving.
Precision, Depth, and Durability Comparison
Laser marking offers exceptional precision for fine details and surface-level designs, making it ideal for intricate logos or serial numbers without altering material thickness. Laser engraving penetrates deeper, creating permanent, tactile markings that enhance durability and resist wear even under harsh conditions. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize high-precision surface marking or long-lasting, deeply etched designs for maximum durability.
Common Industrial Applications
Laser marking is widely used in electronics, automotive, and medical device industries for creating precise, permanent identification such as barcodes, serial numbers, and logos on metal or plastic surfaces without altering the material's depth. Laser engraving suits industrial applications requiring deeper material removal for tactile or decorative effects, including tool identification, mold making, and circuit board manufacturing. Your choice between laser marking and engraving depends on the desired durability and surface detail essential for product traceability and quality control.
Speed, Efficiency, and Cost Considerations
Laser marking offers faster processing speeds compared to laser engraving due to its surface alteration technique without material removal, enhancing overall efficiency in high-volume production. While laser engraving produces deeper, more durable marks ideal for long-term traceability, it consumes more power and time, increasing operational costs. Cost considerations favor laser marking for applications requiring rapid, cost-effective identification, whereas laser engraving suits scenarios demanding high precision and permanence despite higher expenses.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Laser marking offers a precise, shallow method ideal for high-speed applications and materials sensitive to heat, while laser engraving provides deeper, more durable designs suitable for creating tactile surfaces and lasting impressions. Evaluating factors such as material type, desired mark depth, production speed, and budget helps determine the optimal technique. Understanding these distinctions ensures your project benefits from the most effective, high-quality laser customization.
Conclusion: Laser Marking or Engraving—Which Is Better?
Laser marking offers high-speed, precise surface identification ideal for applications requiring non-invasive, durable marks without altering material thickness. Laser engraving delivers deeper, more tactile designs suitable for permanent, detailed customization on metals, plastics, and wood. The choice depends on project requirements for depth, visibility, and material compatibility, with laser marking favored for subtle branding and engraving preferred for lasting, three-dimensional effects.
Laser marking vs Laser engraving Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com