Light pipes and fiber optics both transmit light but differ significantly in structure and application; light pipes use solid, rigid materials to guide light typically over short distances with minimal bending, while fiber optics utilize flexible, glass or plastic fibers capable of transmitting data over long distances with high bandwidth and low loss. Discover how your choice between these two technologies can impact your lighting or communication projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
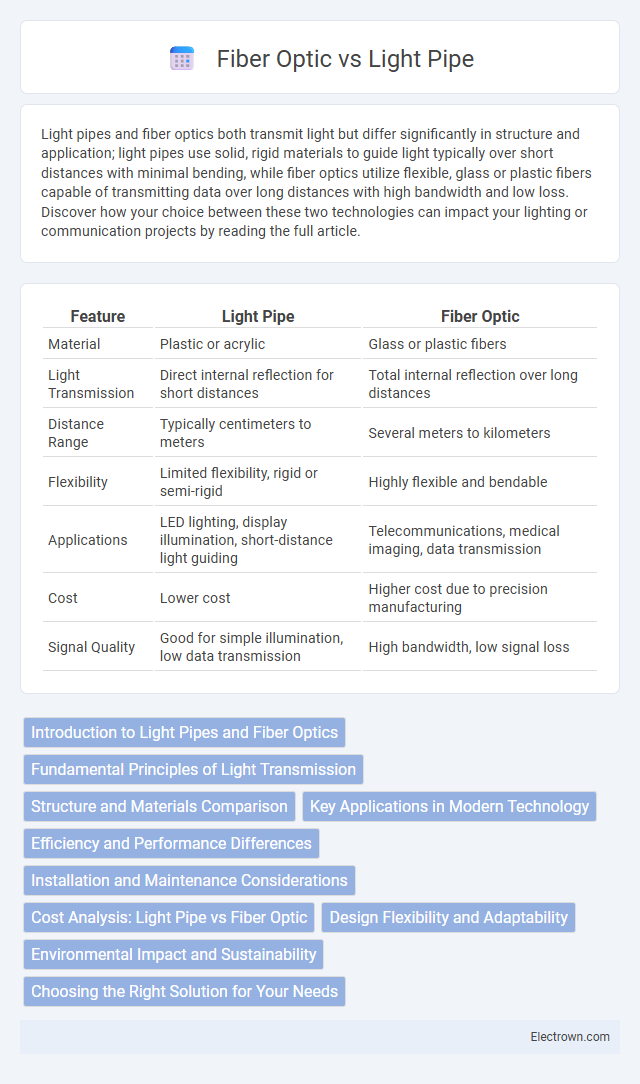
| Feature | Light Pipe | Fiber Optic |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic or acrylic | Glass or plastic fibers |
| Light Transmission | Direct internal reflection for short distances | Total internal reflection over long distances |
| Distance Range | Typically centimeters to meters | Several meters to kilometers |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, rigid or semi-rigid | Highly flexible and bendable |
| Applications | LED lighting, display illumination, short-distance light guiding | Telecommunications, medical imaging, data transmission |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to precision manufacturing |
| Signal Quality | Good for simple illumination, low data transmission | High bandwidth, low signal loss |
Introduction to Light Pipes and Fiber Optics
Light pipes are optical components designed to guide light between two points using total internal reflection within a transparent medium, often used for short-distance light transmission in electronic devices. Fiber optics consist of thin strands of glass or plastic fibers that transmit light signals over long distances with minimal loss, enabling high-speed communication and data transfer. Your choice between light pipes and fiber optics depends on distance requirements and application needs, with fiber optics excelling in telecommunications and light pipes ideal for compact, internal illumination.
Fundamental Principles of Light Transmission
Light pipes transmit light through internal reflection within a solid transparent medium, relying on total internal reflection to guide light along a fixed path without significant loss. Fiber optics utilize a core-cladding structure with a higher refractive index inside the core, enabling light signals to propagate over long distances through multiple internal reflections with minimal attenuation. The fundamental difference lies in fiber optics supporting high-bandwidth data transmission using optical fibers, while light pipes are typically used for simpler light guiding in short distances and low data applications.
Structure and Materials Comparison
Light pipes typically consist of solid transparent materials such as acrylic or polycarbonate, designed with a simple cylindrical or rectangular shape to guide light through total internal reflection. Fiber optic cables are made from flexible glass or plastic fibers, featuring a core surrounded by cladding with a lower refractive index to enable efficient light transmission over long distances. Your choice between these depends on the required transmission distance, flexibility, and precision, as fiber optics provide superior signal quality and range compared to light pipes.
Key Applications in Modern Technology
Light pipes are widely used in electronic devices for efficient internal illumination and indicator signaling due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. Fiber optic cables dominate telecommunications and medical imaging, leveraging their high bandwidth and minimal signal loss over long distances. Your choice between light pipe and fiber optic depends on the need for either simple light transmission within devices or high-speed data transfer across extended networks.
Efficiency and Performance Differences
Fiber optic cables deliver higher efficiency and superior performance compared to light pipes due to their ability to transmit data at faster speeds with minimal signal loss over long distances. Light pipes, constructed from solid or hollow materials, primarily guide visible light for illumination purposes and lack the bandwidth and low attenuation characteristics of fiber optics. Your choice between the two should consider fiber optics' enhanced data transmission capabilities versus light pipes' effectiveness in simple light routing applications.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Light pipe installation involves straightforward alignment and securing within panels or enclosures, often requiring minimal specialized tools, which can reduce overall setup time. Fiber optic systems demand precise connectorization, careful handling to avoid fiber breakage, and specialized splicing equipment, leading to higher installation complexity and maintenance costs. Your choice may depend on the environment's tolerance for complexity and the level of technical expertise available for ongoing system upkeep.
Cost Analysis: Light Pipe vs Fiber Optic
Light pipes offer a cost-effective solution for short-distance light transmission due to their simple design and lower material expenses compared to fiber optic cables. Fiber optics involve higher initial costs driven by advanced manufacturing processes and specialized installation requirements but provide superior performance over long distances and higher bandwidth capacities. For budget-sensitive applications with limited distance, light pipes minimize expenses, while fiber optics justify their investment through enhanced durability and data transmission efficiency in large-scale or mission-critical setups.
Design Flexibility and Adaptability
Light pipes offer greater design flexibility and adaptability for short-distance, low-loss light transmission within compact electronic devices, allowing easy integration into various shapes and sizes. Fiber optic cables excel in long-distance, high-bandwidth communication with superior signal integrity but are less adaptable to tight or intricate layouts due to their fragility and minimum bend radius requirements. Choosing between light pipes and fiber optics depends on your specific application needs, balancing design constraints with performance demands.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Light pipes consume less energy and generate minimal electronic waste due to their simpler materials and design, resulting in a lower environmental footprint compared to fiber optics. Fiber optic cables, while offering superior data transmission over long distances, rely on silica and rare-earth elements whose extraction and disposal can be environmentally challenging. Your choice between these technologies should consider sustainability goals alongside performance needs to minimize ecological impact.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Light pipes offer a cost-effective and simple solution for short-distance, low-loss light transmission, ideal for indicator lighting and display applications. Fiber optic cables provide superior bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them essential for high-speed data communication and telecommunication networks. Selecting the right solution depends on factors like transmission distance, data rate requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Light pipe vs Fiber optic Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com