OLED displays offer vibrant colors and deep blacks with self-emissive pixels, while MicroLED technology provides higher brightness, longer lifespan, and better energy efficiency without burn-in issues. Explore the rest of the article to discover which display technology best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
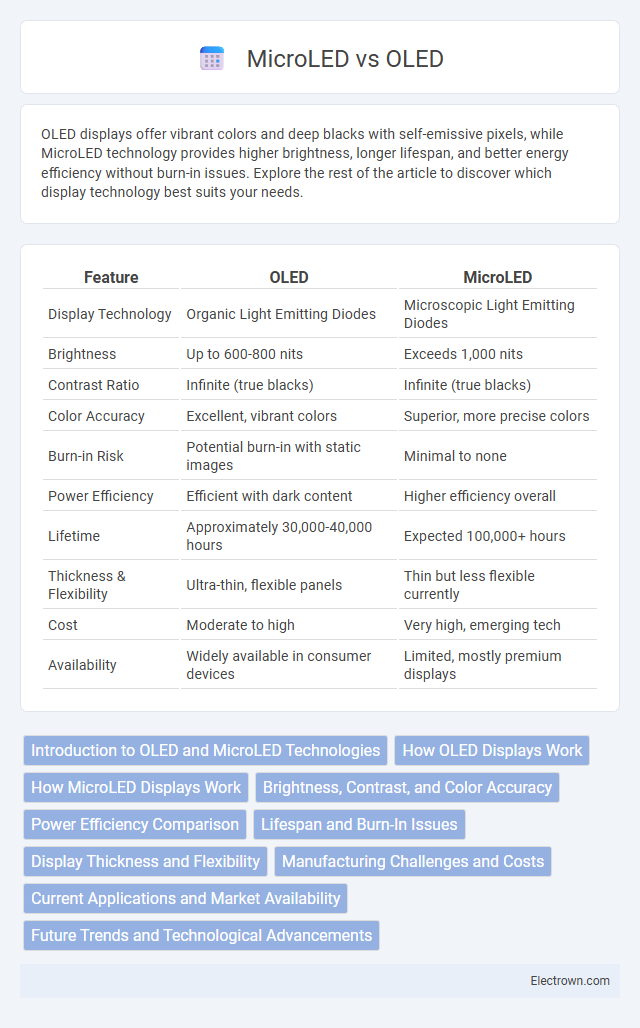
| Feature | OLED | MicroLED |
|---|---|---|
| Display Technology | Organic Light Emitting Diodes | Microscopic Light Emitting Diodes |
| Brightness | Up to 600-800 nits | Exceeds 1,000 nits |
| Contrast Ratio | Infinite (true blacks) | Infinite (true blacks) |
| Color Accuracy | Excellent, vibrant colors | Superior, more precise colors |
| Burn-in Risk | Potential burn-in with static images | Minimal to none |
| Power Efficiency | Efficient with dark content | Higher efficiency overall |
| Lifetime | Approximately 30,000-40,000 hours | Expected 100,000+ hours |
| Thickness & Flexibility | Ultra-thin, flexible panels | Thin but less flexible currently |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Very high, emerging tech |
| Availability | Widely available in consumer devices | Limited, mostly premium displays |
Introduction to OLED and MicroLED Technologies
OLED technology utilizes organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through, enabling thinner displays with deep blacks and vibrant colors. MicroLED, composed of tiny inorganic LEDs, offers higher brightness, longer lifespan, and improved energy efficiency compared to OLED. Your choice between these display types depends on preferences for color accuracy, longevity, and power consumption.
How OLED Displays Work
OLED displays operate by using organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through them, enabling each pixel to produce its own light independently. This self-emissive technology results in deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios compared to traditional backlit displays. The efficient pixel-level illumination in OLED screens contributes to thinner display panels and faster response times, enhancing overall image quality and energy efficiency.
How MicroLED Displays Work
MicroLED displays function by using microscopic LEDs as individual pixels, each emitting its own light without the need for backlighting, resulting in higher brightness and contrast compared to OLEDs. These tiny LEDs are self-emissive, which allows MicroLED screens to deliver deeper blacks and more vivid colors while maintaining energy efficiency. Your viewing experience benefits from the enhanced durability and superior image quality inherent to MicroLED technology.
Brightness, Contrast, and Color Accuracy
MicroLED displays surpass OLED with higher brightness levels, reaching up to 10,000 nits compared to OLED's typical 600-800 nits, making them ideal for bright environments. OLED excels in contrast due to its self-emissive pixels that produce perfect blacks by turning off individually, whereas MicroLED achieves high contrast through independent LED modulation but may have slight blooming effects. Both technologies offer exceptional color accuracy, with MicroLED providing wider color gamuts and longer lifespan without burn-in, while OLED delivers rich, vibrant colors with deep saturation.
Power Efficiency Comparison
OLED displays consume less power when displaying darker images due to individual pixel lighting, making them more efficient for content with darker scenes. MicroLED technology offers superior power efficiency overall, especially at higher brightness levels, by using inorganic LEDs that emit light more efficiently and reduce energy waste. Your choice depends on usage patterns, with OLED favoring low-brightness scenarios and MicroLED excelling in bright environments and extended use.
Lifespan and Burn-In Issues
OLED displays offer exceptional color accuracy and contrast but face challenges with limited lifespan and susceptibility to burn-in due to organic material degradation. MicroLED technology provides significantly longer lifespan and superior durability by using inorganic LEDs that resist burn-in while maintaining high brightness and color performance. The inherent stability of MicroLED makes it increasingly preferred for applications requiring prolonged use and consistent image quality.
Display Thickness and Flexibility
MicroLED displays offer superior thinness and enhanced flexibility compared to OLED panels, enabling more innovative and slim device designs. OLED screens are already thin and flexible due to their organic light-emitting layers, but MicroLED's inorganic materials allow for even slimmer profiles and greater durability under bending stress. Your choice between OLED and MicroLED can impact the thickness and flexibility of your device, influencing portability and design possibilities.
Manufacturing Challenges and Costs
OLED displays face manufacturing challenges such as organic material degradation and complex encapsulation processes, leading to higher costs and limited lifespan. MicroLED production requires precise placement of millions of tiny LEDs, posing significant scalability and yield issues, which currently result in expensive fabrication. Both technologies involve costly capital equipment, but MicroLED's nascent manufacturing techniques drive even higher initial expenses compared to OLED.
Current Applications and Market Availability
OLED technology dominates current consumer markets with widespread use in smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices due to its superior contrast and flexibility. MicroLED, still emerging, is gaining traction in high-end displays and large-scale digital signage for its exceptional brightness, durability, and energy efficiency. Your choice between OLED and MicroLED depends on availability and application needs, with OLED offering immediate market access and MicroLED expected to expand rapidly as production costs decline.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
MicroLED technology is rapidly advancing with improved brightness, energy efficiency, and longer lifespan compared to OLED displays, making it a strong contender for future high-end screens. OLED panels offer superior contrast and flexibility but face challenges in longevity and burn-in issues, which ongoing research aims to mitigate through more durable materials and innovative pixel designs. You can expect future display devices to increasingly adopt MicroLED for large-format and outdoor applications, while OLED remains dominant in smartphones and wearable technology due to its thinness and vibrant color reproduction.
OLED vs MicroLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com