QD-LED offers enhanced brightness and color accuracy compared to OLED, making it ideal for vivid displays while OLED provides superior contrast and deeper blacks due to its self-emissive pixels. Discover how these technologies impact your viewing experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
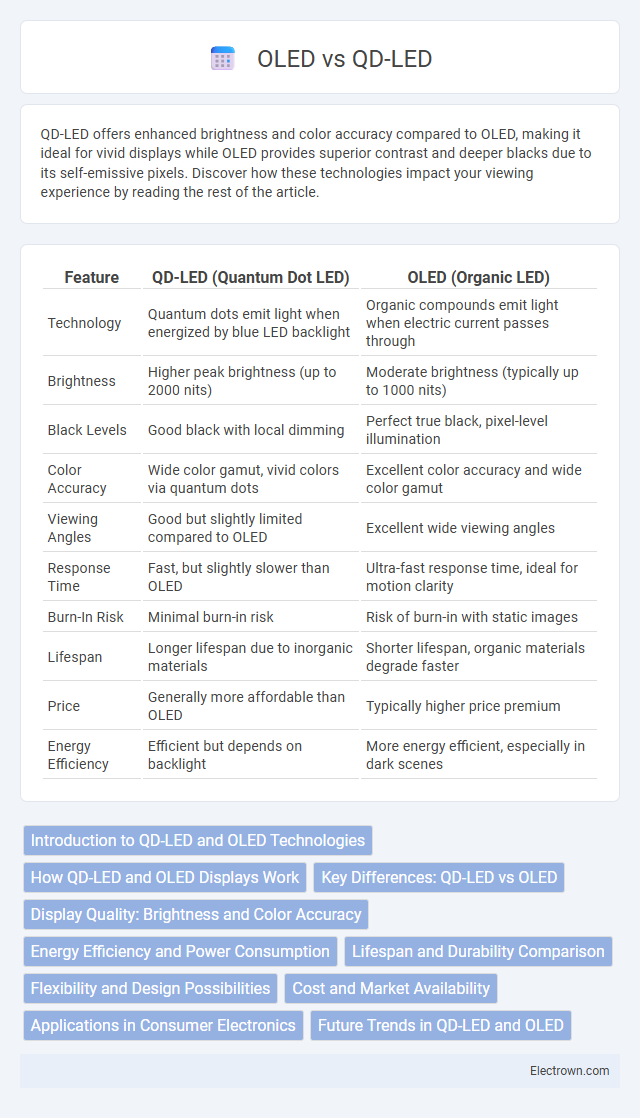
| Feature | QD-LED (Quantum Dot LED) | OLED (Organic LED) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Quantum dots emit light when energized by blue LED backlight | Organic compounds emit light when electric current passes through |
| Brightness | Higher peak brightness (up to 2000 nits) | Moderate brightness (typically up to 1000 nits) |
| Black Levels | Good black with local dimming | Perfect true black, pixel-level illumination |
| Color Accuracy | Wide color gamut, vivid colors via quantum dots | Excellent color accuracy and wide color gamut |
| Viewing Angles | Good but slightly limited compared to OLED | Excellent wide viewing angles |
| Response Time | Fast, but slightly slower than OLED | Ultra-fast response time, ideal for motion clarity |
| Burn-In Risk | Minimal burn-in risk | Risk of burn-in with static images |
| Lifespan | Longer lifespan due to inorganic materials | Shorter lifespan, organic materials degrade faster |
| Price | Generally more affordable than OLED | Typically higher price premium |
| Energy Efficiency | Efficient but depends on backlight | More energy efficient, especially in dark scenes |
Introduction to QD-LED and OLED Technologies
QD-LED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology utilizes nanocrystal quantum dots to produce pure, saturated colors with high brightness and energy efficiency. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology employs organic compounds that emit light when an electric current passes through, offering superior contrast ratios and flexibility in display design. Both technologies represent advanced display solutions, with QD-LED excelling in color accuracy and OLED in contrast and viewing angles.
How QD-LED and OLED Displays Work
QD-LED displays utilize quantum dots that emit light when illuminated by a blue LED backlight, enhancing color accuracy and brightness through precise light modulation. OLED displays consist of organic compounds that emit light directly when an electric current passes through, allowing for true blacks and superior contrast due to pixel-level light emission control. The fundamental difference lies in QD-LED relying on a separate light source and color conversion, whereas OLED achieves self-emission for each pixel.
Key Differences: QD-LED vs OLED
QD-LED displays use quantum dots to enhance color accuracy and brightness by converting blue LED backlight into pure, vivid colors, whereas OLED panels emit light individually from organic compounds, providing superior contrast with true blacks. QD-LED screens typically achieve higher peak brightness and better color volume, making them ideal for bright environments, while OLEDs excel in deep black levels and viewing angles due to their self-emissive technology. In terms of durability, QD-LEDs have a longer lifespan and are less prone to burn-in compared to OLEDs, which can degrade over time with static images.
Display Quality: Brightness and Color Accuracy
QD-LED displays offer significantly higher brightness levels compared to OLED, often reaching up to 1,500 nits or more, making them ideal for well-lit environments. In terms of color accuracy, QD-LED panels achieve a wider color gamut with enhanced color volume due to their quantum dot technology, providing richer and more vibrant hues. OLED screens excel in deep black levels and contrast ratios because each pixel emits its light and can turn off completely, but they generally have lower peak brightness than QD-LED displays.
Energy Efficiency and Power Consumption
QD-LED technology offers higher energy efficiency compared to OLED by using quantum dots that emit light more precisely, reducing power consumption for brighter displays at lower wattage. OLED displays, while capable of deep black levels and vibrant colors, consume more power because each pixel generates light individually, especially for bright or white backgrounds. Choosing QD-LED can optimize your device's battery life and energy use without sacrificing picture quality.
Lifespan and Durability Comparison
QD-LED displays boast a longer lifespan and enhanced durability compared to OLEDs, primarily due to their inorganic quantum dot materials that resist burn-in and degradation over time. OLED panels rely on organic compounds that can deteriorate faster, leading to diminished brightness and potential image retention issues. Consequently, QD-LED technology offers improved longevity for applications demanding extended use and consistent performance.
Flexibility and Design Possibilities
QD-LED displays offer enhanced flexibility with lightweight, thin layers that enable curved and rollable screen designs, pushing the boundaries of innovative device form factors. OLED technology excels in creating ultra-thin, bendable panels with exceptional color accuracy and contrast, allowing seamless integration into flexible smartphones, wearables, and foldable TVs. The superior mechanical resilience of QD-LED materials supports dynamic applications requiring frequent bending without degradation, whereas OLED's organic layers demand more careful handling despite their vivid display capabilities.
Cost and Market Availability
QD-LED displays typically offer a lower production cost compared to OLED due to more established manufacturing processes utilizing inorganic materials, resulting in greater market availability and an expanding range of affordable options. OLED panels, while often delivering superior contrast and color accuracy, remain more expensive to produce and are predominantly found in premium devices with limited mass-market penetration. To maximize value for your budget, consider QD-LED for cost-effective widespread availability or OLED if willing to invest in higher-priced displays with advanced image quality.
Applications in Consumer Electronics
QD-LED technology offers improved color accuracy and brightness, making it ideal for next-generation TVs, monitors, and smartphones, where vibrant and energy-efficient displays are critical. OLED displays excel in flexible and wearable devices due to their thin, lightweight, and bendable nature, widely adopted in smartphones, smartwatches, and VR headsets. The consumer electronics industry leverages QD-LED for enhanced visual performance in large-screen displays, while OLED dominates in compact, flexible gadgets requiring high contrast and deep blacks.
Future Trends in QD-LED and OLED
QD-LED technology is advancing with enhanced color purity and higher brightness efficiency, positioning it as a strong contender for next-generation displays in smartphones and TVs. OLED continues to evolve through flexible and transparent display innovations, targeting wearable devices and foldables while addressing issues like burn-in and lifespan. Future trends indicate a convergence where hybrid displays leveraging quantum dot layers with OLED emitters might deliver superior color accuracy and energy savings.
QD-LED vs OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com