Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a stable reverse breakdown voltage, while photodiodes convert light into electrical current, making them essential for light detection applications. Discover how understanding the key differences between these devices can enhance Your electronic projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
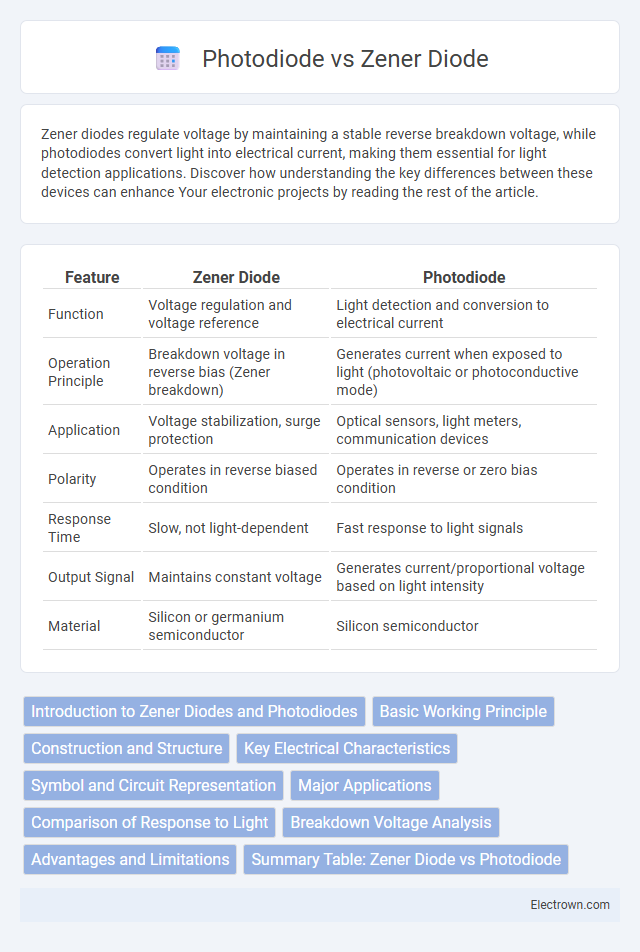
| Feature | Zener Diode | Photodiode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Voltage regulation and voltage reference | Light detection and conversion to electrical current |
| Operation Principle | Breakdown voltage in reverse bias (Zener breakdown) | Generates current when exposed to light (photovoltaic or photoconductive mode) |
| Application | Voltage stabilization, surge protection | Optical sensors, light meters, communication devices |
| Polarity | Operates in reverse biased condition | Operates in reverse or zero bias condition |
| Response Time | Slow, not light-dependent | Fast response to light signals |
| Output Signal | Maintains constant voltage | Generates current/proportional voltage based on light intensity |
| Material | Silicon or germanium semiconductor | Silicon semiconductor |
Introduction to Zener Diodes and Photodiodes
Zener diodes are semiconductor devices designed to operate in reverse breakdown region, providing voltage regulation by maintaining a constant voltage across their terminals. Photodiodes are light-sensitive semiconductors that convert incident photons into electrical current, primarily used in optical communication and sensing applications. Both devices serve distinct electronic roles: Zener diodes stabilize voltage, while photodiodes detect and measure light intensity.
Basic Working Principle
A Zener diode operates by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds a specific breakdown level known as the Zener voltage, maintaining a stable voltage across its terminals. A photodiode generates current when exposed to light by converting photons into electron-hole pairs, operating primarily in reverse bias to measure light intensity. The Zener diode is used for voltage regulation, while the photodiode serves as a light sensor in optical applications.
Construction and Structure
A Zener diode features a heavily doped p-n junction designed to operate in reverse breakdown for voltage regulation, with a compact and uniform semiconductor structure. A photodiode consists of a p-n junction optimized for light absorption, often with a larger surface area and transparent window to enhance photon capture and convert light into current. Your choice depends on whether precise voltage control or efficient light detection is required based on these structural differences.
Key Electrical Characteristics
Zener diodes exhibit a precise breakdown voltage used for voltage regulation, with a sharp voltage drop occurring at the Zener voltage, typically ranging from a few volts to several hundred volts, and maintain stable reverse current. Photodiodes generate current proportional to incident light intensity, operating primarily in reverse bias mode with low dark current and fast response time, making them ideal for optical detection. Your choice depends on whether you need voltage regulation with a defined breakdown voltage or light sensing with high sensitivity and speed.
Symbol and Circuit Representation
The Zener diode symbol features a standard diode arrow with bent edges on the cathode line, representing its voltage regulation function, while its circuit representation often includes it connected in reverse bias across a load to maintain a stable voltage. In contrast, the photodiode symbol resembles a diode with two arrows pointing towards it, indicating light sensitivity, and is typically depicted in circuits with a reversed bias to maximize photocurrent generation under illumination. Both symbols are crucial for identifying device functionality in electronic schematics, with the Zener diode emphasizing voltage stabilization and the photodiode focusing on light detection.
Major Applications
Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation, providing stable reference voltages in power supplies and protecting circuits from overvoltage conditions. Photodiodes are majorly employed in light detection systems, including optical communication, medical devices, and ambient light sensing. The distinct functions of Zener diodes in voltage control and photodiodes in light sensing define their critical roles in electronic and optoelectronic applications.
Comparison of Response to Light
Zener diodes are designed primarily for voltage regulation and exhibit negligible response to light, making them unsuitable for light detection applications. Photodiodes convert light into electrical current, offering high sensitivity and fast response times ideal for optical sensing and communication. Your choice depends on whether you need voltage stabilization (Zener diode) or precise light detection and measurement (photodiode).
Breakdown Voltage Analysis
Zener diodes exhibit a precisely controlled breakdown voltage, typically ranging from a few volts to several hundred volts, which enables stable voltage regulation in electronic circuits. Photodiodes, however, generally operate below their avalanche breakdown region to maintain linearity in light detection, with breakdown voltages often higher and less precisely defined than Zener diodes. Breakdown voltage stability in Zener diodes is critical for voltage reference applications, whereas photodiodes prioritize responsivity and low noise over breakdown voltage characteristics.
Advantages and Limitations
Zener diodes excel in voltage regulation with their precise breakdown voltage characteristics, making them ideal for protecting circuits from voltage spikes, but they are not sensitive to light and cannot convert light signals. Photodiodes, designed to convert light into electrical current, offer high sensitivity and fast response for optical communication and light detection, yet they require external bias and have limited voltage regulation capabilities. Both components serve distinct purposes, with Zener diodes providing stable voltage control and photodiodes enabling efficient optical signal detection.
Summary Table: Zener Diode vs Photodiode
Zener diodes regulate voltage by operating in reverse breakdown, providing a stable reference voltage critical for power supplies and voltage regulation circuits. Photodiodes convert light into electrical current, enabling precise light detection used in optical communication and sensing devices. Your choice depends on whether you need voltage stabilization (Zener diode) or light detection capabilities (photodiode).
Zener diode vs Photodiode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com