AC choppers regulate the voltage and current in alternating current circuits by rapidly switching the AC supply on and off, enabling efficient control of power to AC motors and devices. Understanding the differences between AC and DC choppers can enhance your ability to select the right power control method for your application; read on to explore their key features and uses.
Table of Comparison
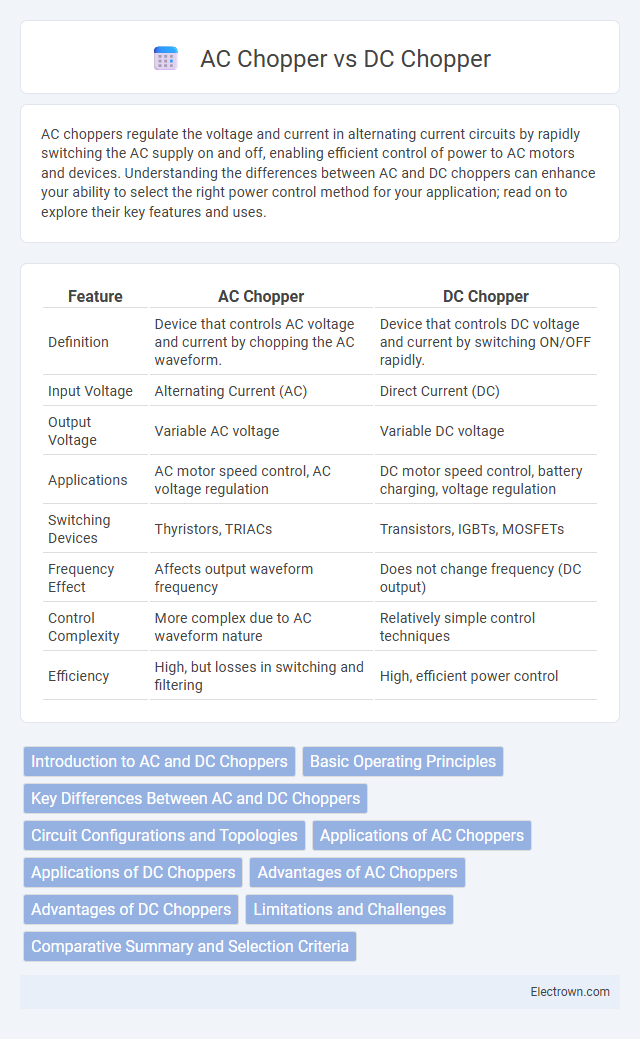
| Feature | AC Chopper | DC Chopper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Device that controls AC voltage and current by chopping the AC waveform. | Device that controls DC voltage and current by switching ON/OFF rapidly. |
| Input Voltage | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Output Voltage | Variable AC voltage | Variable DC voltage |
| Applications | AC motor speed control, AC voltage regulation | DC motor speed control, battery charging, voltage regulation |
| Switching Devices | Thyristors, TRIACs | Transistors, IGBTs, MOSFETs |
| Frequency Effect | Affects output waveform frequency | Does not change frequency (DC output) |
| Control Complexity | More complex due to AC waveform nature | Relatively simple control techniques |
| Efficiency | High, but losses in switching and filtering | High, efficient power control |
Introduction to AC and DC Choppers
AC choppers regulate alternating current voltage by controlling the power flow through semiconductor devices, enabling precise speed control in AC motors and efficient power conversion. DC choppers modulate direct current by rapidly switching semiconductor switches on and off, allowing adjustable voltage levels for applications like electric vehicles and DC motor drives. Both devices enhance energy efficiency and system performance but operate based on different electrical principles and are suited for distinct types of loads.
Basic Operating Principles
AC choppers regulate voltage by controlling the output waveform through semiconductor switches like thyristors or triacs, enabling phase angle control for alternating current. DC choppers adjust the voltage by rapidly switching a semiconductor device on and off, varying the duty cycle to maintain a stable direct current output. Both devices efficiently manage power by controlling the conduction period of their respective signals, optimizing energy delivery in various applications.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Choppers
AC choppers regulate power by controlling the input AC voltage through phase angle or pulse-width modulation techniques, whereas DC choppers directly modulate DC voltage by switching electronic devices on and off rapidly. AC choppers often involve complex circuitry to convert and control alternating current, while DC choppers use simpler configurations like buck or boost converters for voltage control. The key differences lie in their input type, control methods, and applications, where AC choppers manage AC loads and DC choppers commonly provide variable DC outputs for motor drives and power supplies.
Circuit Configurations and Topologies
AC choppers typically use bidirectional switches like triacs or IGBTs and employ configurations such as single-phase or three-phase half-controlled and fully-controlled circuits to modulate AC voltage. DC choppers utilize unidirectional switches like MOSFETs or IGBTs arranged in topologies including buck, boost, buck-boost, and Cuk converters for efficient DC voltage regulation. Your choice of chopper circuit depends on the application's power requirements and the desired control complexity in managing voltage and current waveforms.
Applications of AC Choppers
AC choppers are primarily used in controlling the voltage and current supplied to AC loads such as induction heaters, toroidal coil heating systems, and variable frequency drives for electric motors. These devices excel in applications requiring precise power control and energy efficiency, including light dimmers, fan speed controllers, and voltage regulators. Your industrial processes benefit from AC choppers by achieving smooth power modulation and improved performance in heating and motor speed control applications.
Applications of DC Choppers
DC choppers are widely used in applications requiring precise speed control of DC motors, such as electric vehicles, industrial drives, and traction systems. They offer efficient voltage regulation in battery-powered devices and renewable energy systems like solar power converters. DC choppers also enhance performance in power supplies and welding equipment by providing fast and reliable voltage control.
Advantages of AC Choppers
AC choppers offer precise control of voltage and current, making them highly efficient for varying load conditions in industrial applications. They reduce harmonic distortion and improve power factor compared to DC choppers, resulting in smoother motor operation and lower energy losses. Your systems benefit from enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance costs due to the robust design and better thermal performance of AC chopper circuits.
Advantages of DC Choppers
DC choppers offer precise speed control for DC motors by varying the voltage supplied, resulting in higher efficiency and reduced power losses compared to AC choppers. They provide rapid response to load changes and enable smooth torque control, enhancing the performance of electric vehicles and industrial drives. Their simpler circuit design and regenerative braking capability contribute to energy savings and prolonged equipment lifespan.
Limitations and Challenges
AC choppers face challenges such as complex control circuits and difficulty in achieving smooth voltage regulation due to the alternating nature of the current, which affects power quality and increases harmonic distortion. DC choppers, while providing better voltage control and faster response, encounter limitations in handling high power levels and generating electromagnetic interference that requires effective filtering. Your choice between AC and DC choppers should consider these trade-offs based on the application's power requirements and control precision.
Comparative Summary and Selection Criteria
AC choppers regulate voltage and current in AC circuits primarily for controlling power in devices like induction motors, while DC choppers modulate DC voltage for applications such as electric vehicle drives and battery-powered systems. Selection criteria hinge on the type of load and source voltage; AC choppers are preferred for alternating current systems requiring variable AC output, whereas DC choppers suit scenarios demanding precise DC voltage control with high efficiency. Performance factors such as switching frequency, harmonics generation, and control complexity also influence the choice, with DC choppers offering simpler control and better dynamic response in DC applications.
AC chopper vs DC chopper Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com