Analog control provides continuous signal variation for precise adjustments, while digital control uses discrete signals offering greater accuracy and easier programmability. Explore the rest of the article to understand which control method best suits your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
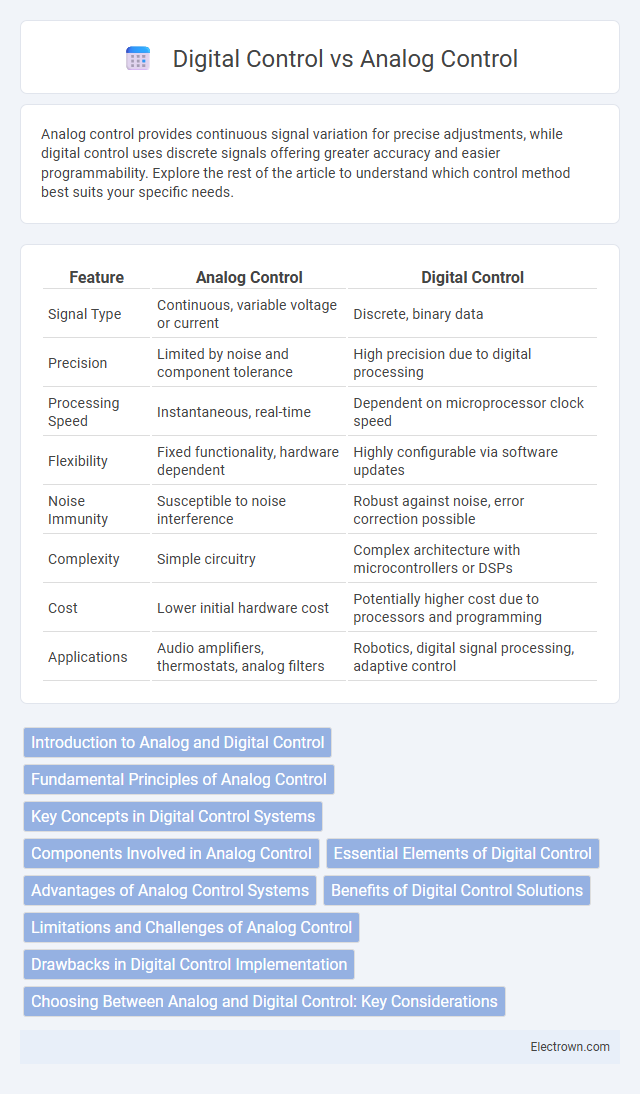
| Feature | Analog Control | Digital Control |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Continuous, variable voltage or current | Discrete, binary data |
| Precision | Limited by noise and component tolerance | High precision due to digital processing |
| Processing Speed | Instantaneous, real-time | Dependent on microprocessor clock speed |
| Flexibility | Fixed functionality, hardware dependent | Highly configurable via software updates |
| Noise Immunity | Susceptible to noise interference | Robust against noise, error correction possible |
| Complexity | Simple circuitry | Complex architecture with microcontrollers or DSPs |
| Cost | Lower initial hardware cost | Potentially higher cost due to processors and programming |
| Applications | Audio amplifiers, thermostats, analog filters | Robotics, digital signal processing, adaptive control |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Control
Analog control processes continuous signals through devices like amplifiers and resistors, enabling real-time adjustments with smooth signal variation. Digital control relies on discrete signals using microcontrollers or digital processors, offering precision and programmability for complex systems. Your choice depends on application requirements such as response speed, accuracy, and system complexity.
Fundamental Principles of Analog Control
Analog control relies on continuous signals to regulate system behavior, using real-time variations in voltage, current, or other physical quantities to adjust output. It operates through proportional, integral, and derivative functions, processing feedback to maintain stability and desired performance. Your system benefits from smooth signal transitions and immediate response without the need for discrete sampling inherent in digital control systems.
Key Concepts in Digital Control Systems
Digital control systems utilize discrete-time signals and microprocessors to implement control algorithms, enabling precise adjustments and programmability. Key concepts include sampling, quantization, and discrete-time system stability, which are essential for converting analog inputs into digital data for processing. Your understanding of digital controllers hinges on mastering these principles to design systems that achieve accurate and reliable performance.
Components Involved in Analog Control
Analog control systems primarily involve components such as operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and transistors to regulate continuous signals. Sensors convert physical parameters into analog voltages that are processed by these components to maintain desired system outputs. Feedback loops using analog components enable real-time adjustments based on signal variations without discrete binary states.
Essential Elements of Digital Control
Digital control systems rely on essential elements such as sensors to convert physical signals into digital data, microprocessors or controllers to process this data using algorithms, and actuators to execute control commands. Unlike analog control, which uses continuous signals, digital control systems operate via discrete-time signals for better precision and flexibility. Memory components store control programs and data, enabling advanced functionalities like adaptive control and real-time system monitoring.
Advantages of Analog Control Systems
Analog control systems offer continuous, real-time signal processing that enables precise and smooth regulation of variables such as temperature, pressure, or speed. Their simplicity, lower latency, and superior response time make them ideal for applications requiring fast and accurate control without the need for complex conversions. You benefit from increased reliability and minimal signal distortion in environments where continuous monitoring and adjustments are critical.
Benefits of Digital Control Solutions
Digital control solutions offer enhanced precision and flexibility compared to analog control by utilizing microprocessors and software algorithms, enabling real-time data processing and adaptive system adjustments. These systems improve scalability and integration capabilities with modern IoT and automation platforms, leading to more efficient and reliable performance. Your operations can benefit from easier troubleshooting, reduced noise interference, and the ability to implement complex control strategies through digital control technologies.
Limitations and Challenges of Analog Control
Analog control systems face limitations such as signal degradation due to noise interference and component tolerances, which reduce precision and reliability. The continuous nature of analog signals makes them susceptible to drift over time, requiring frequent calibration and maintenance. Scalability and integration with modern digital systems pose challenges as analog control lacks the flexibility and programmability inherent in digital control architectures.
Drawbacks in Digital Control Implementation
Digital control systems often face challenges like limited sampling rates, which can introduce aliasing and reduce system responsiveness. Quantization errors due to finite word length in digital processors lead to precision loss and signal distortion. Moreover, digital implementation requires complex algorithms and real-time processing capabilities, increasing system cost and design complexity compared to analog control.
Choosing Between Analog and Digital Control: Key Considerations
Choosing between analog and digital control depends on factors like system complexity, precision requirements, and environmental conditions. Analog control offers continuous signal processing suitable for real-time applications with minimal latency, while digital control excels in programmability, flexibility, and ease of integration with modern microcontrollers. Cost, noise immunity, and scalability also influence the decision, with digital systems favored for advanced automation and analog preferred in simple or high-speed control tasks.
Analog control vs Digital control Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com