LLC resonant converters offer higher efficiency and better voltage regulation under varying loads compared to series resonant converters, making them ideal for applications requiring stable power supply and reduced electromagnetic interference. Explore the full article to understand how choosing between LLC and series resonant topologies can optimize Your power electronic designs.
Table of Comparison
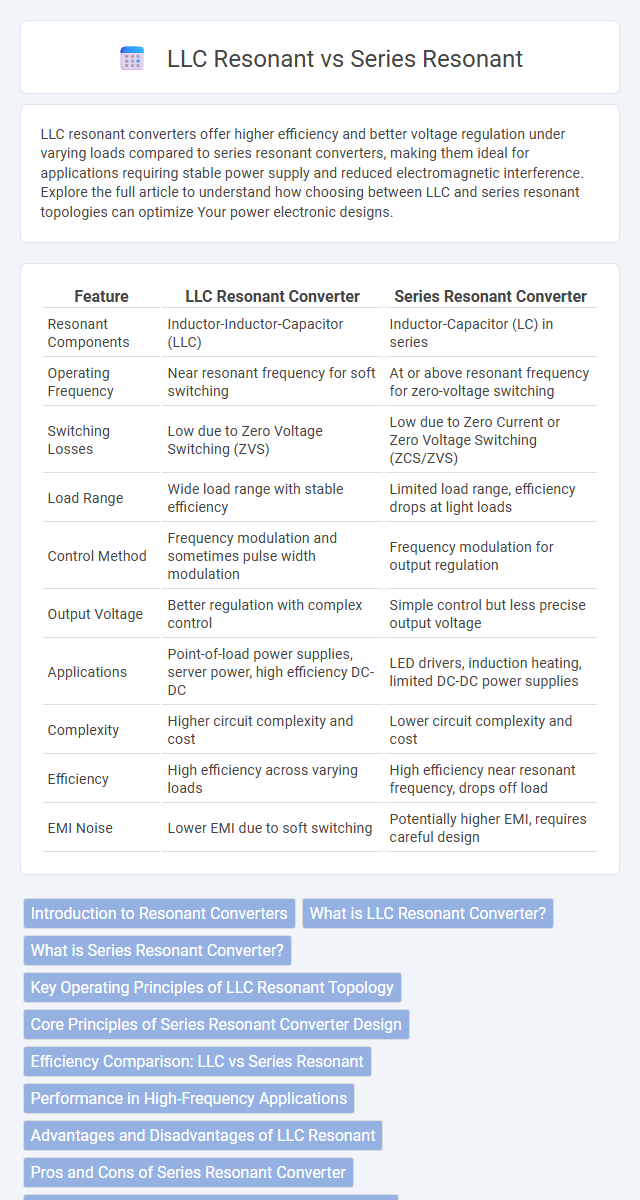
| Feature | LLC Resonant Converter | Series Resonant Converter |
|---|---|---|
| Resonant Components | Inductor-Inductor-Capacitor (LLC) | Inductor-Capacitor (LC) in series |
| Operating Frequency | Near resonant frequency for soft switching | At or above resonant frequency for zero-voltage switching |
| Switching Losses | Low due to Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) | Low due to Zero Current or Zero Voltage Switching (ZCS/ZVS) |
| Load Range | Wide load range with stable efficiency | Limited load range, efficiency drops at light loads |
| Control Method | Frequency modulation and sometimes pulse width modulation | Frequency modulation for output regulation |
| Output Voltage | Better regulation with complex control | Simple control but less precise output voltage |
| Applications | Point-of-load power supplies, server power, high efficiency DC-DC | LED drivers, induction heating, limited DC-DC power supplies |
| Complexity | Higher circuit complexity and cost | Lower circuit complexity and cost |
| Efficiency | High efficiency across varying loads | High efficiency near resonant frequency, drops off load |
| EMI Noise | Lower EMI due to soft switching | Potentially higher EMI, requires careful design |
Introduction to Resonant Converters
Resonant converters utilize either LLC or series resonant topologies to achieve high-efficiency power conversion in electronics. LLC resonant converters feature two inductors and a capacitor forming a tank circuit that enables zero-voltage switching (ZVS) across a wide load range, improving efficiency and reducing electromagnetic interference. Series resonant converters rely on a single inductor and capacitor in series, offering simplicity but typically narrower operating frequency ranges and less efficient switching compared to LLC designs.
What is LLC Resonant Converter?
LLC resonant converters utilize a combination of inductors (L) and capacitors (C) arranged to create a resonant tank that achieves zero-voltage switching (ZVS) for high efficiency and reduced electromagnetic interference. Unlike series resonant converters that rely on a single resonant element, the LLC topology allows for better load regulation and higher power density by operating near the resonant frequency with an added magnetizing inductance (L). This results in improved efficiency and performance in applications such as power supplies for data centers, EV chargers, and consumer electronics.
What is Series Resonant Converter?
A Series Resonant Converter is a type of DC-DC converter that utilizes a series resonant tank, consisting of an inductor and a capacitor, to achieve efficient energy transfer at a specific resonant frequency. This converter operates by switching at the resonance point where impedance is minimal, allowing for zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and reduced switching losses. Series resonant converters are commonly employed in applications requiring high efficiency, precise voltage regulation, and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Key Operating Principles of LLC Resonant Topology
LLC resonant topology operates based on the resonance between an inductor (L) and two capacitors (C and C in an LLC converter), achieving zero-voltage switching (ZVS) to improve efficiency and reduce switching losses. It utilizes a series resonant tank and a parallel resonant capacitor to control the output voltage and current through frequency modulation, enabling soft switching over a wide load range. This operating principle allows LLC converters to achieve high efficiency, low electromagnetic interference (EMI), and compact size in power supply applications.
Core Principles of Series Resonant Converter Design
Series resonant converters operate by utilizing a resonant tank composed of an inductor and capacitor connected in series, allowing the circuit to achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and reduce switching losses. The core design principle involves tuning the resonant frequency to match the switching frequency, ensuring efficient energy transfer and minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI). Control of load and switching frequency is critical to maintain resonance conditions, optimize output voltage regulation, and enhance the overall converter efficiency.
Efficiency Comparison: LLC vs Series Resonant
LLC resonant converters typically offer higher efficiency than series resonant converters due to their ability to achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS) over a wider load range, reducing switching losses significantly. Series resonant converters, while simpler, often suffer from higher switching losses and lower efficiency at light loads because they rely heavily on zero-current switching (ZCS) but lack the flexibility of LLC topologies. Your choice in power applications impacts efficiency, with LLC resonant designs generally preferred for optimizing performance in variable load conditions.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications
LLC resonant converters excel in high-frequency applications due to their ability to achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS), reducing switching losses and electromagnetic interference, thereby enhancing efficiency and thermal management. Series resonant converters primarily rely on zero-current switching (ZCS), which can limit their performance at very high frequencies due to increased switching stresses and lower efficiency. Your choice between LLC and series resonant topologies should consider the specific frequency range and efficiency requirements of your high-frequency power conversion system.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LLC Resonant
LLC resonant converters provide higher efficiency and better voltage regulation compared to series resonant converters due to their ability to achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS) over a wider load range, reducing switching losses and electromagnetic interference. They offer greater design flexibility with adjustable resonant tank components, allowing optimized performance for varying load conditions, but their increased circuit complexity can lead to higher initial costs and more challenging control implementation. Despite these trade-offs, LLC resonant topologies are preferred in applications demanding high power density, low noise, and improved thermal management.
Pros and Cons of Series Resonant Converter
Series resonant converters offer high efficiency at fixed frequencies, making them ideal for applications requiring precise voltage regulation and reduced switching losses. However, their performance drops under varying load conditions due to limited load range flexibility, and the requirement for tight component tolerances increases design complexity and cost. You must consider these trade-offs when choosing between series resonant and LLC resonant topologies for your power supply needs.
Application Areas: LLC vs Series Resonant Choices
LLC resonant converters are widely used in applications requiring high efficiency and wide load ranges, such as server power supplies, electric vehicle chargers, and renewable energy systems due to their soft-switching capabilities and reduced electromagnetic interference. Series resonant converters excel in applications needing high-frequency operation with simple control schemes, including induction heating, plasma generation, and RF power amplification, where precise frequency tuning aligns with load variations. Your choice between LLC and series resonant topologies depends on factors like efficiency targets, load variability, and specific application requirements for switching losses and control complexity.
LLC resonant vs Series resonant Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com