IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) and IGBTD (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor with Diode) differ primarily in the inclusion of an integrated diode in the IGBTD, improving switching performance and reducing losses in high-power applications. Exploring these distinctions can help you choose the right device for your power electronics needs--read on to understand the key differences and applications.
Table of Comparison
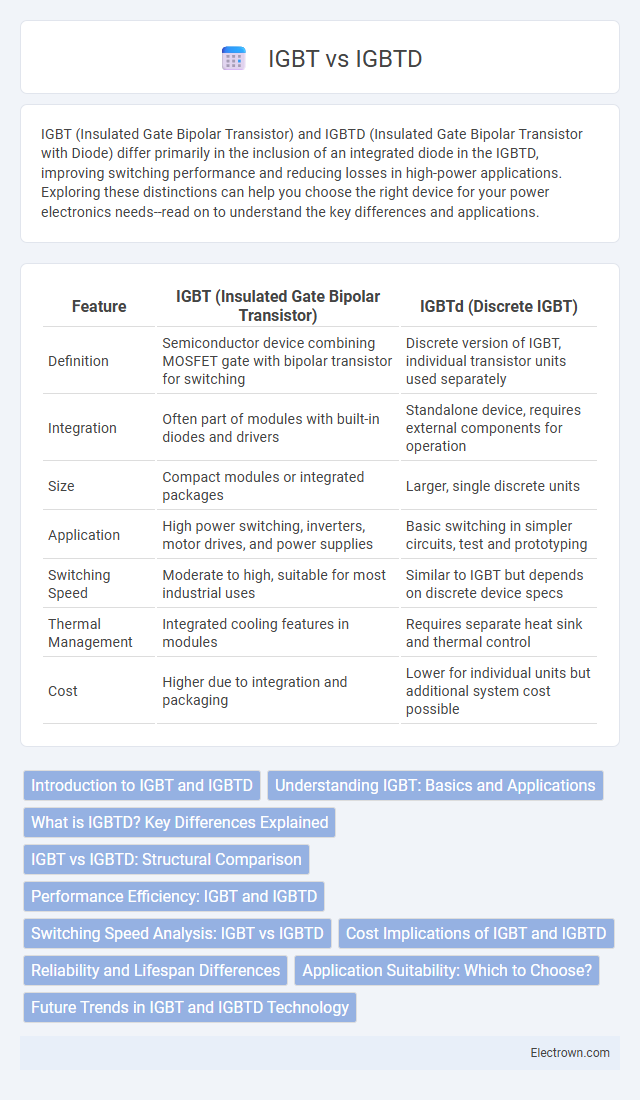
| Feature | IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) | IGBTd (Discrete IGBT) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Semiconductor device combining MOSFET gate with bipolar transistor for switching | Discrete version of IGBT, individual transistor units used separately |
| Integration | Often part of modules with built-in diodes and drivers | Standalone device, requires external components for operation |
| Size | Compact modules or integrated packages | Larger, single discrete units |
| Application | High power switching, inverters, motor drives, and power supplies | Basic switching in simpler circuits, test and prototyping |
| Switching Speed | Moderate to high, suitable for most industrial uses | Similar to IGBT but depends on discrete device specs |
| Thermal Management | Integrated cooling features in modules | Requires separate heat sink and thermal control |
| Cost | Higher due to integration and packaging | Lower for individual units but additional system cost possible |
Introduction to IGBT and IGBTD
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) combine the high input impedance of MOSFETs with the low on-state power loss of bipolar transistors, making them essential for high-efficiency power switching in applications like inverters and motor drives. IGBT Drivers (IGBTDs) are specialized circuits designed to effectively control the switching and protection of IGBTs by providing optimal gate voltage, ensuring fast switching response, and preventing device damage. Understanding the distinct roles of IGBTs as power semiconductors and IGBTDs as control elements is crucial for designing reliable and efficient power electronic systems.
Understanding IGBT: Basics and Applications
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) are semiconductor devices widely used for switching and amplifying electrical power in applications such as motor drives, inverters, and power supplies. IGBTs combine the high input impedance and fast switching of MOSFETs with the low on-state power loss of bipolar transistors, making them essential in industrial and renewable energy systems. Unlike IGBT drivers (IGBTD), which control the operation of IGBTs, the core IGBT device operates directly as a power transistor managing voltage and current in high-efficiency electrical circuits.
What is IGBTD? Key Differences Explained
IGBTD, or Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Driver, is a specialized semiconductor device designed to efficiently control and drive IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) in high-power applications. Unlike a standard IGBT, an IGBTD integrates a driver circuit within the transistor package, enabling faster switching speeds, reduced power loss, and enhanced thermal management. Understanding the key differences between IGBT and IGBTD helps optimize your power electronics design for improved performance and reliability.
IGBT vs IGBTD: Structural Comparison
The IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) features a three-layer structure combining MOSFET input and bipolar output characteristics, providing efficient switching and conduction capabilities. In contrast, the IGBTD (IGBT with diode) integrates an anti-parallel freewheeling diode within the transistor package, enhancing performance in AC motor drives and power conversion by enabling reverse current flow. Understanding the structural differences between IGBT and IGBTD helps you select the optimal device for applications requiring efficient power management and reduced switching losses.
Performance Efficiency: IGBT and IGBTD
IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) and IGBTD (IGBT with Driver) both offer high performance efficiency for power electronics applications. IGBTD integrates a driver module, resulting in faster switching speeds and improved thermal management over standard IGBTs, enhancing overall system efficiency. Your choice depends on the need for compact design and reduced power losses in high-frequency operations.
Switching Speed Analysis: IGBT vs IGBTD
IGBTs exhibit faster switching speeds compared to IGBTDs due to their simplified gate structure and reduced charge storage, enabling switching frequencies up to hundreds of kHz. IGBTDs, combining IGBT and thyristor features, sacrifice switching speed for higher current and voltage ratings, typically operating at lower frequencies around tens of kHz. The trade-off in switching speed impacts efficiency and thermal performance, making IGBTs preferable for high-frequency inverter applications while IGBTDs suit high-power industrial systems requiring robust current handling.
Cost Implications of IGBT and IGBTD
IGBTs typically have lower upfront costs and are widely used in applications requiring efficient switching and high reliability. IGBTDs, integrating IGBT and thyristor characteristics, often involve higher manufacturing complexity and initial investment but provide superior performance in high-voltage, high-current environments. Cost implications of adopting IGBTD technology include potential savings in system-level components and maintenance due to improved efficiency and thermal management.
Reliability and Lifespan Differences
IGBT modules (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) and IGBTDs (Integrated Gate Bipolar Transistor Drivers) differ significantly in reliability and lifespan, with IGBT modules offering robust performance under high voltage and current conditions due to their simplified design. IGBTDs integrate driver circuits, which can introduce additional failure points, potentially reducing overall reliability and requiring more careful thermal management. Your selection should consider the operational environment and longevity requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Application Suitability: Which to Choose?
IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) is ideal for general power switching and motor control applications due to its high efficiency and fast switching capabilities. IGBTD (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Driver) integrates a driver circuit, making it better suited for complex systems requiring precise gate control and protection features. For your project, choose IGBT for straightforward power management and IGBTD when enhanced control and reliability are critical.
Future Trends in IGBT and IGBTD Technology
Future trends in IGBT and IGBTD technology emphasize enhanced switching speeds and higher efficiency for power electronics applications. Innovations in wide-bandgap semiconductor materials, such as silicon carbide (SiC), are driving improvements in thermal performance and voltage handling capabilities. The integration of advanced gate driver designs and improved packaging techniques ensures greater durability and energy savings in industrial and automotive sectors.
igbt vs igbtd Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com