SAW filters offer excellent performance at higher frequencies with lower insertion loss, making them ideal for applications in mobile devices and wireless communication. Exploring the differences between SAW and BAW filters will help you choose the right technology for your specific needs. Read the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
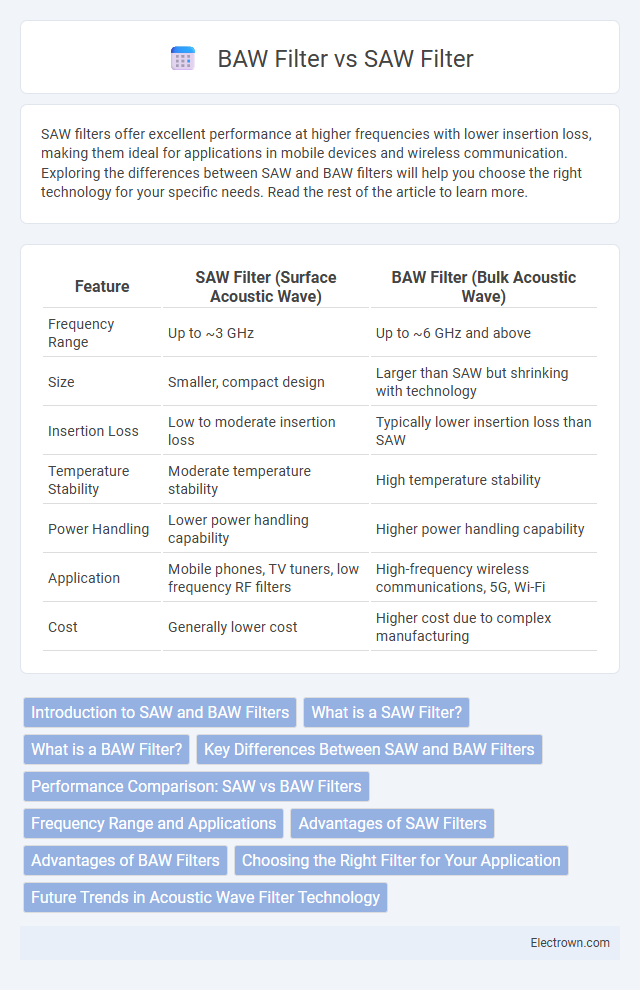
| Feature | SAW Filter (Surface Acoustic Wave) | BAW Filter (Bulk Acoustic Wave) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Up to ~3 GHz | Up to ~6 GHz and above |
| Size | Smaller, compact design | Larger than SAW but shrinking with technology |
| Insertion Loss | Low to moderate insertion loss | Typically lower insertion loss than SAW |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate temperature stability | High temperature stability |
| Power Handling | Lower power handling capability | Higher power handling capability |
| Application | Mobile phones, TV tuners, low frequency RF filters | High-frequency wireless communications, 5G, Wi-Fi |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to complex manufacturing |
Introduction to SAW and BAW Filters
Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) filters utilize acoustic waves traveling along the surface of a piezoelectric substrate to achieve frequency selection, commonly employed in RF front-end modules for mobile communication devices due to their compact size and high performance at lower GHz frequencies. Bulk Acoustic Wave (BAW) filters operate using acoustic waves propagating through the bulk of a piezoelectric material, offering superior performance in higher frequency ranges, typically above 2 GHz, with better power handling and lower insertion loss. Both SAW and BAW filters are critical components in RF systems, with their selection influenced by target frequency, bandwidth, and device integration requirements.
What is a SAW Filter?
A SAW filter, or Surface Acoustic Wave filter, is a type of electronic filter that uses acoustic waves traveling along the surface of a piezoelectric material to transmit signals while blocking unwanted frequencies. Widely used in radio frequency (RF) applications, SAW filters offer high selectivity, low insertion loss, and compact size, making them ideal for mobile phones, GPS devices, and wireless communication systems. Their ability to efficiently filter signals in the high-frequency range (typically up to a few GHz) distinguishes them from BAW filters, which perform better at higher microwave frequencies.
What is a BAW Filter?
A BAW (Bulk Acoustic Wave) filter utilizes acoustic waves propagating through the bulk of a piezoelectric material to achieve high-frequency signal filtering. It offers superior performance in terms of lower insertion loss and higher power handling compared to SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) filters, making it ideal for 5G applications and advanced wireless communication systems. BAW filters support frequencies typically above 2 GHz, providing better integration into compact RF front-end modules.
Key Differences Between SAW and BAW Filters
SAW filters use surface acoustic waves to filter high-frequency signals primarily up to 3 GHz, making them ideal for applications like mobile phones and Wi-Fi. BAW filters, operating with bulk acoustic waves, handle higher frequencies above 3 GHz, offering better performance in terms of power handling and thermal stability for 5G technology and radar systems. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate filter based on frequency range, application requirements, and device constraints.
Performance Comparison: SAW vs BAW Filters
SAW filters excel in high-frequency applications up to 3 GHz with low insertion loss and excellent selectivity, making them ideal for RF front-end modules in mobile devices. BAW filters outperform SAW filters at frequencies above 3 GHz, offering superior power handling, wider bandwidth, and better temperature stability for 5G and advanced wireless communication systems. Your choice between SAW and BAW filters should align with specific frequency requirements and performance criteria to optimize signal integrity and device efficiency.
Frequency Range and Applications
SAW filters operate primarily in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 3 GHz, making them ideal for applications such as mobile phones, TV broadcasting, and GPS devices due to their high selectivity and low insertion loss. BAW filters cover higher frequencies, typically from 1.5 GHz up to 40 GHz, which suits advanced wireless communication protocols like 5G, radar systems, and satellite communications where superior performance at millimeter-wave frequencies is required. The choice between SAW and BAW filters depends largely on the operating frequency and the application's demand for power handling, size, and integration with RF front-end modules.
Advantages of SAW Filters
SAW filters offer superior cost-effectiveness and compact size compared to BAW filters, making them ideal for high-volume consumer electronics. Their excellent frequency stability and low insertion loss enhance signal quality in applications like mobile phones and GPS devices. SAW filters also provide simpler manufacturing processes, resulting in faster production cycles and lower overall expenses.
Advantages of BAW Filters
BAW filters offer higher frequency operation and better performance in high-frequency bands compared to SAW filters, making them ideal for 5G and advanced wireless communication systems. Their smaller size and superior power handling also enhance device integration and durability. You benefit from improved signal quality and reduced interference in demanding RF environments with BAW filter technology.
Choosing the Right Filter for Your Application
SAW filters excel in high-frequency applications with narrow bandwidth requirements, making them ideal for mobile devices and GPS systems. BAW filters offer superior performance in higher frequency ranges above 3 GHz with better power handling and thermal stability, suited for 5G and advanced wireless communications. Your choice depends on the specific frequency range, power, and bandwidth needs of your application to ensure optimal signal integrity and system performance.
Future Trends in Acoustic Wave Filter Technology
Future trends in acoustic wave filter technology emphasize the integration of BAW (Bulk Acoustic Wave) filters for 5G and beyond, driven by their superior frequency performance and miniaturization capabilities compared to SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) filters. Advances in materials like lithium niobate and aluminum nitride enhance BAW filter efficiency and power handling, enabling higher bandwidth and lower insertion loss critical for next-generation wireless devices. The growth of IoT and autonomous systems further accelerates the demand for compact, high-performance BAW filters, positioning them as the preferred choice in evolving RF front-end modules.
SAW Filter vs BAW Filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com