Log periodic antennas offer a wide frequency range with consistent performance, making them ideal for applications requiring multi-band operation, while Yagi-Uda antennas provide higher gain and directivity for narrow frequency bands. Explore the rest of the article to understand which antenna suits Your specific communication needs best.
Table of Comparison
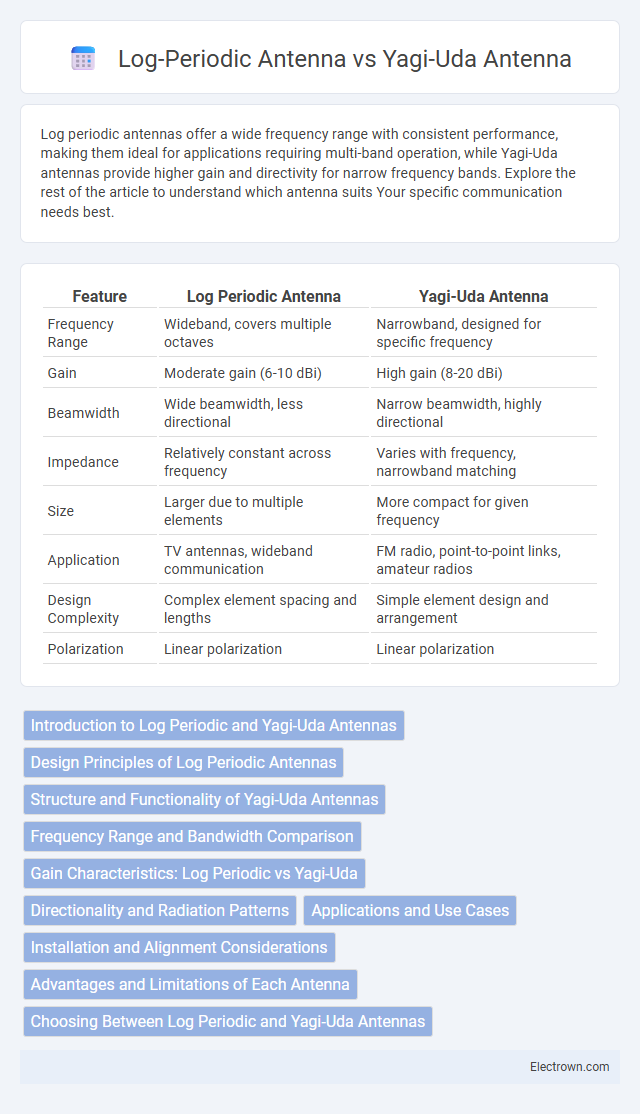
| Feature | Log Periodic Antenna | Yagi-Uda Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | Wideband, covers multiple octaves | Narrowband, designed for specific frequency |
| Gain | Moderate gain (6-10 dBi) | High gain (8-20 dBi) |
| Beamwidth | Wide beamwidth, less directional | Narrow beamwidth, highly directional |
| Impedance | Relatively constant across frequency | Varies with frequency, narrowband matching |
| Size | Larger due to multiple elements | More compact for given frequency |
| Application | TV antennas, wideband communication | FM radio, point-to-point links, amateur radios |
| Design Complexity | Complex element spacing and lengths | Simple element design and arrangement |
| Polarization | Linear polarization | Linear polarization |
Introduction to Log Periodic and Yagi-Uda Antennas
Log periodic antennas feature a series of elements with varying lengths and spacings, designed to provide wideband frequency coverage and consistent performance across a broad spectrum. The Yagi-Uda antenna, characterized by a single driven element with multiple parasitic elements, offers high gain and directivity primarily over a narrow frequency range. Your choice between these antennas depends on whether wide frequency versatility or focused signal strength is the priority for your application.
Design Principles of Log Periodic Antennas
Log periodic antennas operate on a design principle where elements vary continuously in length and spacing according to a logarithmic function, enabling consistent performance across a wide frequency range. The alternating element lengths create a frequency-dependent active region, allowing the antenna to maintain relatively constant impedance and radiation characteristics. This design contrasts with the fixed-element spacing and length of Yagi-Uda antennas, which are optimized for narrowband, directional gain.
Structure and Functionality of Yagi-Uda Antennas
Yagi-Uda antennas consist of a driven element, a reflector, and multiple directors arranged linearly to enhance signal directionality and gain. Their design focuses on maximizing forward radiation and minimizing interference from unwanted directions by adjusting element spacing and lengths. Your choice of a Yagi-Uda antenna improves signal focus in point-to-point communication, making it ideal for applications requiring high directivity.
Frequency Range and Bandwidth Comparison
Log periodic antennas offer a wide frequency range and broad bandwidth, making them ideal for applications requiring multi-band operation with consistent performance. Yagi-Uda antennas provide higher gain but operate effectively over a narrow bandwidth, typically optimized for specific frequencies. Your choice depends on whether a wide frequency coverage or focused signal strength is more critical for your requirements.
Gain Characteristics: Log Periodic vs Yagi-Uda
Log periodic antennas exhibit moderate and relatively uniform gain over a wide frequency range, typically ranging from 6 to 10 dBi, making them suitable for broadband applications. In contrast, Yagi-Uda antennas provide higher gain values, often between 10 to 20 dBi, but their narrowband design limits performance to a specific frequency. The Yagi-Uda's superior gain stems from its focused directional elements, while the log periodic's element spacing and length variation prioritize wideband frequency coverage.
Directionality and Radiation Patterns
Log periodic antennas exhibit wideband frequency coverage with moderate directionality and consistent radiation patterns across their operating range, making them ideal for scanning multiple frequencies. Yagi-Uda antennas deliver high directionality and gain with a narrow bandwidth, producing a focused radiation pattern that enhances signal strength in a specific direction. The Yagi's radiation pattern is more concentrated and precise compared to the broader, more uniform pattern of log periodic antennas.
Applications and Use Cases
Log periodic antennas excel in wideband applications such as spectrum monitoring, electronic warfare, and frequency scanning due to their consistent impedance and gain over a broad frequency range. Yagi-Uda antennas are preferred for narrowband applications requiring high directional gain and signal strength, including amateur radio, television reception, and point-to-point communication links. Your choice depends on whether you need broad frequency agility or focused signal gain for specific communication tasks.
Installation and Alignment Considerations
Log periodic antennas require precise mechanical alignment due to their wide frequency range, where slight deviations can impact performance across bands. Yagi-Uda antennas demand careful directional alignment towards the signal source to maximize gain and front-to-back ratio, often needing more robust mounting hardware for larger elements. Your choice should factor in ease of installation and the need for accurate positioning to optimize signal quality and reliability.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Antenna
Log periodic antennas offer a broad frequency range with consistent gain and impedance, making them ideal for applications requiring multi-band performance and wideband signal reception. Yagi-Uda antennas provide higher gain and directivity within a narrow frequency band, optimizing signal strength and noise rejection for specific frequencies but limiting versatility. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize frequency agility and coverage (log periodic) or maximum gain and focused transmission (Yagi-Uda).
Choosing Between Log Periodic and Yagi-Uda Antennas
Choosing between log periodic and Yagi-Uda antennas depends on application requirements such as frequency range and gain. Log periodic antennas provide wide bandwidth and consistent impedance, making them ideal for multi-frequency use and signal scanning. Yagi-Uda antennas offer higher gain and directivity within a narrow frequency band, suitable for long-distance communication and focused signal reception.
Log periodic antenna vs Yagi-Uda antenna Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com