SSPA amplifiers offer higher reliability and efficiency with solid-state components, while TWT amplifiers excel in high power output and broadband applications but are bulkier and require more maintenance. Discover which amplifier suits Your specific needs by exploring the differences in detail in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
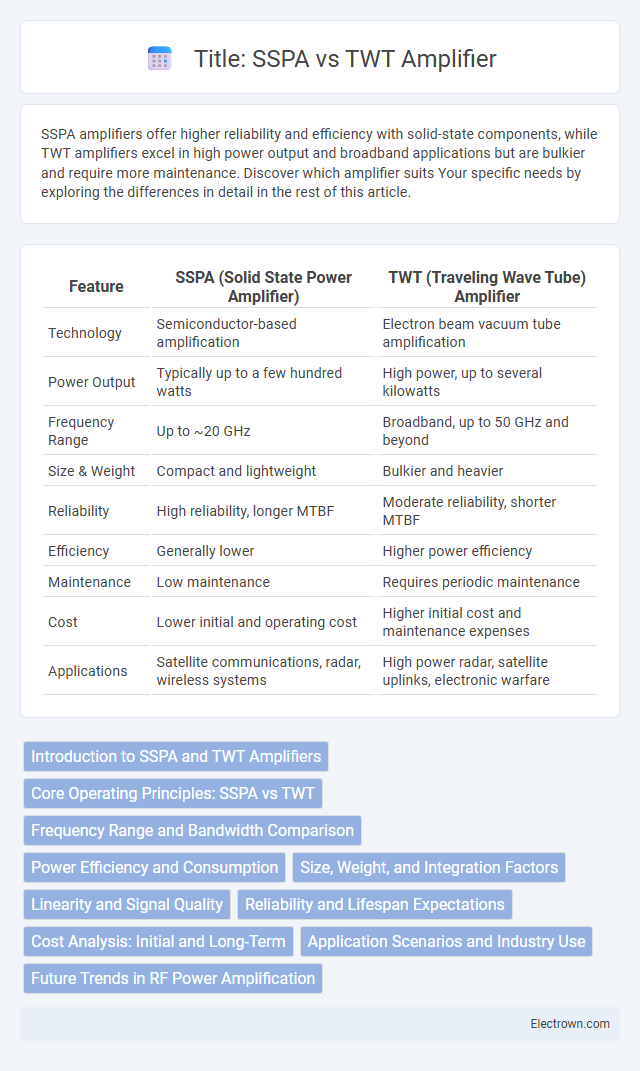
| Feature | SSPA (Solid State Power Amplifier) | TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Semiconductor-based amplification | Electron beam vacuum tube amplification |
| Power Output | Typically up to a few hundred watts | High power, up to several kilowatts |
| Frequency Range | Up to ~20 GHz | Broadband, up to 50 GHz and beyond |
| Size & Weight | Compact and lightweight | Bulkier and heavier |
| Reliability | High reliability, longer MTBF | Moderate reliability, shorter MTBF |
| Efficiency | Generally lower | Higher power efficiency |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Requires periodic maintenance |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating cost | Higher initial cost and maintenance expenses |
| Applications | Satellite communications, radar, wireless systems | High power radar, satellite uplinks, electronic warfare |
Introduction to SSPA and TWT Amplifiers
Solid State Power Amplifiers (SSPAs) utilize semiconductor devices like Gallium Nitride (GaN) or Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) transistors to amplify RF signals with high efficiency and reliability, making them suitable for modern communication systems. Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers employ vacuum tube technology to deliver high power amplification across wide bandwidths, especially effective in satellite and radar applications. SSPAs are favored for compactness and linearity, whereas TWT amplifiers excel in providing higher output power levels at microwave frequencies.
Core Operating Principles: SSPA vs TWT
Solid State Power Amplifiers (SSPAs) use semiconductor devices such as gallium nitride (GaN) transistors to amplify signals through electron flow in solid materials, offering high reliability and linearity. Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers operate by amplifying signals via an electron beam interacting with a slow-wave structure inside a vacuum tube, providing high power output and wide bandwidth. Your choice between SSPA and TWT depends on the required power level and operational environment, with SSPAs favored for compact and efficient applications, while TWTs excel in high-power, high-frequency scenarios.
Frequency Range and Bandwidth Comparison
SSPA (Solid State Power Amplifiers) typically operate efficiently across a wide frequency range, spanning from hundreds of MHz up to tens of GHz, making them versatile for various telecommunications and radar applications. TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifiers excel in higher frequency bands, often from 1 GHz to over 100 GHz, and provide broader instantaneous bandwidths, essential for satellite communications and electronic warfare systems. The broader bandwidth capability of TWT amplifiers contrasts with the narrower bandwidth but higher linearity and reliability advantages of SSPAs.
Power Efficiency and Consumption
SSPA (Solid State Power Amplifiers) generally offer higher power efficiency, converting more electrical input into output RF power, which reduces overall power consumption compared to TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifiers. Your system benefits from SSPAs through lower heat dissipation and reduced energy costs, especially in continuous operation scenarios. In contrast, TWT amplifiers consume more power due to their vacuum tube technology but can deliver higher peak power output in specialized applications.
Size, Weight, and Integration Factors
SSPA amplifiers typically offer a more compact size and lighter weight compared to TWT amplifiers, making them ideal for applications where space and weight constraints are critical. The solid-state design of SSPAs enables easier integration with modern electronic systems and improved reliability, reducing maintenance needs. Your choice between SSPA and TWT amplifiers largely depends on the balance between power requirements and integration capabilities within your system design.
Linearity and Signal Quality
SSPA (Solid State Power Amplifier) offers superior linearity compared to TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifiers, ensuring minimal signal distortion and high fidelity in communication systems. TWT amplifiers tend to exhibit nonlinear behavior at high power levels, resulting in increased intermodulation distortion and reduced signal quality. Choosing an SSPA can enhance your system's overall performance by maintaining signal integrity and reducing the need for complex linearization techniques.
Reliability and Lifespan Expectations
SSPA (Solid-State Power Amplifiers) generally offer higher reliability due to fewer moving parts and robust semiconductor components, resulting in longer lifespan expectations compared to TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifiers. TWT amplifiers, while capable of high power output, involve vacuum tubes that can degrade over time, leading to more frequent maintenance and shorter operational life. Your choice between SSPA and TWT should consider the critical need for consistent performance and reduced downtime in your specific application.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
SSPA (Solid State Power Amplifier) generally features a lower initial cost due to simpler design and mass-produced semiconductor components, making it cost-effective for short-term investments. TWT (Traveling Wave Tube) amplifiers exhibit higher upfront expenses driven by complex vacuum tube manufacturing and specialized maintenance requirements. Over the long term, SSPA benefits from lower operational costs and enhanced reliability, whereas TWT amplifiers may incur increased maintenance and replacement expenses despite their superior power efficiency in certain high-frequency applications.
Application Scenarios and Industry Use
SSPA amplifiers excel in applications requiring consistent linear gain and high efficiency, such as satellite communication, radar systems, and electronic warfare due to their solid-state reliability and compact size. TWT amplifiers are favored in scenarios demanding high power output and wide bandwidth, including deep space communication, broadcasting, and high-frequency radar, thanks to their superior amplification at microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies. Your choice depends on performance needs, with SSPAs suited for stable, low-maintenance environments and TWT amplifiers ideal for high-power, broad-spectrum industrial uses.
Future Trends in RF Power Amplification
Future trends in RF power amplification emphasize the integration of Solid-State Power Amplifiers (SSPAs) due to their superior reliability, linearity, and compact size compared to Traveling Wave Tube (TWT) amplifiers. SSPAs leverage advancements in semiconductor materials such as GaN and GaAs to achieve higher power efficiency and bandwidth, which are critical for next-generation wireless communication and radar systems. Your choice for future-proof RF applications will likely favor SSPAs as they align better with evolving demands for scalable, energy-efficient, and miniaturized solutions.
SSPA vs TWT amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com