A TR module integrates the transmit and receive functions in a single unit, offering faster switching speeds and improved reliability compared to a traditional T/R switch that mechanically toggles between transmit and receive modes. Discover how choosing the right component can enhance Your communication system's performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
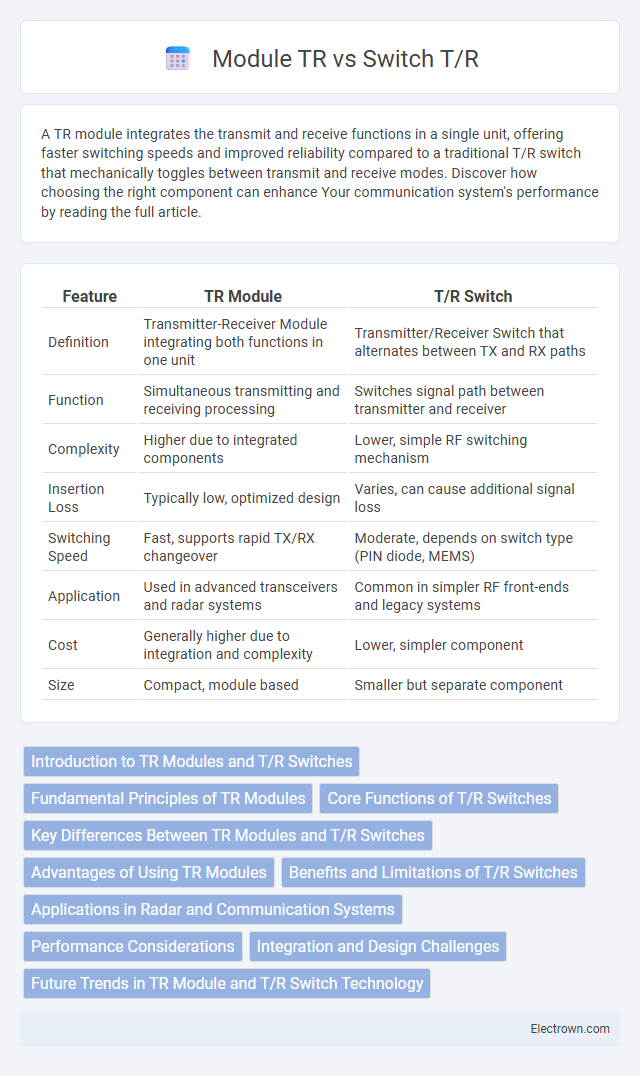
| Feature | TR Module | T/R Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transmitter-Receiver Module integrating both functions in one unit | Transmitter/Receiver Switch that alternates between TX and RX paths |
| Function | Simultaneous transmitting and receiving processing | Switches signal path between transmitter and receiver |
| Complexity | Higher due to integrated components | Lower, simple RF switching mechanism |
| Insertion Loss | Typically low, optimized design | Varies, can cause additional signal loss |
| Switching Speed | Fast, supports rapid TX/RX changeover | Moderate, depends on switch type (PIN diode, MEMS) |
| Application | Used in advanced transceivers and radar systems | Common in simpler RF front-ends and legacy systems |
| Cost | Generally higher due to integration and complexity | Lower, simpler component |
| Size | Compact, module based | Smaller but separate component |
Introduction to TR Modules and T/R Switches
TR modules and T/R switches are essential components in radar and communication systems, enabling efficient signal transmission and reception. A TR module integrates multiple functions such as power amplification and switching, offering compact and high-performance solutions. Your system benefits from the TR module's ability to replace discrete T/R switches, enhancing reliability and reducing insertion loss.
Fundamental Principles of TR Modules
TR modules operate by integrating transmit and receive functions into a single compact device using PIN diodes or FETs to rapidly switch between signal paths, enabling efficient isolation and protection of sensitive receiver components during transmission. Unlike traditional T/R switches that mechanically toggle between transmit and receive modes, TR modules leverage solid-state components for faster switching speeds and improved reliability in radar and communication systems. Your system's performance benefits from TR modules' ability to minimize insertion loss and maximize linearity, ensuring better signal integrity and reduced noise figure.
Core Functions of T/R Switches
T/R switches primarily enable rapid switching between transmit and receive modes in communication systems, ensuring signal integrity and minimizing losses. These switches protect sensitive receiver components from high-power transmitted signals by isolating the transmit path from the receive path. Your system's efficiency and protection heavily depend on the T/R switch's ability to handle power levels and switching speed effectively.
Key Differences Between TR Modules and T/R Switches
TR modules integrate both transmit and receive switching functions within a single compact unit, offering improved isolation and reduced insertion loss compared to standalone T/R switches. While T/R switches primarily serve to alternate signal paths between transmit and receive antennas, TR modules provide enhanced linearity and power handling capabilities critical for modern radar and communication systems. The advanced design of TR modules supports higher frequency operation and minimizes signal distortion, making them superior for high-performance applications.
Advantages of Using TR Modules
TR modules offer seamless integration of transmit and receive functions in a compact design, improving system reliability and reducing insertion loss compared to traditional T/R switches. Their solid-state construction ensures faster switching speeds and enhanced durability, minimizing signal distortion and boosting overall communication efficiency. By incorporating a TR module, Your RF system benefits from simplified circuitry, lower power consumption, and superior isolation performance.
Benefits and Limitations of T/R Switches
T/R switches offer efficient switching between transmit and receive modes, reducing the need for separate components and minimizing signal loss in RF systems. They provide compactness and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for compact transceiver designs, but may introduce insertion loss and limited power handling compared to a dedicated TR module. Understanding these trade-offs can help you choose the best option based on system requirements such as power, isolation, and size constraints.
Applications in Radar and Communication Systems
The TR module offers advanced active switching capabilities that enhance signal control and reduce insertion loss in radar and communication systems compared to traditional T/R switches. You benefit from improved linearity and power handling in phased array radars, enabling faster switching speeds and better waveform agility essential for modern adaptive radar functionality. Communication systems employing TR modules achieve higher efficiency and reliability, supporting seamless transmit and receive operations in complex electromagnetic environments.
Performance Considerations
The TR module offers superior linearity and lower insertion loss compared to a T/R switch, enhancing overall signal quality in high-frequency applications. Improved isolation in TR modules reduces signal leakage and interference, which is critical for maintaining system performance in sensitive RF environments. Your choice of TR module or T/R switch significantly impacts the efficiency and reliability of transceiver systems, especially under demanding operational conditions.
Integration and Design Challenges
The TR module streamlines integration by combining transmit and receive functions into a single compact unit, reducing PCB space and simplifying system design compared to separate T/R switches. However, integrating a TR module requires careful thermal management and electromagnetic compatibility considerations to maintain signal integrity and prevent interference. Your system design must address these challenges to fully leverage the compactness and performance benefits offered by TR modules over traditional T/R switches.
Future Trends in TR Module and T/R Switch Technology
Future trends in TR module technology emphasize increased integration, higher power efficiency, and enhanced thermal management to support 5G and beyond wireless communication systems. Advancements in semiconductor materials such as GaN and SiC drive improved performance and miniaturization in T/R switches, enabling faster switching speeds and reduced insertion losses. The convergence of TR modules with intelligent control algorithms and AI-enabled adaptive beamforming signals a shift towards more dynamic and resilient RF front-end architectures.
TR module vs T/R switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com