Power diodes are designed for high current and voltage applications, offering robust performance but slower switching speeds, while fast recovery diodes excel in circuits requiring rapid switching due to their reduced reverse recovery time. Explore the rest of the article to understand which diode best suits your specific electronic needs.
Table of Comparison
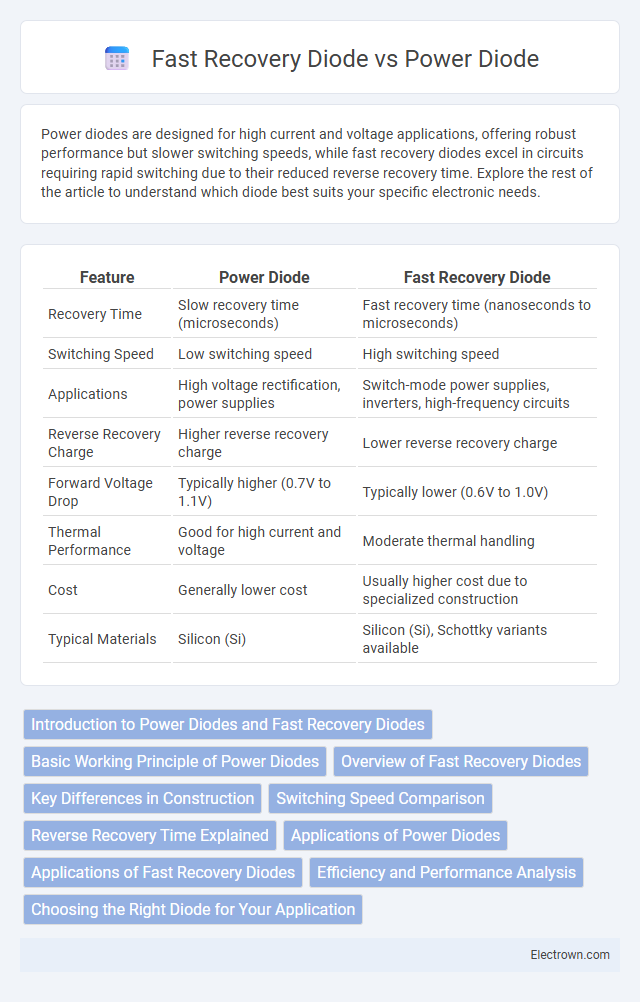
| Feature | Power Diode | Fast Recovery Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Recovery Time | Slow recovery time (microseconds) | Fast recovery time (nanoseconds to microseconds) |
| Switching Speed | Low switching speed | High switching speed |
| Applications | High voltage rectification, power supplies | Switch-mode power supplies, inverters, high-frequency circuits |
| Reverse Recovery Charge | Higher reverse recovery charge | Lower reverse recovery charge |
| Forward Voltage Drop | Typically higher (0.7V to 1.1V) | Typically lower (0.6V to 1.0V) |
| Thermal Performance | Good for high current and voltage | Moderate thermal handling |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Usually higher cost due to specialized construction |
| Typical Materials | Silicon (Si) | Silicon (Si), Schottky variants available |
Introduction to Power Diodes and Fast Recovery Diodes
Power diodes are designed to handle high voltage and current levels with low forward voltage drop, making them ideal for rectification in power supplies and industrial applications. Fast recovery diodes feature significantly reduced reverse recovery time compared to standard power diodes, allowing them to switch off quickly and minimize switching losses in high-frequency circuits. Your choice between these two depends on the application's switching speed requirements and efficiency demands.
Basic Working Principle of Power Diodes
Power diodes operate based on the principle of allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, using a PN junction with a relatively long recovery time. Fast recovery diodes share the same fundamental operation but are engineered with a shorter reverse recovery time to enhance switching speed and reduce power loss in high-frequency applications. The recovery time difference is key, with power diodes optimized for high voltage and current handling, whereas fast recovery diodes prioritize rapid switching performance.
Overview of Fast Recovery Diodes
Fast recovery diodes feature a significantly shorter reverse recovery time compared to standard power diodes, making them ideal for high-frequency switching applications. They reduce switching losses and electromagnetic interference in circuits such as inverters and power supplies. Your electronic designs benefit from faster switching speeds and improved efficiency when incorporating fast recovery diodes.
Key Differences in Construction
Power diodes are typically constructed with a thick, heavily doped P-N junction designed for high voltage and current handling, featuring a simple, robust structure to withstand surges and long recovery times. Fast recovery diodes incorporate a lightly doped, optimized P-N junction with specialized layer structures to minimize charge storage and enable rapid switching performance. The construction differences result in power diodes having slower switching speeds but higher surge tolerance, while fast recovery diodes deliver faster turn-off times suitable for high-frequency applications.
Switching Speed Comparison
Power diodes typically exhibit slower switching speeds due to their larger junction capacitance and higher charge storage, making them less efficient for high-frequency applications. Fast recovery diodes are engineered to minimize recovery time and reduce reverse recovery charge, enabling significantly quicker switching and improved performance in circuits with rapid switching requirements. Understanding the switching speed differences helps you select the appropriate diode to enhance efficiency and reduce power loss in your electronic designs.
Reverse Recovery Time Explained
Power diodes generally have a longer reverse recovery time due to their construction, which causes slower removal of stored charge when switching from forward to reverse bias. Fast recovery diodes are designed to minimize this reverse recovery time, significantly improving switching speed and efficiency in high-frequency applications. The reduced reverse recovery time in fast recovery diodes leads to lower power losses and less electromagnetic interference compared to standard power diodes.
Applications of Power Diodes
Power diodes are widely used in high-voltage rectification, power supplies, and inverters due to their high current capacity and robustness in handling large electrical loads. Their slow recovery time makes them ideal for applications where switching speed is less critical, such as battery chargers and power factor correction circuits. Your choice of a power diode ensures efficient energy conversion in industrial power systems and heavy-duty electrical devices.
Applications of Fast Recovery Diodes
Fast recovery diodes are extensively used in high-frequency switching applications such as inverters, power supplies, and motor drives due to their ability to minimize switching losses and reduce electromagnetic interference. These diodes excel in circuits requiring rapid transition from conduction to blocking state, making them ideal for use in bridge rectifiers and snubber circuits. Their fast reverse recovery time enhances efficiency and performance in modern power electronics where switching speeds are critical.
Efficiency and Performance Analysis
Power diodes offer high efficiency with low forward voltage drop, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal power loss and robust performance under high current conditions. Fast recovery diodes improve efficiency in switching applications by significantly reducing reverse recovery time, thereby minimizing switching losses and enhancing overall system speed. Your choice between these diodes should consider the specific switching frequency and power handling requirements to optimize performance.
Choosing the Right Diode for Your Application
Selecting the right diode depends on the switching speed and reverse recovery time required by your application. Power diodes are ideal for high-current, low-frequency circuits due to their robust construction and ability to handle large forward currents with slower recovery times. Fast recovery diodes are better suited for high-frequency switching applications, offering quicker reverse recovery to reduce switching losses and improve efficiency in power converters and inverters.
Power diode vs fast recovery diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com