A diode allows current to flow in only one direction, protecting circuits from reverse polarity, while a Zener diode is designed to allow current to flow in reverse when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, making it ideal for voltage regulation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your choice between these components affects circuit performance and stability.
Table of Comparison
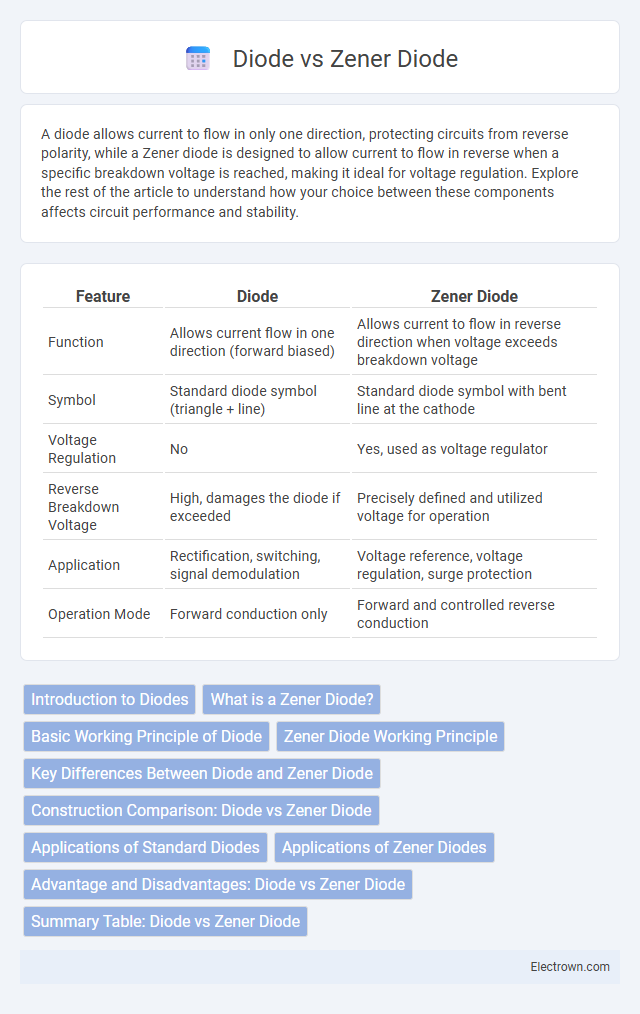
| Feature | Diode | Zener Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Allows current flow in one direction (forward biased) | Allows current to flow in reverse direction when voltage exceeds breakdown voltage |
| Symbol | Standard diode symbol (triangle + line) | Standard diode symbol with bent line at the cathode |
| Voltage Regulation | No | Yes, used as voltage regulator |
| Reverse Breakdown Voltage | High, damages the diode if exceeded | Precisely defined and utilized voltage for operation |
| Application | Rectification, switching, signal demodulation | Voltage reference, voltage regulation, surge protection |
| Operation Mode | Forward conduction only | Forward and controlled reverse conduction |
Introduction to Diodes
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction, primarily used for rectification. Zener diodes, a specialized type of diode, operate in reverse breakdown region to provide voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage. Both diodes are essential in electronic circuits, with standard diodes focusing on current control and Zener diodes ensuring voltage stability.
What is a Zener Diode?
A Zener diode is a specialized semiconductor device designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage, known as the Zener voltage, is reached. It functions primarily as a voltage regulator, maintaining a stable output voltage despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. Your electronic circuits benefit from Zener diodes by achieving reliable voltage control, distinct from the standard diode's rectification role.
Basic Working Principle of Diode
A diode allows current to flow in one direction by permitting electrons to move from the anode to the cathode when forward biased, blocking current in reverse bias. A Zener diode operates similarly but is designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when voltage exceeds a specific breakdown threshold, known as the Zener voltage. Your selection between a standard diode and a Zener diode depends on whether you need simple rectification or voltage regulation.
Zener Diode Working Principle
A Zener diode operates by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage reaches the designed Zener breakdown voltage, maintaining a stable and precise voltage across its terminals. Unlike a regular diode that blocks reverse current, the Zener diode exploits the controlled breakdown to provide voltage regulation and protection in circuits. Its unique doping profile and thin depletion region enable this stable breakdown without damaging the device, making it essential in voltage reference and surge suppression applications.
Key Differences Between Diode and Zener Diode
A standard diode allows current to flow in one direction while blocking it in reverse, primarily used for rectification. A Zener diode, designed to operate in reverse breakdown region, maintains a stable voltage, making it ideal for voltage regulation. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right diode for your circuit's specific voltage and current requirements.
Construction Comparison: Diode vs Zener Diode
A standard diode consists of a simple PN junction designed primarily for forward conduction, allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking reverse current. The Zener diode features a similar PN junction but is heavily doped to enable controlled breakdown under reverse voltage, known as the Zener voltage, without damaging the device. Your choice depends on whether you need basic rectification or voltage regulation, with construction differences directly influencing their respective electrical characteristics.
Applications of Standard Diodes
Standard diodes are widely used for rectification in power supplies, converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) efficiently. They serve as protection devices in circuits by preventing reverse polarity damage and controlling voltage spikes. Your electronic designs benefit from standard diodes in signal demodulation, voltage regulation, and switching applications.
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation in electronic circuits, maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. They are essential in protecting sensitive components by acting as voltage clamps in power supplies and surge protectors. Your devices benefit from their reliable voltage stabilization and noise reduction capabilities in various applications.
Advantage and Disadvantages: Diode vs Zener Diode
Standard diodes offer efficient current flow in one direction with low forward voltage drop, making them ideal for rectification, but they lack voltage regulation capabilities found in Zener diodes. Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, which is advantageous in voltage stabilization circuits but comes with higher power dissipation and noise compared to standard diodes. While standard diodes benefit from simplicity and low cost, Zener diodes are indispensable for protecting circuits from overvoltage but require careful heat management due to their power limitations.
Summary Table: Diode vs Zener Diode
The diode primarily allows current to flow in one direction with a typical forward voltage drop around 0.7V for silicon types, whereas the Zener diode operates in reverse bias, maintaining a stable reference voltage known as the Zener voltage. Standard diodes serve rectification and signal clipping functions, while Zener diodes are designed for voltage regulation and protection circuits. Key parameters include forward voltage, breakdown voltage, and power dissipation, with Zener diodes having a specified breakdown voltage to ensure precise voltage control.
Diode vs Zener diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com