Planar diodes feature a flat junction with the diode's active area created through surface diffusion, offering improved reliability and easier integration in semiconductor devices. Understanding the key differences between planar and mesa diodes can help optimize your electronic designs; explore the full article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
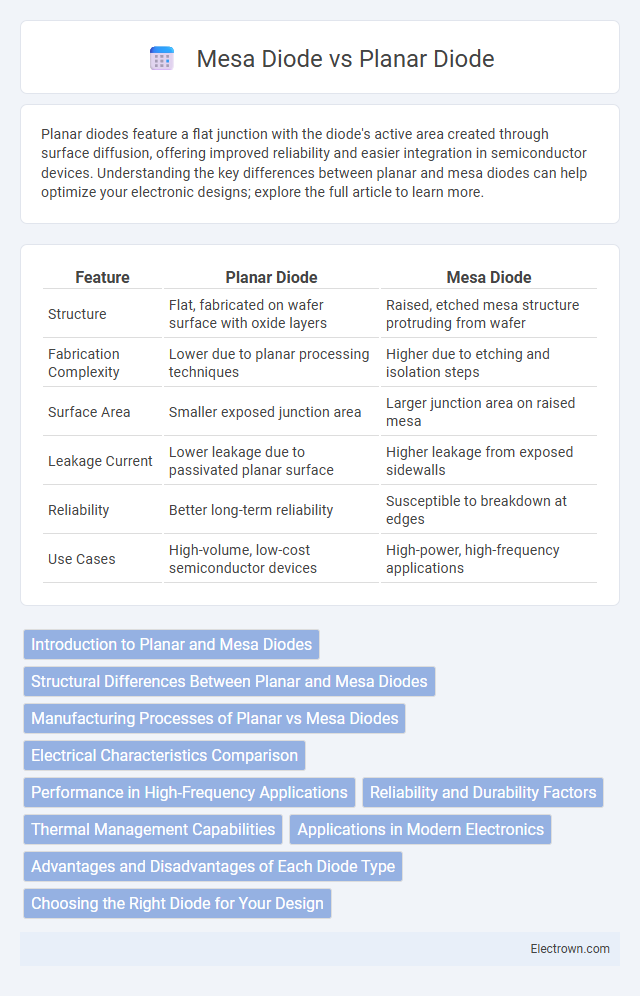
| Feature | Planar Diode | Mesa Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat, fabricated on wafer surface with oxide layers | Raised, etched mesa structure protruding from wafer |
| Fabrication Complexity | Lower due to planar processing techniques | Higher due to etching and isolation steps |
| Surface Area | Smaller exposed junction area | Larger junction area on raised mesa |
| Leakage Current | Lower leakage due to passivated planar surface | Higher leakage from exposed sidewalls |
| Reliability | Better long-term reliability | Susceptible to breakdown at edges |
| Use Cases | High-volume, low-cost semiconductor devices | High-power, high-frequency applications |
Introduction to Planar and Mesa Diodes
Planar diodes feature a flat semiconductor surface with junctions formed by diffusion or ion implantation, resulting in lower surface leakage and enhanced reliability. Mesa diodes are characterized by etched, raised structures that expose the junction edges, often leading to increased surface recombination and leakage currents. Understanding the structural differences between planar and mesa diodes helps optimize your choice for specific applications requiring varying levels of performance and stability.
Structural Differences Between Planar and Mesa Diodes
Planar diodes feature a flat, layered structure where the p-n junction is created by diffusion or ion implantation on a flat semiconductor wafer, offering low surface leakage currents and easy integration into IC fabrication. Mesa diodes have a raised, etched mesa structure that exposes the p-n junction on the top surface, resulting in increased surface area but higher surface recombination and leakage current. Understanding these structural differences helps optimize Your device choice for performance, reliability, and fabrication complexity in semiconductor applications.
Manufacturing Processes of Planar vs Mesa Diodes
Planar diodes are manufactured through photolithographic techniques that create a flat surface with diffused junctions beneath, allowing for precise control of the junction depth and better surface passivation. Mesa diodes involve etching trenches around the junction, forming a raised mesa structure that exposes the p-n junction edges but increases surface recombination and leakage currents. Your choice between these depends on factors like manufacturing complexity, device reliability, and performance in your specific semiconductor application.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Planar diodes exhibit lower leakage currents and higher breakdown voltages compared to mesa diodes due to their refined surface passivation and minimized surface states. Mesa diodes typically have higher capacitance and increased series resistance caused by their exposed junction edges, affecting switching speed and power efficiency. Your choice between planar and mesa diodes should consider these electrical characteristics based on the application requirements for low noise and high reliability.
Performance in High-Frequency Applications
Planar diodes exhibit superior high-frequency performance due to their low parasitic capacitance and reduced junction area, enabling faster switching speeds and lower signal distortion. Mesa diodes, while simpler to fabricate, typically have higher junction capacitance and surface recombination effects that limit their efficiency in microwave and millimeter-wave circuits. Advanced planar diode designs are preferred in RF and high-frequency semiconductor devices for their enhanced cut-off frequency and minimal noise characteristics.
Reliability and Durability Factors
Planar diodes offer superior reliability and durability due to their surface passivation and reduced defect density, minimizing leakage currents and enhancing long-term stability. Mesa diodes, with exposed sidewalls, are more susceptible to surface contamination and damage, often leading to increased leakage and reduced lifespan. You will benefit from planar diode technology in applications demanding consistent performance and robust device longevity.
Thermal Management Capabilities
Planar diodes demonstrate superior thermal management capabilities due to their flat, extended surface area that enhances heat dissipation, reducing thermal resistance significantly compared to mesa diodes. Mesa diodes, with their elevated junction structure, tend to concentrate heat in a smaller volume, leading to higher localized temperatures and potential thermal stress. Your choice of diode impacts device reliability, as planar diodes typically offer improved thermal stability in high-power applications.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Planar diodes are widely used in high-frequency communication devices due to their low noise and fast switching capabilities, making them ideal for RF and microwave applications. Mesa diodes, with their robust structure, are often employed in power rectification and sensing devices where durability and high current handling are required. Your choice between the two depends on the specific electronic application, balancing factors like frequency response, power capacity, and device reliability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Diode Type
Planar diodes offer advantages such as superior surface passivation, leading to reduced surface leakage currents and enhanced reliability in high-frequency applications, while their fabrication process provides better reproducibility and integration with planar technologies. However, planar diodes generally require more complex manufacturing steps and can exhibit higher series resistance compared to mesa diodes. Mesa diodes feature simpler fabrication and lower series resistance due to their vertical structure, which facilitates efficient current flow, but suffer from increased surface recombination and vulnerability to edge breakdown, impacting their performance in high-voltage devices.
Choosing the Right Diode for Your Design
When choosing the right diode for your design, understanding the structural differences between planar and mesa diodes is crucial. Planar diodes offer superior surface passivation and reduced leakage currents, making them ideal for high-frequency and low-noise applications. Mesa diodes, with their simpler fabrication and higher breakdown voltages, suit power-handling designs where ruggedness is a priority.
Planar diode vs mesa diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com