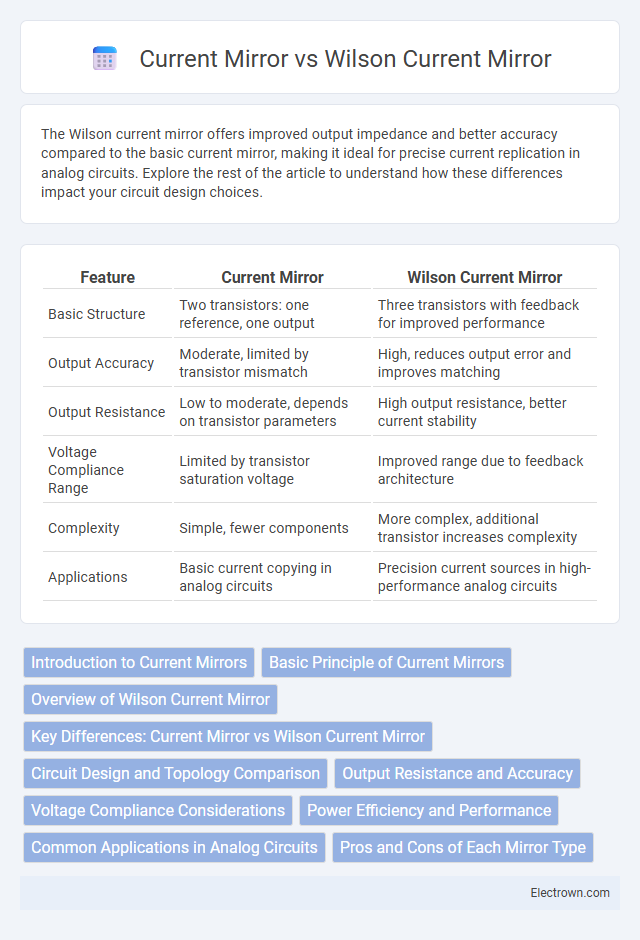
The Wilson current mirror offers improved output impedance and better accuracy compared to the basic current mirror, making it ideal for precise current replication in analog circuits. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your circuit design choices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Current Mirror | Wilson Current Mirror |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Structure | Two transistors: one reference, one output | Three transistors with feedback for improved performance |
| Output Accuracy | Moderate, limited by transistor mismatch | High, reduces output error and improves matching |
| Output Resistance | Low to moderate, depends on transistor parameters | High output resistance, better current stability |
| Voltage Compliance Range | Limited by transistor saturation voltage | Improved range due to feedback architecture |
| Complexity | Simple, fewer components | More complex, additional transistor increases complexity |
| Applications | Basic current copying in analog circuits | Precision current sources in high-performance analog circuits |
Introduction to Current Mirrors
Current mirrors replicate a reference current to provide stable biasing and improve linearity in analog circuits. The basic current mirror, often implemented with two matched transistors, offers simplicity but can exhibit significant output resistance and limited accuracy. The Wilson current mirror enhances performance by using a three-transistor configuration that increases output impedance and reduces mismatch, ensuring your circuit maintains precise current replication under varying conditions.
Basic Principle of Current Mirrors
Current mirrors replicate a reference current to provide a stable output current in analog circuits. The basic current mirror uses two matched transistors to copy current, but it suffers from limited output resistance and accuracy. The Wilson current mirror improves performance by adding a third transistor, enhancing output impedance and minimizing error, making it a better choice if you need precise current replication in your designs.
Overview of Wilson Current Mirror
Wilson current mirror improves accuracy and output resistance compared to the basic current mirror by employing a three-transistor configuration that compensates for base currents. It reduces the effect of transistor parameter variations, providing better current replication in analog circuits. This design enhances performance in precision biasing and current regulation applications.
Key Differences: Current Mirror vs Wilson Current Mirror
The key differences between a basic current mirror and a Wilson current mirror lie in accuracy and output impedance; the Wilson current mirror uses an additional transistor to significantly improve output resistance and reduce the error caused by the base currents. While a standard current mirror suffers from finite output impedance and mismatch errors, the Wilson topology provides better current matching and stability, especially in analog integrated circuits. The Wilson current mirror is preferred in precision applications requiring low distortion and high linearity due to its improved transistor matching and minimized systematic errors.
Circuit Design and Topology Comparison
The current mirror circuit uses a simple two-transistor arrangement providing basic current replication but suffers from limited output impedance and accuracy due to base current errors. The Wilson current mirror incorporates an additional transistor in a feedback configuration, significantly improving output impedance and reducing current error by minimizing the influence of transistor base currents. The topology of the Wilson mirror enhances current matching and stability, making it more suitable for precision analog applications compared to the conventional current mirror design.
Output Resistance and Accuracy
Wilson current mirrors offer significantly higher output resistance compared to basic current mirrors, enhancing their ability to maintain constant current over varying load voltages. This increased output resistance results in improved accuracy and better current matching, making Wilson current mirrors preferable in precision analog circuits. Your designs benefit from reduced error margins and improved performance when using Wilson configurations for current replication.
Voltage Compliance Considerations
Voltage compliance in current mirrors significantly impacts their performance and accuracy, especially in low-voltage applications. The Wilson current mirror offers improved voltage compliance compared to the basic current mirror, allowing it to maintain accurate current replication at lower output voltages by using an additional transistor for feedback and better output impedance. Your choice depends on the minimum voltage available for proper operation, as the Wilson mirror requires less voltage drop, enhancing efficiency in modern low-voltage integrated circuits.
Power Efficiency and Performance
The Wilson current mirror offers improved power efficiency and higher output impedance compared to the basic current mirror, resulting in better current accuracy and reduced voltage drops. It minimizes the impact of transistor mismatches and Early effect, enhancing performance in precision analog circuits. Your design benefits from the Wilson mirror's superior linearity and lower power consumption, especially in low-voltage applications.
Common Applications in Analog Circuits
Current mirrors are widely used in biasing and reference current generation in analog circuits due to their simplicity and accuracy. The Wilson current mirror improves output impedance and reduces error caused by base current, making it ideal for precision analog applications such as operational amplifiers and differential amplifiers. Wilson current mirrors are preferred in integrated circuit design where stable, high-quality current replication is critical for performance and linearity.
Pros and Cons of Each Mirror Type
Current mirrors are essential for biasing and signal amplification in analog circuits, with the basic current mirror offering simplicity, low power consumption, and ease of implementation but suffering from limited output resistance and accuracy due to channel-length modulation effects. The Wilson current mirror improves performance by providing higher output resistance and better current matching, enhancing accuracy and stability, but at the cost of increased circuit complexity and slightly higher power consumption. Choosing the right mirror depends on Your circuit requirements for precision versus simplicity and power constraints.
Current mirror vs Wilson current mirror Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com