Charge pumps efficiently convert voltage levels using capacitors without inductors, ideal for small, low-power applications, while voltage regulators provide stable and precise output voltage by dissipating excess power, suited for varying load conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand which solution best fits your power management needs.
Table of Comparison
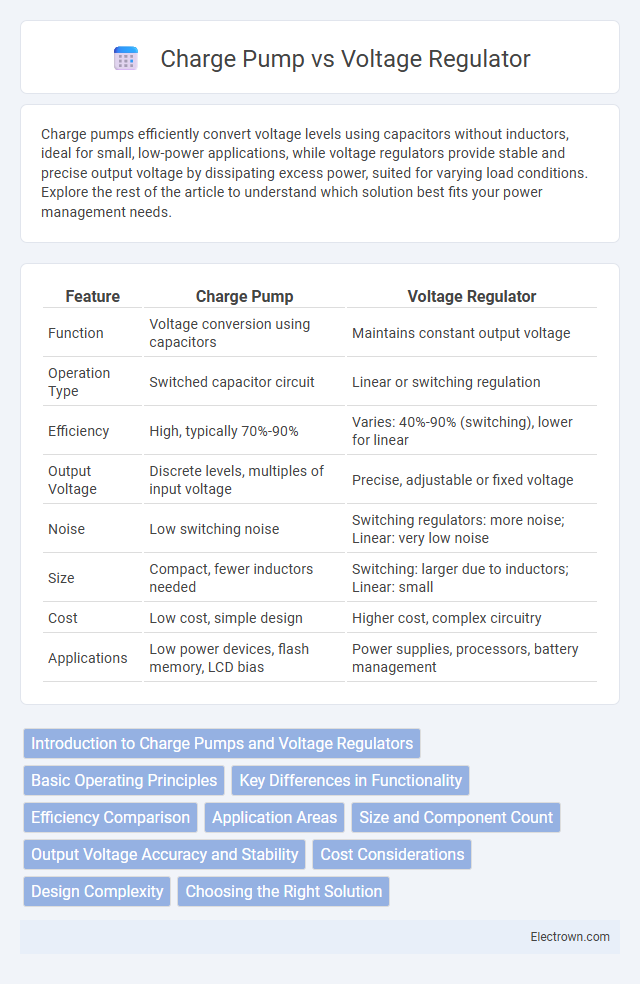
| Feature | Charge Pump | Voltage Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Voltage conversion using capacitors | Maintains constant output voltage |
| Operation Type | Switched capacitor circuit | Linear or switching regulation |
| Efficiency | High, typically 70%-90% | Varies: 40%-90% (switching), lower for linear |
| Output Voltage | Discrete levels, multiples of input voltage | Precise, adjustable or fixed voltage |
| Noise | Low switching noise | Switching regulators: more noise; Linear: very low noise |
| Size | Compact, fewer inductors needed | Switching: larger due to inductors; Linear: small |
| Cost | Low cost, simple design | Higher cost, complex circuitry |
| Applications | Low power devices, flash memory, LCD bias | Power supplies, processors, battery management |
Introduction to Charge Pumps and Voltage Regulators
Charge pumps are DC-DC converters that use capacitors to increase or invert voltage without inductors, making them compact and efficient for low-power applications. Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage or load variations, ensuring stable power supply for sensitive electronic devices. Understanding the differences helps you select the right component for optimizing power management in your circuits.
Basic Operating Principles
Charge pumps operate by switching capacitors to transfer and multiply voltage levels without inductors, using discrete charging and discharging cycles. Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage by continuously adjusting current flow through active devices like transistors or linear components based on feedback mechanisms. Charge pumps are efficient for small voltage adjustments and low current applications, while voltage regulators handle broader voltage ranges and higher load currents with precise regulation.
Key Differences in Functionality
Charge pumps transfer energy using capacitors to increase or invert voltage, making them efficient for low-power applications with simple voltage conversion needs. Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of fluctuations in input voltage or load current, ensuring stable and reliable power for sensitive electronic devices. Your choice depends on whether you require efficient voltage stepping or precise voltage stabilization in your circuit.
Efficiency Comparison
Charge pumps typically achieve high efficiency in low-power applications by converting voltage through capacitive switching without inductors, often exceeding 80-90% efficiency under optimal load conditions. Voltage regulators, especially switching regulators, maintain efficiency ranging from 70% to over 95% depending on design and load, but linear regulators are less efficient, sometimes below 50%, due to continuous power dissipation as heat. The choice between charge pump and voltage regulator depends on factors like load current, input-output voltage differential, and power efficiency requirements within specific electronic designs.
Application Areas
Charge pumps are commonly used in compact electronics requiring voltage doubling or inversion, such as OLED displays, EEPROM programming, and battery-powered devices due to their efficiency and small size. Voltage regulators are essential in power management for maintaining stable output voltages in applications including microcontrollers, communication equipment, and automotive electronics. Both components optimize power delivery, with charge pumps excelling in low-current, space-constrained environments and voltage regulators dominating high-current, precision-demanding systems.
Size and Component Count
Charge pumps typically occupy a smaller PCB footprint and require fewer external components compared to voltage regulators, making them ideal for compact designs. Voltage regulators often need larger inductors and capacitors, increasing both the overall size and component count of the circuit. Choosing a charge pump can simplify your design by minimizing space and part complexity without compromising voltage conversion needs.
Output Voltage Accuracy and Stability
Charge pumps typically offer moderate output voltage accuracy but can experience voltage ripple and instability under varying load conditions due to their switching nature. Voltage regulators provide superior output voltage stability and precision, maintaining consistent voltage levels despite fluctuations in input voltage and load current. Low-dropout (LDO) regulators are especially effective for applications demanding high accuracy and minimal output noise.
Cost Considerations
Charge pumps offer a cost-effective solution for voltage regulation in low-power applications due to their simple architecture and fewer external components compared to linear voltage regulators. Voltage regulators, especially linear and switching types, generally incur higher costs because of their complex circuitry and greater thermal management requirements. For budget-sensitive designs, charge pumps reduce overall system expenses by minimizing component count and PCB space.
Design Complexity
Charge pumps exhibit lower design complexity due to their simple circuitry that relies on capacitors and switches to increase or invert voltage without inductors. Voltage regulators, especially linear and switching types, involve more intricate designs with feedback control loops, error amplifiers, and sometimes inductive components for efficient voltage stabilization. The reduced component count in charge pumps typically translates to easier integration in compact devices, whereas voltage regulators require careful layout and tuning to maintain stability and performance under varying loads.
Choosing the Right Solution
Choosing between a charge pump and a voltage regulator depends on your power efficiency needs and circuit complexity. Charge pumps provide a compact, cost-effective solution for voltage conversion without inductors, ideal for low current applications and space-constrained designs. Voltage regulators offer stable voltage output with better load regulation and can handle higher current demands, making them suitable for complex or high-power circuits requiring precise voltage control.
Charge pump vs voltage regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com