NPN transistors are single bipolar junction transistors used for switching and amplification, while NPN-NPN transistors refer to a pair or Darlington configuration of two NPN transistors combined to provide higher current gain and better performance. Discover how these differences impact Your electronics projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
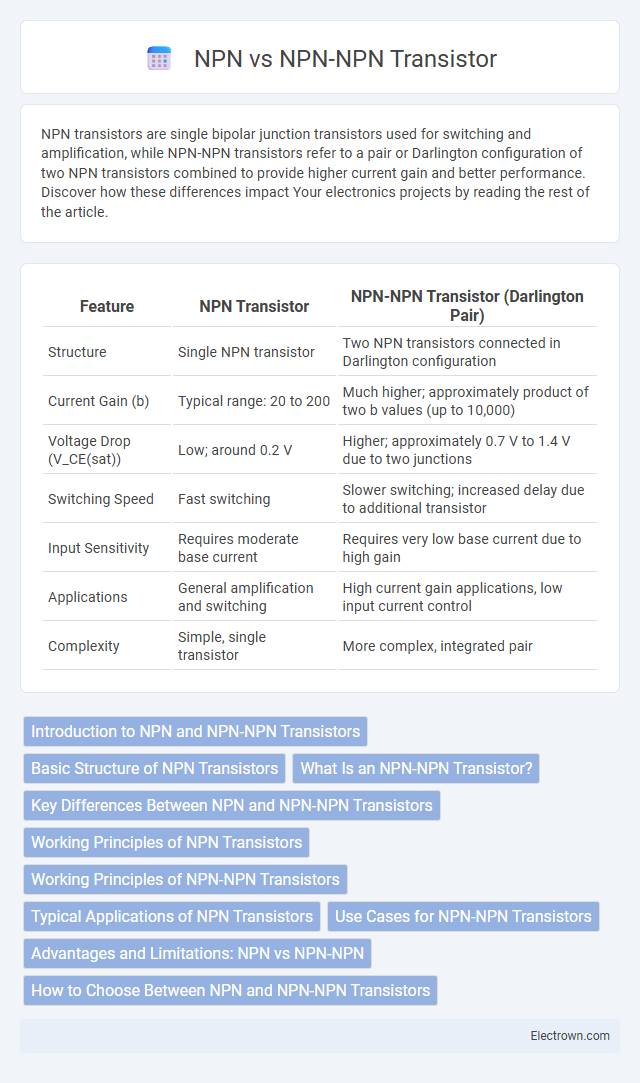
| Feature | NPN Transistor | NPN-NPN Transistor (Darlington Pair) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single NPN transistor | Two NPN transistors connected in Darlington configuration |
| Current Gain (b) | Typical range: 20 to 200 | Much higher; approximately product of two b values (up to 10,000) |
| Voltage Drop (V_CE(sat)) | Low; around 0.2 V | Higher; approximately 0.7 V to 1.4 V due to two junctions |
| Switching Speed | Fast switching | Slower switching; increased delay due to additional transistor |
| Input Sensitivity | Requires moderate base current | Requires very low base current due to high gain |
| Applications | General amplification and switching | High current gain applications, low input current control |
| Complexity | Simple, single transistor | More complex, integrated pair |
Introduction to NPN and NPN-NPN Transistors
NPN transistors are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) with a layer of p-type semiconductor between two n-type layers, commonly used for switching and amplification due to their ability to conduct current when a positive voltage is applied to the base. The term NPN-NPN transistor typically refers to configuration in transistor arrays or Darlington pairs, where two NPN transistors are connected to achieve higher current gain and improved switching performance. Both NPN and NPN-NPN transistors play crucial roles in electronic circuits, with the latter offering enhanced amplification and faster response suited for high-power and high-frequency applications.
Basic Structure of NPN Transistors
NPN transistors consist of two n-type semiconductor layers separated by a thin p-type layer, forming an n-p-n sandwich structure central to their operation as current amplifiers. Each NPN junction has distinct emitter, base, and collector terminals, where the emitter emits electrons into the base and the collector collects them, facilitating current flow. The basic structure enables efficient electron flow from emitter to collector under forward bias conditions, making NPN transistors suitable for high-speed switching and amplification applications.
What Is an NPN-NPN Transistor?
An NPN-NPN transistor is a complex semiconductor device consisting of two NPN transistors connected in a configuration that enhances current amplification and switching capabilities. This arrangement allows for higher gain and improved performance in applications requiring rapid switching and signal amplification. Understanding your circuit requirements helps determine whether an NPN-NPN transistor provides a significant advantage over a single NPN transistor.
Key Differences Between NPN and NPN-NPN Transistors
NPN transistors are single bipolar junction transistors (BJT) with one N-type layer, one P-type layer, and another N-type layer, commonly used for switching and amplification. NPN-NPN transistors refer to multi-transistor configurations, often Darlington pairs, combining two NPN transistors to achieve higher current gain and input impedance. The key differences lie in complexity, gain capacity, and switching speed, with NPN-NPN devices offering superior amplification but slower response due to increased transistor count.
Working Principles of NPN Transistors
NPN transistors operate by allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter when a small current is applied to the base, enabling amplification and switching functions. The base-emitter junction is forward biased, allowing electrons to flow into the base region, while the base-collector junction is reverse biased, controlling the larger current flow. Your circuit's performance depends on this precise control of electron movement, making NPN transistors essential in many electronic applications.
Working Principles of NPN-NPN Transistors
NPN-NPN transistors consist of two NPN bipolar junction transistors connected in a configuration that allows for amplification and switching functions with enhanced current gain and faster response times. The working principle relies on the interaction between the two NPN transistors, where the first transistor amplifies the input signal and drives the base of the second transistor, resulting in a cumulative current amplification effect. This arrangement improves overall transistor performance in high-frequency and high-speed circuits by optimizing carrier injection and reducing transit time.
Typical Applications of NPN Transistors
NPN transistors are widely used in switching circuits, amplification, and signal processing due to their high electron mobility, which allows efficient current flow from the collector to the emitter. Common applications include digital logic circuits, power amplifiers, and low-side switching in automotive and industrial controls. Your designs benefit from their versatility in driving loads, such as relays and LEDs, especially in NPN-NPN transistor configurations for multi-stage amplification.
Use Cases for NPN-NPN Transistors
NPN-NPN transistors are commonly used in push-pull amplifier circuits where high current gain and efficient switching are required for driving loads such as speakers and motors. These configurations offer improved linearity and reduced distortion compared to single NPN transistor stages, making them ideal for audio amplification and power regulation applications. Your designs benefit from enhanced performance and stability when incorporating NPN-NPN transistor pairs in complementary circuits.
Advantages and Limitations: NPN vs NPN-NPN
NPN transistors offer faster switching speeds and higher electron mobility, making them ideal for high-frequency applications, while NPN-NPN configurations provide enhanced current amplification through cascading stages but introduce increased complexity and potential signal delay. The simpler structure of single NPN transistors ensures easier integration and reliability in straightforward circuits, whereas NPN-NPN transistor arrangements enable greater gain and improved performance in multi-stage amplifiers at the cost of higher power consumption and design challenges. Choosing between NPN and NPN-NPN transistors depends on the specific requirements for amplification, frequency response, and circuit complexity.
How to Choose Between NPN and NPN-NPN Transistors
Choosing between NPN and NPN-NPN transistors depends on your circuit's requirements for current amplification and switching complexity. NPN transistors are ideal for simple amplification and switching tasks with moderate current, while NPN-NPN transistor pairs offer higher gain and are suited for more complex applications needing improved performance and stability. Evaluate your project's voltage, current handling, and gain specifications to determine the best transistor type for your design.
NPN vs NPN-NPN transistor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com