SPM (Statistical Parametric Mapping) and IPM (Image Processing Methods) differ primarily in their application focus; SPM is extensively used for analyzing brain imaging data through statistical models, while IPM encompasses a broader range of techniques for enhancing and extracting features from images across various fields. To understand which method best suits Your specific imaging needs and the distinct advantages they offer, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
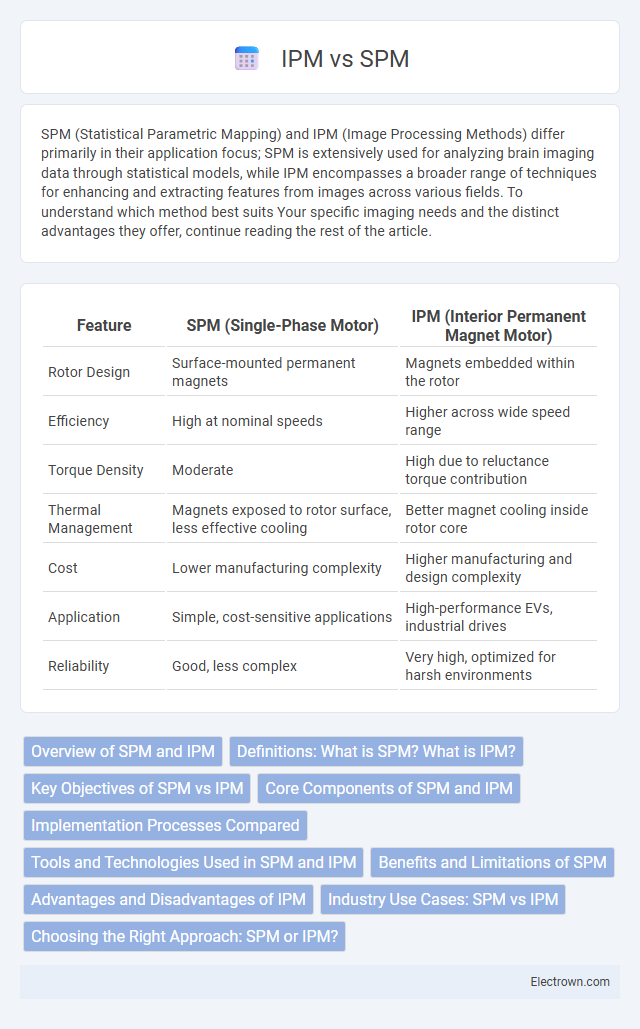
| Feature | SPM (Single-Phase Motor) | IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet Motor) |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor Design | Surface-mounted permanent magnets | Magnets embedded within the rotor |
| Efficiency | High at nominal speeds | Higher across wide speed range |
| Torque Density | Moderate | High due to reluctance torque contribution |
| Thermal Management | Magnets exposed to rotor surface, less effective cooling | Better magnet cooling inside rotor core |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing complexity | Higher manufacturing and design complexity |
| Application | Simple, cost-sensitive applications | High-performance EVs, industrial drives |
| Reliability | Good, less complex | Very high, optimized for harsh environments |
Overview of SPM and IPM
Surface Plasmon Microscopy (SPM) utilizes the excitation of surface plasmons on metal films to achieve high-resolution imaging of nanoscale features, providing sensitive detection of refractive index changes. Integrated Photonics Microscopy (IPM) combines photonic circuits with microscopy techniques to enhance imaging capabilities by integrating light manipulation and detection on a single chip, offering compact and scalable solutions for optical sensing. Both SPM and IPM leverage distinct optical phenomena for high-resolution, label-free imaging but differ in their underlying mechanisms and integration approaches.
Definitions: What is SPM? What is IPM?
SPM (Single-Phase Motor) is an electric motor that operates on a single-phase power supply, commonly used in household appliances and small machinery due to its simple design and cost-effectiveness. IPM (Interior Permanent Magnet) motor features magnets embedded inside the rotor, offering high efficiency, compact size, and improved performance in electric vehicles and industrial applications. Both SPM and IPM motors differ in construction and performance characteristics, with IPM motors providing better torque density and efficiency compared to traditional SPM designs.
Key Objectives of SPM vs IPM
SPM (Strategic Portfolio Management) focuses on aligning projects and programs with an organization's long-term strategic goals, optimizing resource allocation to maximize business value. IPM (Integrated Project Management) aims to coordinate individual project processes, ensuring seamless execution, effective risk management, and cross-functional collaboration. While SPM prioritizes strategic decision-making and investment optimization, IPM emphasizes operational efficiency and project-level integration.
Core Components of SPM and IPM
SPM (Strategic Performance Management) centers on core components such as goal setting, performance measurement, and strategy alignment to enhance organizational effectiveness. IPM (Integrated Pest Management) focuses on core elements like pest monitoring, threshold levels, and control tactics that emphasize sustainable and environmentally friendly pest control. Both SPM and IPM rely on data-driven processes and continuous assessment to optimize outcomes within their respective fields.
Implementation Processes Compared
Single Project Management (SPM) centers on managing one project with defined goals, utilizing tailored processes such as scope definition, scheduling, and resource allocation specific to that project. Integrated Project Management (IPM) involves coordinating multiple projects or program components, emphasizing standardized processes, inter-project communication, and centralized oversight to optimize alignment and resource sharing across the portfolio. Implementation in SPM often relies on project-specific tools and teams, whereas IPM requires robust systems for synchronization, risk management, and performance tracking across multiple, interrelated projects.
Tools and Technologies Used in SPM and IPM
SPM (Sales Performance Management) leverages advanced analytics platforms, CRM software integrations, and incentive compensation management tools to optimize sales strategies and monitor performance. IPM (Integrated Project Management) utilizes project management software such as Microsoft Project, Jira, and Asana, alongside collaborative communication tools and resource allocation systems to streamline project workflows. Both SPM and IPM incorporate AI-powered forecasting and data visualization technologies to enhance decision-making and efficiency.
Benefits and Limitations of SPM
Single Project Management (SPM) offers streamlined focus and resource allocation, enhancing project-specific efficiency and task prioritization. It excels in managing the nuances and unique demands of individual projects but can limit broader organizational insight and flexibility compared to Integrated Project Management (IPM). SPM's primary limitation lies in its potential isolation from company-wide goals, risking misalignment with overall strategic objectives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IPM
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) offers significant advantages including reduced chemical pesticide use, leading to lower environmental impact and increased sustainability in agricultural practices. It promotes beneficial insects, improves pest resistance management, and supports crop health through diverse control methods like biological, cultural, and mechanical tactics. However, IPM can have disadvantages such as requiring extensive knowledge, monitoring, and labor, potentially increasing operational complexity and costs compared to Single Pest Management (SPM).
Industry Use Cases: SPM vs IPM
SPM (Strategic Performance Management) is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, finance, and healthcare to align organizational goals with measurable outcomes, driving long-term strategic success. IPM (Integrated Project Management) is preferred in construction, IT, and engineering sectors for coordinating complex projects, optimizing resource allocation, and ensuring timely delivery. Your choice between SPM and IPM depends on whether the focus is on overarching strategic alignment or detailed project execution within your industry.
Choosing the Right Approach: SPM or IPM?
Selecting between Statistical Process Monitoring (SPM) and Integrated Pest Management (IPM) hinges on the specific industry context and goals; SPM excels in manufacturing for quality control through real-time data analysis and statistical tools, while IPM is vital in agriculture for sustainable pest control using biological, chemical, and cultural methods. Decision-makers must evaluate factors such as environmental impact, resource availability, and desired outcome precision. Incorporating domain-specific data and performance metrics ensures an optimized approach tailored to operational needs.
SPM vs IPM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com