SBS (Side-by-Side) and SCS (Split-Column Spreadsheet) are two different data presentation formats used for comparing information efficiently. Understanding their unique benefits can help Your analysis process become more organized and clear; explore the rest of the article to discover which method suits your needs best.
Table of Comparison
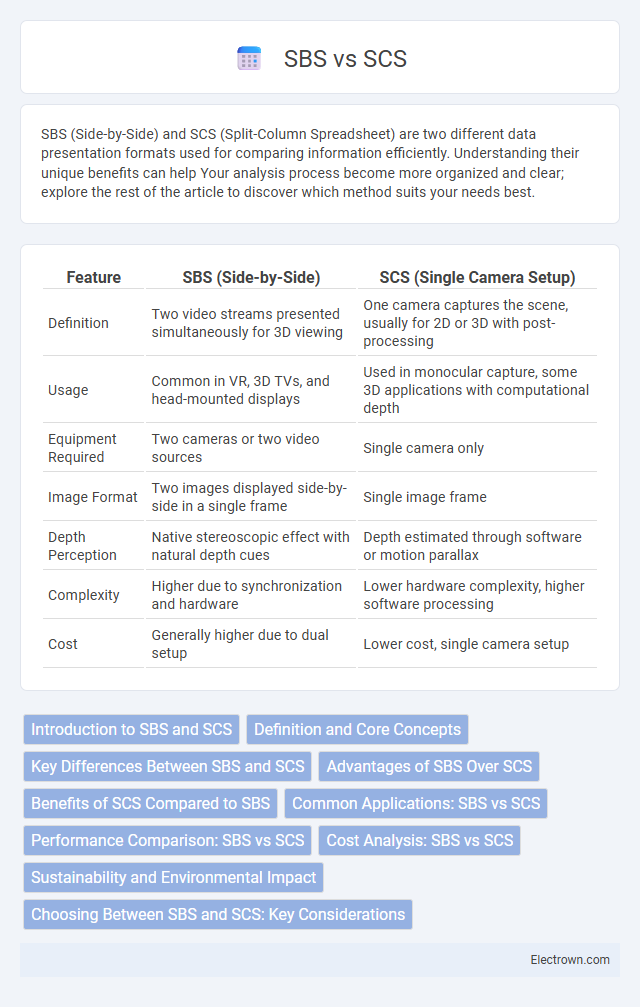
| Feature | SBS (Side-by-Side) | SCS (Single Camera Setup) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two video streams presented simultaneously for 3D viewing | One camera captures the scene, usually for 2D or 3D with post-processing |
| Usage | Common in VR, 3D TVs, and head-mounted displays | Used in monocular capture, some 3D applications with computational depth |
| Equipment Required | Two cameras or two video sources | Single camera only |
| Image Format | Two images displayed side-by-side in a single frame | Single image frame |
| Depth Perception | Native stereoscopic effect with natural depth cues | Depth estimated through software or motion parallax |
| Complexity | Higher due to synchronization and hardware | Lower hardware complexity, higher software processing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to dual setup | Lower cost, single camera setup |
Introduction to SBS and SCS
SBS (Small Bowel Syndrome) is a malabsorption disorder caused by the surgical removal or dysfunction of significant portions of the small intestine, leading to nutrient and fluid absorption challenges. SCS (Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome) is a vestibular disorder characterized by an abnormal opening in the bone overlying the superior semicircular canal, resulting in symptoms like vertigo and hearing disturbances. Both SBS and SCS affect different organ systems but require specialized diagnostic and therapeutic approaches tailored to their pathophysiology.
Definition and Core Concepts
SBS (Small Bowel Series) is a radiographic examination used to visualize the small intestine by tracking the passage of a contrast material, primarily identifying structural abnormalities and motility issues. SCS (Superior Cervical Sympathectomy) is a surgical procedure targeting the sympathetic nerves at the upper cervical level to manage conditions like hyperhidrosis and certain vascular disorders. Both SBS and SCS serve diagnostic and therapeutic roles but operate within distinct anatomical regions and clinical applications.
Key Differences Between SBS and SCS
SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) is a block copolymer known for its elastomeric properties and is commonly used in modifying asphalt for improved flexibility and temperature resistance. SCS (Silicone Cross-Linked Silicone) refers to silicone-based materials with cross-linked structures, offering superior thermal stability and chemical resistance. Key differences include SBS's enhanced elasticity and cost-effectiveness for road construction versus SCS's higher temperature endurance and inert properties ideal for specialized industrial applications.
Advantages of SBS Over SCS
SBS (Split Beam Steering) offers enhanced maneuverability and precise directional control compared to SCS (Single Channel Steering), making it ideal for complex navigation environments. Its ability to independently adjust multiple beam angles improves signal targeting and reduces interference, leading to superior communication reliability. If you require optimal performance in dynamic conditions, SBS provides a significant advantage over traditional SCS systems.
Benefits of SCS Compared to SBS
SCS (Spinal Cord Stimulation) offers targeted pain relief by delivering electrical impulses directly to the spinal cord, reducing the need for opioids commonly associated with SBS (Sympathetic Blockade Stimulation). Patients using SCS report improved quality of life and greater functional mobility due to its adjustable programming and minimally invasive implantation. Furthermore, SCS demonstrates longer-lasting effects with fewer side effects compared to SBS, making it a preferred option for chronic neuropathic pain management.
Common Applications: SBS vs SCS
SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) is commonly used in road construction, waterproofing membranes, and roofing materials due to its excellent elasticity and durability. SCS (Styrene-Co-Butadiene-Styrene) is typically applied in adhesives, sealants, and flexible packaging where improved chemical resistance and flexibility are required. Your choice between SBS and SCS depends on whether you prioritize weather resistance and mechanical strength or enhanced chemical stability and flexibility.
Performance Comparison: SBS vs SCS
SBS (Small Backup Server) offers faster data processing speeds and lower latency compared to SCS (Standard Cloud Storage), making it ideal for real-time applications and quick recovery. SCS excels in scalability and cost efficiency for large-volume data storage but may experience higher access latency under heavy workloads. Performance benchmarks reveal SBS achieves up to 30% faster read/write speeds, while SCS prioritizes durability and backup redundancy over raw performance.
Cost Analysis: SBS vs SCS
Cost analysis between SBS (Small Business Server) and SCS (Standard Cloud Solution) reveals distinct financial implications depending on your organizational needs. SBS generally involves upfront hardware and software licensing costs, coupled with ongoing maintenance expenses, whereas SCS operates on a subscription-based model with predictable monthly fees that include updates and support. Evaluating your budget for initial investments versus operational expenses will guide your choice between the capital-intensive SBS and the scalable, cost-efficient SCS.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
SBS (Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene) and SCS (Sulfur-Cured Silicone) differ significantly in sustainability and environmental impact. SBS is petroleum-based, contributing to higher carbon emissions and limited biodegradability, while SCS, derived from silicon, offers greater durability and lower toxicity with improved recyclability. Your choice of SCS supports greener practices by reducing ecological footprint and enhancing material lifespan.
Choosing Between SBS and SCS: Key Considerations
Choosing between SBS (Simultaneous Bilateral Stimulation) and SCS (Selective Cortical Stimulation) depends on the specific clinical goals and patient conditions, with SBS often preferred for comprehensive bilateral activation in neuromodulation. SCS targets localized cortical areas, offering precision in treating focal neurological disorders, while SBS provides broader neural engagement beneficial in symmetrical brain function restoration. Evaluating factors such as desired stimulation area, therapeutic objectives, and patient tolerance is essential for optimizing treatment outcomes.
SBS vs SCS Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com