Zener diodes regulate voltage by operating in the breakdown region at a precise reverse voltage, providing stable reference voltages, while avalanche diodes handle higher voltage spikes by breaking down through impact ionization without damage. Discover how these differences affect your circuit design and which diode suits your application by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
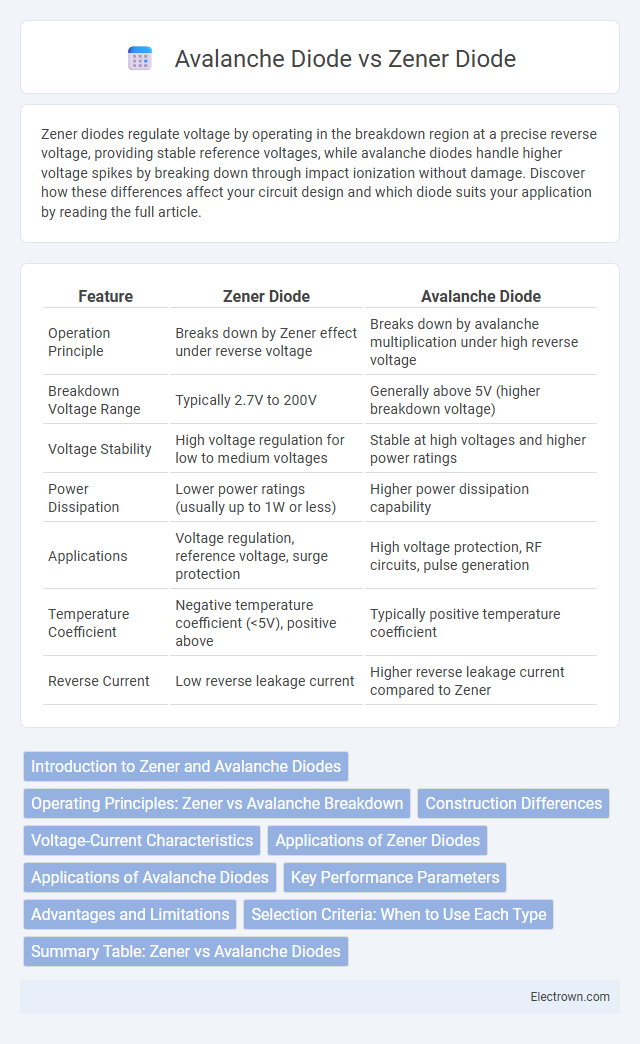
| Feature | Zener Diode | Avalanche Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Operation Principle | Breaks down by Zener effect under reverse voltage | Breaks down by avalanche multiplication under high reverse voltage |
| Breakdown Voltage Range | Typically 2.7V to 200V | Generally above 5V (higher breakdown voltage) |
| Voltage Stability | High voltage regulation for low to medium voltages | Stable at high voltages and higher power ratings |
| Power Dissipation | Lower power ratings (usually up to 1W or less) | Higher power dissipation capability |
| Applications | Voltage regulation, reference voltage, surge protection | High voltage protection, RF circuits, pulse generation |
| Temperature Coefficient | Negative temperature coefficient (<5V), positive above | Typically positive temperature coefficient |
| Reverse Current | Low reverse leakage current | Higher reverse leakage current compared to Zener |
Introduction to Zener and Avalanche Diodes
Zener diodes are designed to operate in the breakdown region at precise voltage levels, providing voltage regulation through controlled reverse breakdown. Avalanche diodes function by allowing avalanche breakdown when the reverse voltage exceeds a critical threshold, used mainly for protection against voltage spikes. Both types exploit different breakdown mechanisms to maintain circuit stability and protect sensitive components.
Operating Principles: Zener vs Avalanche Breakdown
Zener diodes operate based on Zener breakdown, which occurs at low reverse voltages due to strong electric fields causing electron tunneling within a heavily doped p-n junction. Avalanche diodes rely on avalanche breakdown, where high reverse voltage accelerates carriers to ionize atoms, creating a chain reaction of current multiplication in a lightly doped junction. Understanding these distinct mechanisms helps you select the appropriate diode for voltage regulation and protection applications.
Construction Differences
Zener diodes have a heavily doped p-n junction, allowing them to break down at a precise reverse voltage without damage, ideal for voltage regulation. Avalanche diodes feature a more lightly doped p-n junction that withstands higher breakdown voltages via avalanche multiplication, suitable for high-voltage applications. Your choice depends on the specific breakdown voltage range and stability requirements dictated by these construction differences.
Voltage-Current Characteristics
Zener diodes exhibit a sharp breakdown voltage, known as the Zener voltage, where they maintain a nearly constant voltage over a wide range of reverse current, making them ideal for voltage regulation. In contrast, avalanche diodes experience breakdown due to impact ionization at higher reverse voltages, with a less abrupt voltage-current characteristic and typically higher breakdown voltage than Zener diodes. Both diodes operate in reverse bias, but Zener diodes provide more precise voltage clamping under low breakdown voltages, while avalanche diodes handle higher power and voltage surges.
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are widely used for voltage regulation in power supplies, ensuring stable output voltages despite input fluctuations. They serve as voltage references in precision circuits and protect sensitive electronic components from overvoltage by clamping voltage spikes. These diodes are also integral in waveform clipping and voltage shunting to maintain circuit safety and performance.
Applications of Avalanche Diodes
Avalanche diodes are primarily used in high-voltage protection circuits due to their capability to handle large transient voltages through avalanche breakdown without damage. They serve as voltage regulators in surge suppressors and lightning arresters, protecting sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes. Their fast response time and high energy absorption capacity make them ideal for reverse polarity protection and clipping circuits in communication systems.
Key Performance Parameters
Zener diodes are designed for precise voltage regulation with a stable breakdown voltage typically between 2.4V and 200V, characterized by a sharp and controlled Zener breakdown region ensuring minimal voltage variation under varying current. Avalanche diodes feature higher breakdown voltages, often above 6V, with controlled avalanche multiplication providing robust surge protection and higher energy dissipation capabilities. Your choice depends on whether you require voltage regulation with tight voltage tolerance (Zener diode) or high voltage surge absorption with energy handling (avalanche diode).
Advantages and Limitations
Zener diodes provide precise voltage regulation with sharp breakdown voltage, making them ideal for voltage reference and protection circuits, while avalanche diodes handle higher surge currents and offer superior ruggedness in transient voltage suppression. Zener diodes struggle with stability at higher voltages and limited power ratings, whereas avalanche diodes may exhibit less precise voltage regulation and higher leakage currents. Understanding these trade-offs helps you select the right diode for your circuit's voltage control and protection needs.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each Type
Zener diodes are ideal for precise voltage regulation in low-voltage applications up to around 200V, providing stable reference voltages by operating in the breakdown region. Avalanche diodes are preferred for higher voltage scenarios and transient voltage suppression, as they can handle larger surge currents without damage. Your choice depends on the voltage range and current capacity required for the specific protection or regulation task.
Summary Table: Zener vs Avalanche Diodes
Zener diodes operate primarily in the breakdown region with a precisely controlled voltage, typically below 5V, for voltage regulation and reference applications, while avalanche diodes work at higher breakdown voltages, relying on avalanche multiplication for voltage clamping and surge protection. Zener diodes exhibit a sharp, stable breakdown voltage due to quantum tunneling, whereas avalanche diodes provide robust avalanche breakdown at voltages usually above 6V, ensuring stable operation under high surge currents. Temperature coefficient differs as Zener diodes show a negative temperature coefficient at low voltages, contrasting with the positive coefficient in avalanche diodes at high voltages, influencing their respective circuit applications.
Zener vs avalanche diode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com