SOI MOSFETs offer reduced parasitic capacitance and improved performance under high-frequency conditions compared to Bulk MOSFETs, which are more prone to leakage currents due to their bulk substrate structure. Discover how these differences can impact your circuit design by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
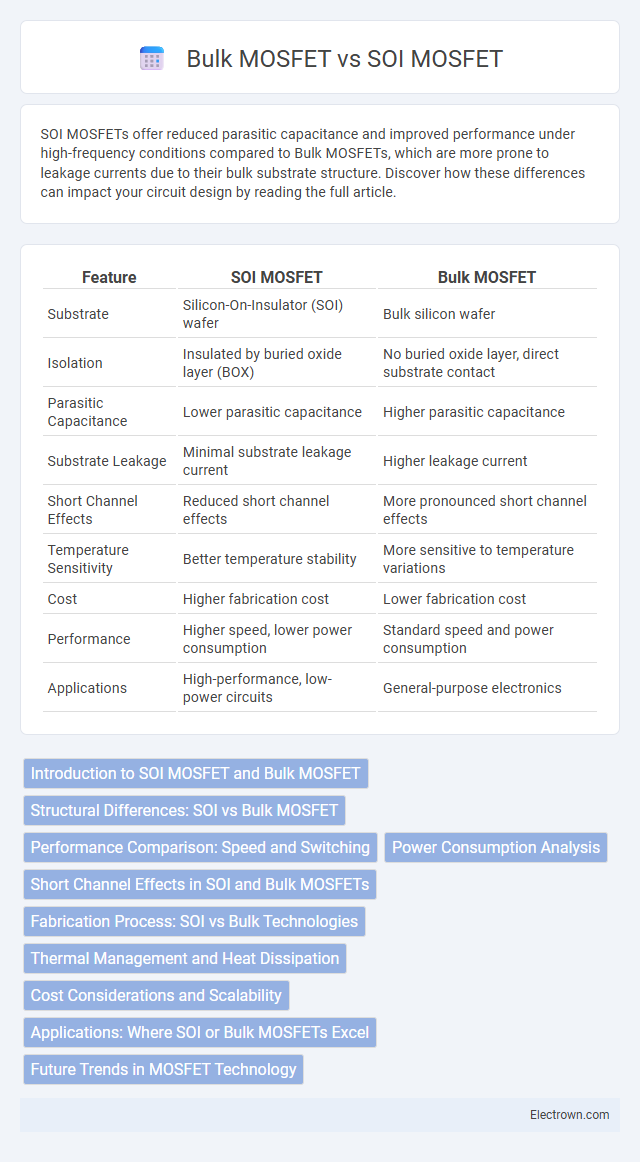
| Feature | SOI MOSFET | Bulk MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) wafer | Bulk silicon wafer |
| Isolation | Insulated by buried oxide layer (BOX) | No buried oxide layer, direct substrate contact |
| Parasitic Capacitance | Lower parasitic capacitance | Higher parasitic capacitance |
| Substrate Leakage | Minimal substrate leakage current | Higher leakage current |
| Short Channel Effects | Reduced short channel effects | More pronounced short channel effects |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Better temperature stability | More sensitive to temperature variations |
| Cost | Higher fabrication cost | Lower fabrication cost |
| Performance | Higher speed, lower power consumption | Standard speed and power consumption |
| Applications | High-performance, low-power circuits | General-purpose electronics |
Introduction to SOI MOSFET and Bulk MOSFET
SOI MOSFETs (Silicon-On-Insulator Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors) are fabricated on a thin insulating layer of silicon dioxide, which reduces parasitic capacitance and improves switching speed compared to Bulk MOSFETs, which are built directly on a silicon substrate. The insulating layer in SOI MOSFETs also enhances device isolation, reduces leakage currents, and improves radiation hardness, making them suitable for high-performance and low-power applications. Bulk MOSFETs remain widely used due to their lower manufacturing costs and mature fabrication processes despite higher leakage and slower switching speeds.
Structural Differences: SOI vs Bulk MOSFET
SOI MOSFETs feature a thin insulating layer of silicon dioxide beneath the silicon substrate, isolating the transistor body from the bulk wafer, while Bulk MOSFETs are fabricated directly on a continuous silicon substrate without such insulation. This buried oxide layer in SOI devices minimizes parasitic capacitances and leakage currents, enhancing performance and reducing short-channel effects. In contrast, Bulk MOSFETs experience higher junction capacitance and body charge coupling due to the direct substrate contact, impacting speed and power efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Switching
SOI MOSFETs exhibit faster switching speeds and reduced parasitic capacitance compared to Bulk MOSFETs, resulting in enhanced high-frequency performance and lower power dissipation. The isolation layer in SOI technology minimizes leakage currents, improving switching efficiency and overall device speed. Bulk MOSFETs suffer from higher junction capacitance and substrate coupling, which limits their switching speed and increases power loss during operation.
Power Consumption Analysis
SOI MOSFETs exhibit significantly lower power consumption compared to Bulk MOSFETs due to reduced parasitic capacitance and minimized leakage current from their buried oxide layer. The isolation in SOI devices eliminates substrate coupling, resulting in improved switching speed and decreased dynamic power dissipation. Power efficiency in SOI technology is especially advantageous for low-voltage and high-frequency applications, as it substantially mitigates short-channel effects and junction leakage.
Short Channel Effects in SOI and Bulk MOSFETs
Short channel effects (SCE) in SOI MOSFETs are significantly reduced compared to bulk MOSFETs due to the insulating buried oxide layer, which limits charge coupling and lowers drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL). Bulk MOSFETs experience pronounced SCE such as threshold voltage roll-off and increased leakage currents because the channel is directly influenced by the substrate potential. The intrinsic isolation in SOI devices enhances electrostatic control, enabling improved device scalability and reduced off-state leakage in advanced technology nodes.
Fabrication Process: SOI vs Bulk Technologies
SOI MOSFETs are fabricated using a silicon-on-insulator substrate, where a thin silicon layer is separated from the bulk silicon wafer by a buried oxide layer, enhancing device isolation and reducing parasitic capacitance. Bulk MOSFETs are manufactured directly on a thick silicon substrate, making the process simpler but more prone to parasitic effects and leakage currents. Your choice between SOI and bulk technologies depends on the desired trade-off between fabrication complexity and device performance in high-speed or low-power applications.
Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation
SOI MOSFETs offer superior thermal isolation due to the buried oxide layer, which reduces substrate coupling and heat conduction compared to Bulk MOSFETs. However, this insulation also leads to challenges in heat dissipation, requiring advanced thermal management solutions to prevent device overheating. To optimize Your circuit's thermal performance, careful consideration of heat sinks and substrate design is essential when using SOI technology.
Cost Considerations and Scalability
SOI MOSFETs typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to the complex fabrication process involving silicon-on-insulator wafers, while Bulk MOSFETs benefit from established, cost-efficient bulk silicon production techniques. Scalability favors Bulk MOSFETs in cost-sensitive high-volume applications because of their simpler process integration and economies of scale. SOI MOSFETs offer superior performance at advanced technology nodes but can face cost challenges when scaling beyond niche or high-performance markets.
Applications: Where SOI or Bulk MOSFETs Excel
SOI MOSFETs excel in high-frequency applications and low-power, high-performance integrated circuits due to their reduced parasitic capacitance and improved short-channel effects, making them ideal for RF and mobile devices. Bulk MOSFETs remain dominant in cost-sensitive, high-voltage, and power management applications where their mature manufacturing process provides robustness and scalability for general-purpose electronics. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and speed (SOI) or cost and power handling capabilities (Bulk).
Future Trends in MOSFET Technology
SOI MOSFETs offer superior performance in scaling and power efficiency compared to Bulk MOSFETs, making them a leading choice for next-generation semiconductor devices. Advances in ultra-thin body SOI structures and novel gate dielectrics are driving improvements in leakage current reduction and switching speeds. Emerging applications in 5G communications, IoT, and AI accelerators increasingly rely on SOI MOSFET technology to meet stringent power and performance requirements.
SOI MOSFET vs Bulk MOSFET Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com