DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) and SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation differ primarily in bandwidth efficiency and power usage, with SSBSC transmitting only one sideband to reduce bandwidth and improve signal-to-noise ratio compared to the two sidebands used in DSBSC. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the optimal modulation technique for your communication system; read on to explore detailed comparisons and applications of DSBSC and SSBSC.
Table of Comparison
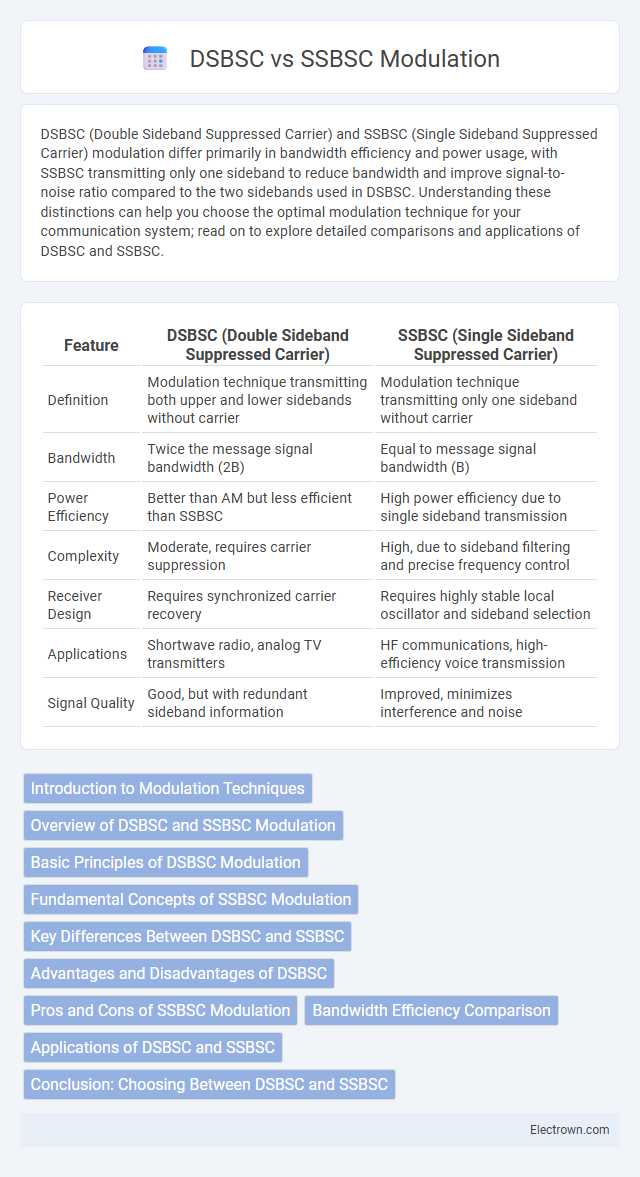
| Feature | DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) | SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modulation technique transmitting both upper and lower sidebands without carrier | Modulation technique transmitting only one sideband without carrier |
| Bandwidth | Twice the message signal bandwidth (2B) | Equal to message signal bandwidth (B) |
| Power Efficiency | Better than AM but less efficient than SSBSC | High power efficiency due to single sideband transmission |
| Complexity | Moderate, requires carrier suppression | High, due to sideband filtering and precise frequency control |
| Receiver Design | Requires synchronized carrier recovery | Requires highly stable local oscillator and sideband selection |
| Applications | Shortwave radio, analog TV transmitters | HF communications, high-efficiency voice transmission |
| Signal Quality | Good, but with redundant sideband information | Improved, minimizes interference and noise |
Introduction to Modulation Techniques
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) and SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) are modulation techniques used in communication systems to efficiently transmit information by varying the amplitude of a carrier wave while suppressing the carrier itself. DSBSC transmits both sidebands, doubling the bandwidth requirements, whereas SSBSC transmits only one sideband, significantly reducing bandwidth and power consumption. Understanding these modulation schemes helps optimize Your signal transmission by balancing complexity, bandwidth efficiency, and power usage in various communication applications.
Overview of DSBSC and SSBSC Modulation
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation transmits both sidebands without the carrier, optimizing power efficiency and bandwidth usage but requiring coherent detection for demodulation. SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation further improves spectral efficiency by transmitting only one sideband, either the upper or lower, significantly reducing bandwidth and power consumption compared to DSBSC. Both modulation schemes are widely used in communication systems where bandwidth conservation and signal clarity are critical, with SSBSC preferred for long-distance voice transmission due to its reduced bandwidth and minimized interference.
Basic Principles of DSBSC Modulation
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation involves transmitting both sidebands of the carrier frequency while suppressing the carrier itself, effectively reducing power consumption and bandwidth usage compared to conventional AM. The modulated signal is generated by multiplying the message signal with the carrier wave, resulting in a spectrum centered around the carrier frequency but without the carrier component. This method improves signal efficiency and reduces interference, making it suitable for communication systems requiring efficient bandwidth utilization.
Fundamental Concepts of SSBSC Modulation
SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation transmits information by isolating and sending only one sideband, eliminating the carrier and the other sideband to improve bandwidth efficiency compared to DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier). This method reduces the required bandwidth to half that of DSBSC, enhancing spectral efficiency and minimizing power consumption in your communication system. By focusing on the fundamental concept of suppressing the carrier and one sideband, SSBSC modulation is ideal for long-distance and high-capacity transmission where bandwidth conservation is critical.
Key Differences Between DSBSC and SSBSC
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation transmits both upper and lower sidebands, resulting in a wider bandwidth and less spectral efficiency compared to SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier), which transmits only one sideband, significantly reducing bandwidth usage. DSBSC requires a coherent demodulator and has simpler transmitter design, while SSBSC demands more complex filtering and carrier recovery techniques but improves power efficiency and reduces interference. Understanding these key differences helps optimize your communication system's bandwidth and power requirements effectively.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DSBSC
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation offers bandwidth efficiency and improved power utilization by eliminating the carrier, resulting in reduced transmitted power compared to traditional AM. Its primary disadvantage lies in the requirement for coherent demodulation and a locally generated carrier at the receiver, complicating the receiver design and synchronization. While DSBSC reduces bandwidth compared to AM, it is less bandwidth-efficient than SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier), which transmits only one sideband, further reducing bandwidth and power usage.
Pros and Cons of SSBSC Modulation
SSBSC modulation offers high spectral efficiency by transmitting only one sideband, which reduces bandwidth usage and minimizes power consumption compared to DSBSC. However, it requires more complex and precise carrier suppression and demodulation techniques, making receiver design challenging and costly. Your communication system benefits from SSBSC when bandwidth efficiency is critical, despite the increased implementation complexity.
Bandwidth Efficiency Comparison
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation transmits both sidebands, resulting in a bandwidth equal to twice the message signal's bandwidth, whereas SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) transmits only one sideband, effectively halving the bandwidth required. This makes SSBSC modulation significantly more bandwidth-efficient, ideal for communication systems where spectral efficiency is critical. Your choice of modulation impacts spectrum utilization and potential interference, with SSBSC providing a more compact signal footprint compared to DSBSC.
Applications of DSBSC and SSBSC
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation is widely used in analog communication systems such as AM stereo broadcasting and point-to-point radio links, where bandwidth efficiency and reduced power consumption are important. SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation finds applications in long-distance HF radio communications, marine and aviation transmissions, as it significantly reduces bandwidth and power usage while improving signal clarity over noisy channels. Your communication system's choice between DSBSC and SSBSC depends on the trade-off between system complexity and spectral efficiency required for the application.
Conclusion: Choosing Between DSBSC and SSBSC
DSBSC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation offers simplicity and ease of implementation, making it suitable for applications where bandwidth is less constrained. SSBSC (Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier) modulation provides superior bandwidth efficiency by transmitting only one sideband, reducing power consumption and interference, which is critical in long-distance communication systems. Selecting between DSBSC and SSBSC depends on the priority of spectral efficiency versus system complexity, with SSBSC favored for bandwidth-limited scenarios and DSBSC for simpler transmitter design and reasonable bandwidth availability.
DSBSC vs SSBSC modulation Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com