A shunt regulator controls voltage by diverting excess current across a parallel path, making it suitable for low-power applications, while a series regulator adjusts voltage by varying resistance in series with the load, offering better efficiency and noise reduction. Explore the differences in design, performance, and application to determine which regulator best fits your needs.
Table of Comparison
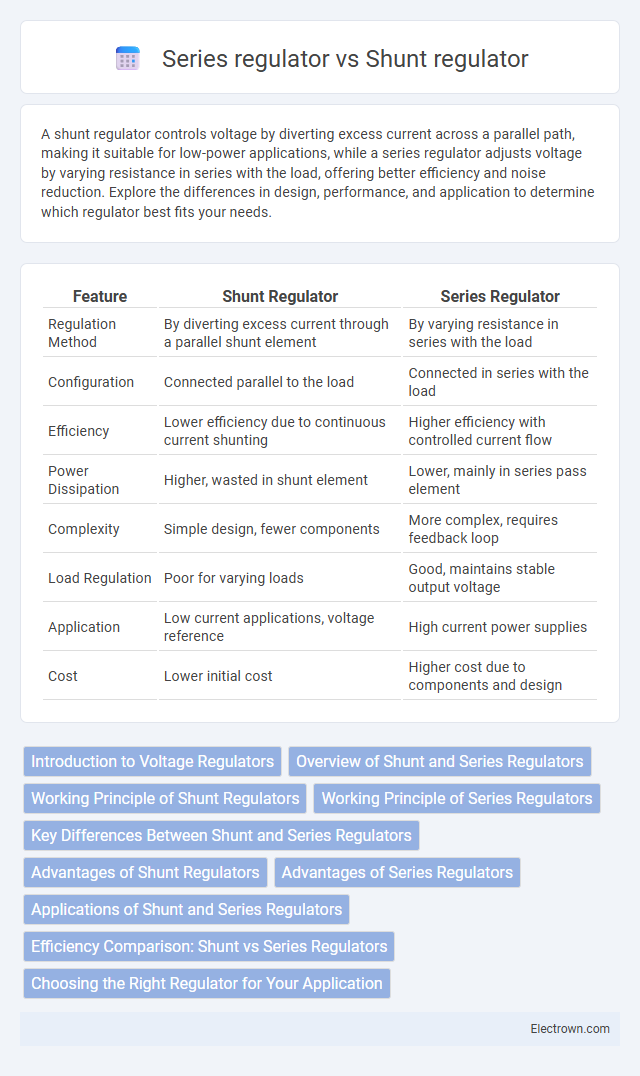
| Feature | Shunt Regulator | Series Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Regulation Method | By diverting excess current through a parallel shunt element | By varying resistance in series with the load |
| Configuration | Connected parallel to the load | Connected in series with the load |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to continuous current shunting | Higher efficiency with controlled current flow |
| Power Dissipation | Higher, wasted in shunt element | Lower, mainly in series pass element |
| Complexity | Simple design, fewer components | More complex, requires feedback loop |
| Load Regulation | Poor for varying loads | Good, maintains stable output voltage |
| Application | Low current applications, voltage reference | High current power supplies |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to components and design |
Introduction to Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators maintain consistent voltage levels to protect electrical devices from fluctuations. Shunt regulators control voltage by diverting excess current through a parallel path, making them ideal for low current applications. Series regulators regulate voltage by adjusting a variable resistor in series with the load, offering higher efficiency and better performance for varying load demands.
Overview of Shunt and Series Regulators
Shunt regulators maintain a constant voltage by diverting excess current through a parallel path, making them simple and cost-effective for low-power applications. Series regulators control voltage by adjusting a transistor in series with the load, offering higher efficiency and better voltage regulation under varying load conditions. The choice between shunt and series regulators depends on power requirements, efficiency goals, and complexity constraints in electronic circuit design.
Working Principle of Shunt Regulators
Shunt regulators maintain voltage by diverting excess current away from the load, using a parallel component such as a transistor or zener diode to regulate voltage across the load. The regulator operates by shunting current through the parallel element, ensuring the output voltage remains constant despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. Understanding the working principle helps you choose the right regulator type for applications requiring simple voltage stabilization with low current efficiency.
Working Principle of Series Regulators
Series regulators maintain output voltage by varying the resistance of a pass transistor placed in series with the load, controlled by a feedback loop that senses output voltage changes. These regulators adjust the transistor's conduction to drop excess voltage, ensuring a stable output despite input voltage or load variations. The working principle hinges on continuous regulation through the transistor's operation in the active region to provide precise voltage control.
Key Differences Between Shunt and Series Regulators
Shunt regulators control voltage by diverting excess current parallel to the load, while series regulators adjust voltage by varying the resistance in series with the load, providing better efficiency and voltage regulation. Shunt regulators are simpler and cheaper but less efficient due to continuous current flow, whereas series regulators offer improved performance with less heat dissipation. The choice between them depends on application requirements such as load current, voltage stability, and power consumption.
Advantages of Shunt Regulators
Shunt regulators provide simpler design and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for low-power applications. They offer fast response to voltage changes by shunting excess current directly to ground, enhancing voltage stability. Their ability to operate with minimal components contributes to improved reliability and easier maintenance in electronic circuits.
Advantages of Series Regulators
Series regulators offer superior voltage regulation by adjusting resistance in the power path, maintaining a stable output despite input voltage variations or load changes. They provide higher efficiency compared to shunt regulators by minimizing power dissipation, especially in low dropout designs. These regulators also generate less heat and support higher output current capabilities, making them ideal for precision and high-power applications.
Applications of Shunt and Series Regulators
Shunt regulators are commonly used in low-power applications such as voltage reference circuits and precision voltage sources due to their simplicity and fast response to load changes. Series regulators are preferred in high-power and high-efficiency applications like power supplies for microprocessors and communication devices because they provide better voltage regulation and lower power dissipation. Understanding your application's power requirements and voltage stability needs will help determine whether a shunt or series regulator is more suitable.
Efficiency Comparison: Shunt vs Series Regulators
Shunt regulators typically exhibit lower efficiency compared to series regulators because they regulate voltage by shunting excess current away from the load, which results in continuous power dissipation regardless of load conditions. Series regulators improve efficiency by controlling the voltage drop across a pass transistor in series with the load, minimizing power loss especially under varying load currents. Your choice between the two should consider the balance between efficiency requirements and complexity, with series regulators favored in applications demanding higher energy savings.
Choosing the Right Regulator for Your Application
Shunt regulators offer simple voltage stabilization by diverting excess current, making them ideal for low-power applications requiring minimal component count and cost. Series regulators provide better efficiency and precise voltage control by regulating current flow in series with the load, suitable for medium to high-power applications needing stable output under varying loads. Evaluating factors like power dissipation, load current, and required output stability helps in selecting the appropriate regulator type for optimal performance.
Shunt regulator vs series regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com