BMS (Battery Management System) monitors and manages the health, safety, and performance of a battery pack, while ECU (Engine Control Unit) controls various engine functions to optimize vehicle performance and emissions. To understand how these systems impact your vehicle's efficiency and reliability, read on.
Table of Comparison
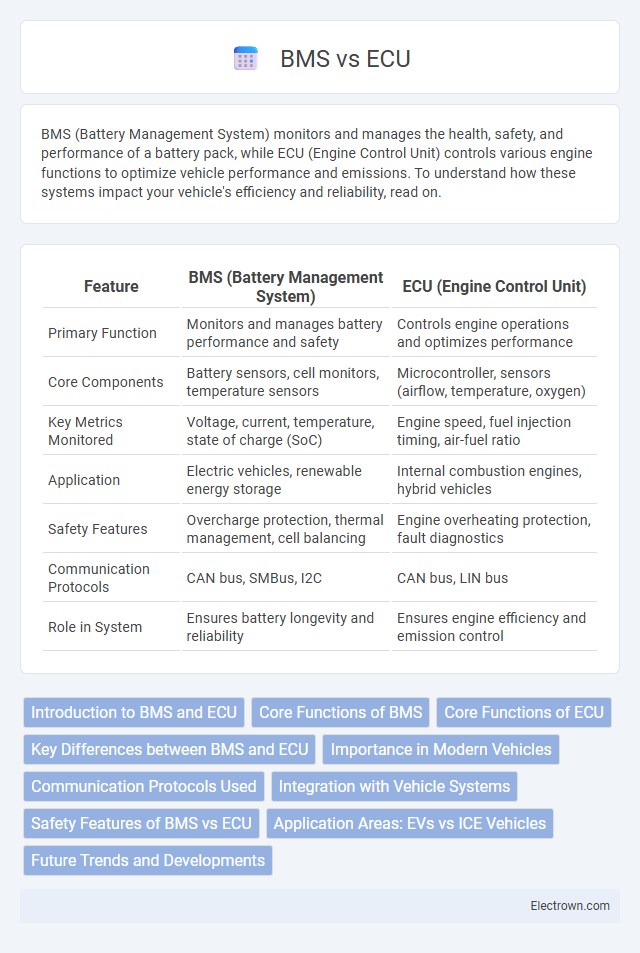
| Feature | BMS (Battery Management System) | ECU (Engine Control Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Monitors and manages battery performance and safety | Controls engine operations and optimizes performance |
| Core Components | Battery sensors, cell monitors, temperature sensors | Microcontroller, sensors (airflow, temperature, oxygen) |
| Key Metrics Monitored | Voltage, current, temperature, state of charge (SoC) | Engine speed, fuel injection timing, air-fuel ratio |
| Application | Electric vehicles, renewable energy storage | Internal combustion engines, hybrid vehicles |
| Safety Features | Overcharge protection, thermal management, cell balancing | Engine overheating protection, fault diagnostics |
| Communication Protocols | CAN bus, SMBus, I2C | CAN bus, LIN bus |
| Role in System | Ensures battery longevity and reliability | Ensures engine efficiency and emission control |
Introduction to BMS and ECU
A Battery Management System (BMS) is a critical electronic system designed to monitor and control rechargeable batteries, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and longevity by managing parameters like voltage, temperature, and state of charge. An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) serves as the central processor in vehicles, handling various functions such as engine control, transmission management, and diagnostics through sensor inputs and actuator outputs. Your understanding of these systems highlights their distinct roles: the BMS focuses on battery health and safety, while the ECU manages overall vehicle operation and efficiency.
Core Functions of BMS
The core functions of a Battery Management System (BMS) include monitoring cell voltages, managing state of charge (SOC), and ensuring battery safety through temperature regulation and fault detection. Unlike an Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which governs broader vehicle functions, the BMS specifically optimizes battery performance and longevity by balancing cell charge and preventing overcharging or deep discharge. Your battery's reliability and efficiency heavily depend on the precise operation of the BMS.
Core Functions of ECU
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) primarily manages engine performance through real-time monitoring and adjustment of fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture to optimize combustion efficiency and reduce emissions. It processes data from sensors such as oxygen, throttle position, and temperature, enabling precise control over engine parameters for improved power output and fuel economy. Unlike the Battery Management System (BMS), which focuses on battery health and safety, the ECU is integral to vehicle driveability and engine diagnostics.
Key Differences between BMS and ECU
The Battery Management System (BMS) primarily monitors and protects the battery pack by managing voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge to ensure safety and longevity. In contrast, the Engine Control Unit (ECU) controls engine functions such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions to optimize vehicle performance and efficiency. Understanding these key differences helps you effectively manage electric and hybrid vehicle systems.
Importance in Modern Vehicles
Battery Management Systems (BMS) and Engine Control Units (ECU) are critical components in modern vehicles, ensuring optimal performance and safety. The BMS monitors and manages battery health, charge levels, and temperature, which is vital for electric and hybrid vehicles, while the ECU controls engine functions, fuel injection, and emissions for combustion engines. Your vehicle relies on these systems to maintain efficiency, reduce emissions, and extend the lifespan of both the battery and engine components.
Communication Protocols Used
Battery Management Systems (BMS) and Engine Control Units (ECU) utilize distinct communication protocols tailored to their functions. BMS often employs protocols such as CAN (Controller Area Network), SMBus (System Management Bus), and I2C for precise battery monitoring and management data exchange. In contrast, ECU primarily relies on CAN, LIN (Local Interconnect Network), and FlexRay protocols to control engine operations and ensure real-time vehicle system communication.
Integration with Vehicle Systems
Battery Management Systems (BMS) are specifically designed to monitor and protect battery cells, providing critical data like state of charge and health, which can be integrated with the vehicle's overall energy management system. Electronic Control Units (ECU) serve as central controllers, managing various subsystems including engine, transmission, and safety features by processing inputs from sensors and executing commands. Your vehicle's seamless performance depends on the effective communication between the BMS and ECU, ensuring optimized energy distribution and system coordination.
Safety Features of BMS vs ECU
Battery Management Systems (BMS) prioritize safety by continuously monitoring cell voltages, temperatures, and state of charge to prevent overcharging, overheating, and short circuits, ensuring battery longevity and user protection. Electronic Control Units (ECU) manage overall vehicle functions but rely on inputs from the BMS for battery safety, primarily focusing on system-level diagnostics and fault management rather than direct cell protection. Your vehicle's safety heavily depends on the BMS's ability to safeguard the battery pack, while the ECU coordinates broader operational controls.
Application Areas: EVs vs ICE Vehicles
Battery Management Systems (BMS) are primarily deployed in electric vehicles (EVs) to monitor and optimize battery performance, ensuring safety, longevity, and efficient energy use. Engine Control Units (ECUs) are integral to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, managing engine functions such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control. While BMS focuses on battery health in EVs, ECUs handle complex engine operations in ICE vehicles, reflecting their distinct application areas.
Future Trends and Developments
BMS and ECU technologies are rapidly evolving with advancements in AI-driven predictive analytics and enhanced communication protocols like CAN FD and Ethernet, enabling more efficient battery management and vehicle control systems. Future developments include increased integration of BMS functions into ECUs for streamlined vehicle architecture and the adoption of solid-state batteries requiring specialized management algorithms. Your ability to leverage these innovations will be critical for optimizing performance, safety, and longevity in next-generation electric vehicles.
BMS vs ECU Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com