Safety relays are specifically designed to ensure the safe operation of machinery by monitoring critical functions and providing fail-safe responses, whereas general relays primarily serve as basic switching devices without specialized safety features. Understanding the key differences between safety relays and general relays will help you make informed decisions when selecting components for your safety-critical applications; continue reading to explore their distinct roles and benefits.
Table of Comparison
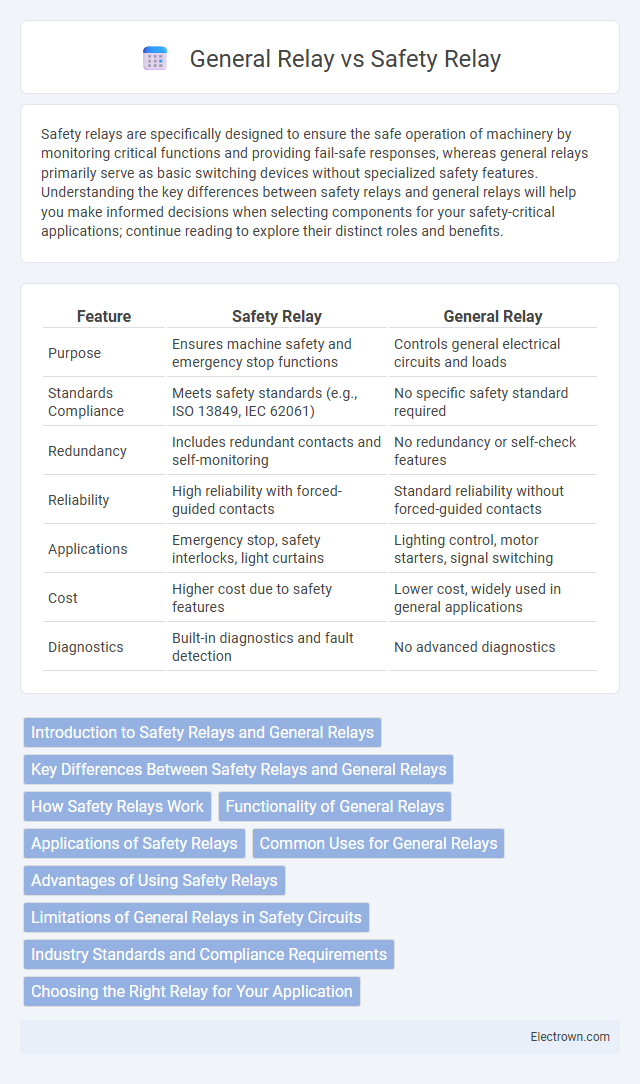
| Feature | Safety Relay | General Relay |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensures machine safety and emergency stop functions | Controls general electrical circuits and loads |
| Standards Compliance | Meets safety standards (e.g., ISO 13849, IEC 62061) | No specific safety standard required |
| Redundancy | Includes redundant contacts and self-monitoring | No redundancy or self-check features |
| Reliability | High reliability with forced-guided contacts | Standard reliability without forced-guided contacts |
| Applications | Emergency stop, safety interlocks, light curtains | Lighting control, motor starters, signal switching |
| Cost | Higher cost due to safety features | Lower cost, widely used in general applications |
| Diagnostics | Built-in diagnostics and fault detection | No advanced diagnostics |
Introduction to Safety Relays and General Relays
Safety relays are specialized devices designed to monitor safety functions and ensure machinery stops or operates safely in hazardous situations, complying with strict international safety standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061. General relays perform basic switching tasks to control electrical circuits but lack the redundant and diagnostic features critical for safety applications. The key distinction lies in safety relays' ability to provide fault detection, self-monitoring, and reliable emergency stop functions crucial for protecting personnel and equipment in industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Safety Relays and General Relays
Safety relays are designed to monitor safety functions and ensure machinery stops immediately during hazardous conditions, featuring redundant circuits and self-monitoring capabilities to comply with international safety standards like ISO 13849 and IEC 61508. General relays primarily switch electrical loads without specialized safety features, making them suitable for standard control tasks but not for critical safety applications. Your choice should prioritize safety relays when human protection and compliance with safety regulations are required.
How Safety Relays Work
Safety relays monitor critical safety functions by continuously checking input signals from emergency stops, safety gates, or light curtains and instantly de-energizing output contacts to shut down hazardous machinery in case of fault detection. They use redundant circuits and cross-monitoring techniques to ensure reliability and prevent dangerous failures, meeting strict safety standards such as ISO 13849 or IEC 62061. Unlike general relays, safety relays incorporate self-testing, fault detection, and forced-guided contacts to maintain fail-safe operation under all conditions.
Functionality of General Relays
General relays function as electrically operated switches that control circuits by opening or closing contacts based on input signals, enabling automation and control in various electrical devices. They provide basic switching operations without integrated safety features, making them suitable for non-critical control tasks. Your choice of relay depends on the need for safety monitoring and compliance, as safety relays incorporate additional functionalities like redundant contacts and self-monitoring to ensure safe operation.
Applications of Safety Relays
Safety relays are primarily used in industrial automation and machinery to ensure emergency stop functions, guard monitoring, and safety door control, providing reliable fault detection and preventing hazardous situations. Unlike general relays, safety relays comply with strict safety standards such as ISO 13849 or IEC 61508, making them essential for applications requiring high-risk mitigation and certified safety performance. Your equipment's protection and operator safety depend significantly on choosing the appropriate safety relay for critical control circuits.
Common Uses for General Relays
General relays are widely used in applications such as motor control, lighting systems, and automation circuits where switching of electrical loads is required without stringent safety standards. These relays provide reliable operation for controlling electrical devices, signal switching, and load isolation in industrial equipment, HVAC systems, and household appliances. Your choice of a general relay is ideal for non-critical tasks where basic electrical isolation and switching functions are sufficient.
Advantages of Using Safety Relays
Safety relays provide enhanced protection by monitoring safety functions such as emergency stops and light curtains, ensuring machine safety compliance with standards like ISO 13849-1. Unlike general relays, safety relays offer fault detection features, redundancy, and feedback loops to prevent hazardous failures and improve system reliability. Your machinery benefits from quicker response times and higher integrity in safety-critical applications when using safety relays over general-purpose relays.
Limitations of General Relays in Safety Circuits
General relays often lack the rigorous certification and redundancy required for safety circuits, making them unsuitable for critical safety applications. Their inability to provide fail-safe operation and diagnostics limits the detection of faults, increasing the risk of undetected failures. Safety relays are designed to overcome these limitations with features like forced guide contacts and monitored feedback loops, ensuring reliable and compliant safety circuit performance.
Industry Standards and Compliance Requirements
Safety relays comply with stringent industry standards such as ISO 13849 and IEC 62061, ensuring reliable performance in critical safety functions to protect operators and machinery. General relays follow less rigorous regulations, primarily focusing on basic operational requirements without guaranteeing fail-safe responses during hazardous conditions. Your safety system should incorporate safety relays to meet compliance requirements and achieve certified risk reduction levels in industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Relay for Your Application
Safety relays are designed to meet strict international safety standards and provide reliable fault detection, making them essential for applications requiring high-risk machine protection. General relays offer basic switching functions without built-in safety features and are suitable for non-critical operations where standard control suffices. Choosing the right relay depends on your application's safety requirements, ensuring compliance and optimal performance in industrial environments.
Safety relay vs General relay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com