Heated seats provide warmth through embedded heating elements, ideal for cold weather comfort, while ventilated seats circulate air to keep you cool and reduce sweating during hot conditions. Explore the rest of the article to discover which seat option best suits Your driving needs.
Table of Comparison
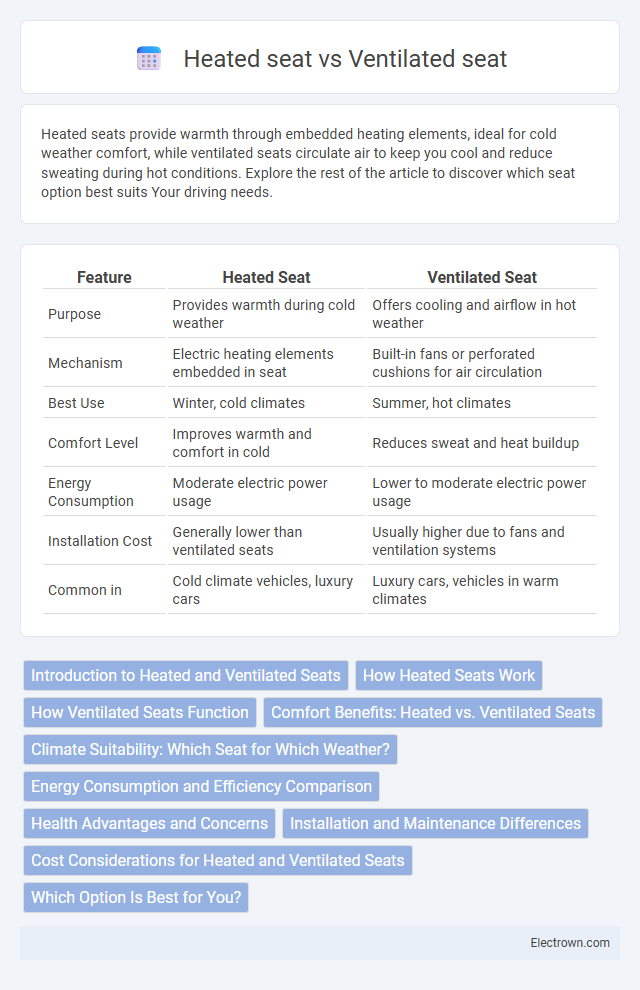
| Feature | Heated Seat | Ventilated Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides warmth during cold weather | Offers cooling and airflow in hot weather |
| Mechanism | Electric heating elements embedded in seat | Built-in fans or perforated cushions for air circulation |
| Best Use | Winter, cold climates | Summer, hot climates |
| Comfort Level | Improves warmth and comfort in cold | Reduces sweat and heat buildup |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate electric power usage | Lower to moderate electric power usage |
| Installation Cost | Generally lower than ventilated seats | Usually higher due to fans and ventilation systems |
| Common in | Cold climate vehicles, luxury cars | Luxury cars, vehicles in warm climates |
Introduction to Heated and Ventilated Seats
Heated seats use electric heating elements embedded in the seat to provide warmth, enhancing comfort during cold weather conditions. Ventilated seats incorporate built-in fans to circulate air, reducing heat and moisture for a cooler seating experience in hot climates. These advanced seat technologies improve overall vehicle comfort by addressing temperature regulation tailored to diverse weather needs.
How Heated Seats Work
Heated seats use electric heating elements embedded within the seat cushions to provide warmth by converting electrical energy into heat. The system is controlled by a thermostat that adjusts the temperature for your comfort, typically offering multiple heat settings. Unlike ventilated seats that circulate air to cool, heated seats rely solely on direct heat to keep you warm during cold conditions.
How Ventilated Seats Function
Ventilated seats function by circulating air through perforations in the seat material, helping to cool the occupant by dissipating heat and moisture. This airflow is often powered by built-in fans or blowers that draw in ambient air, enhancing comfort during hot weather or long drives. Your comfort improves significantly as ventilated seats reduce sweating and maintain a balanced temperature.
Comfort Benefits: Heated vs. Ventilated Seats
Heated seats provide targeted warmth that soothes muscles and enhances comfort during cold weather, improving overall driving experience. Ventilated seats circulate air to reduce heat and moisture, offering cooling relief and preventing discomfort in hot climates. Both technologies optimize seat comfort by addressing temperature extremes, allowing drivers and passengers to maintain an ideal climate regardless of external conditions.
Climate Suitability: Which Seat for Which Weather?
Heated seats are ideal for cold climates, providing warmth by electrically heating the seat surface to enhance comfort during winter or chilly conditions. Ventilated seats are better suited for hot and humid environments, using fans to circulate air through perforations in the seat to reduce sweating and keep occupants cool. Choosing between heated and ventilated seats depends on regional temperature patterns and personal comfort needs.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency Comparison
Heated seats typically consume less energy, using about 50 to 150 watts to provide warmth by warming the seat surface, making them more efficient in colder climates. Ventilated seats use fans and cooling elements, consuming roughly 100 to 250 watts, which can lead to higher energy usage but offer superior comfort in hot weather. Your choice between heated and ventilated seats can impact overall vehicle energy efficiency, especially in electric cars where managing power consumption is essential for maximizing range.
Health Advantages and Concerns
Heated seats improve blood circulation and relieve muscle tension, which can benefit individuals with arthritis or poor circulation during cold weather. Ventilated seats help regulate body temperature and reduce sweating, decreasing the risk of skin irritation and bacterial growth. When choosing between heated and ventilated seats, consider your climate and any pre-existing health conditions to ensure optimal comfort and well-being for your driving experience.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Heated seats typically require wiring connections to the vehicle's electrical system, involving installation of heating pads underneath the seat upholstery, making the process relatively straightforward for professionals. Ventilated seats demand additional components like fans and air ducts integrated into the seat structure, increasing installation complexity and potential points of failure. Maintenance for heated seats often involves checking electrical connections and heating elements, while ventilated seats require regular cleaning of air vents and fan mechanisms to ensure unobstructed airflow and avoid malfunctions.
Cost Considerations for Heated and Ventilated Seats
Heated seats generally incur lower installation and maintenance costs compared to ventilated seats, as they require simpler electrical components and heating elements. Ventilated seats involve more complex systems with fans and air circulation, increasing both initial price and potential repair expenses. Vehicle models with premium trim packages often bundle heated and ventilated seats, impacting overall cost but offering enhanced comfort features.
Which Option Is Best for You?
Heated seats provide warmth during cold weather by using electric heating elements embedded in the seat cushions, making them ideal for colder climates or those who often feel chilly. Ventilated seats use fans to circulate air through perforations in the seat, offering cooling benefits that enhance comfort in hot or humid environments. Your choice depends on your typical climate and personal comfort preferences, with heated seats best for cold conditions and ventilated seats for staying cool during warm weather.
Heated seat vs Ventilated seat Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com