Torque converters provide smooth, efficient power transfer by using fluid coupling, ideal for comfort and easy driving, while dual clutch transmissions offer faster gear shifts and improved performance through mechanical linkage, enhancing your driving experience. Explore the rest of the article to understand which transmission suits your needs best.
Table of Comparison
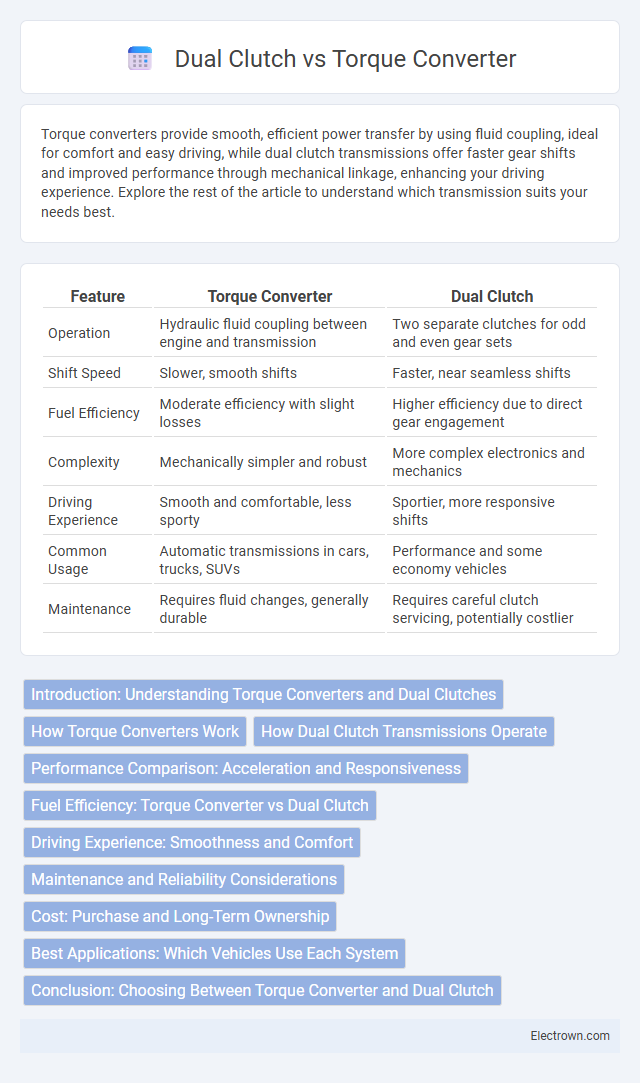
| Feature | Torque Converter | Dual Clutch |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Hydraulic fluid coupling between engine and transmission | Two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets |
| Shift Speed | Slower, smooth shifts | Faster, near seamless shifts |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate efficiency with slight losses | Higher efficiency due to direct gear engagement |
| Complexity | Mechanically simpler and robust | More complex electronics and mechanics |
| Driving Experience | Smooth and comfortable, less sporty | Sportier, more responsive shifts |
| Common Usage | Automatic transmissions in cars, trucks, SUVs | Performance and some economy vehicles |
| Maintenance | Requires fluid changes, generally durable | Requires careful clutch servicing, potentially costlier |
Introduction: Understanding Torque Converters and Dual Clutches
Torque converters use a fluid coupling to transfer engine power smoothly to the transmission, providing seamless torque multiplication ideal for automatic transmissions. Dual clutch systems employ two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling faster and more efficient gear shifts found in performance and sport vehicles. Torque converters excel in comfort and smoothness, while dual clutch transmissions prioritize speed and fuel efficiency.
How Torque Converters Work
Torque converters use a fluid coupling system between the engine and transmission, transferring power through a turbine, impeller, and stator to multiply torque and absorb engine vibrations. This hydraulic mechanism allows smooth acceleration and seamless gear shifts by varying the fluid flow inside the torque converter housing. Compared to dual clutch systems that use mechanically engaged clutches, torque converters provide enhanced drivability and shock-free power delivery, especially in stop-and-go traffic.
How Dual Clutch Transmissions Operate
Dual clutch transmissions (DCT) operate by using two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, enabling seamless gear changes without interrupting power delivery. You experience faster acceleration and improved fuel efficiency as the system pre-selects the next gear while maintaining torque flow through the engaged clutch. This design enhances driving dynamics by reducing shift time and eliminating the torque converter's slip commonly found in traditional automatic transmissions.
Performance Comparison: Acceleration and Responsiveness
Torque converters offer smooth acceleration by using hydraulic fluid to transfer engine power, resulting in slightly slower response times compared to dual-clutch systems. Dual-clutch transmissions deliver faster gear shifts and improved responsiveness through pre-engaged gears, enhancing acceleration performance especially in sporty driving scenarios. Vehicles equipped with dual-clutch systems typically achieve quicker 0-60 mph times due to reduced power interruption during gear changes.
Fuel Efficiency: Torque Converter vs Dual Clutch
Dual clutch transmissions outperform torque converters in fuel efficiency by minimizing power loss through direct gear engagement, resulting in quicker shifts and reduced fuel consumption. Torque converters use fluid coupling that creates more energy slip, decreasing overall efficiency during acceleration. Your vehicle's fuel economy significantly benefits from a dual clutch system, especially in stop-and-go or performance driving scenarios.
Driving Experience: Smoothness and Comfort
Torque converters provide a smooth driving experience by using hydraulic fluid to transfer power, which effectively cushions gear shifts and reduces vibration. Dual clutch systems deliver quicker and more precise gear changes, offering sportier performance but with slightly less smoothness compared to torque converters. Drivers seeking maximum comfort typically prefer torque converters for their seamless shifting and reduced harshness during acceleration.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
Torque converters require less frequent maintenance due to their simpler hydraulic design but may experience fluid overheating and wear over time, necessitating regular transmission fluid changes every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. Dual clutch transmissions demand more attentive upkeep, including periodic software updates and clutch pack servicing, as their complex mechanical components and electronic controls are more prone to wear and potential failure. Reliability for torque converters typically excels in heavy-duty applications, while dual clutch systems offer faster shifts but can suffer from early clutch degradation under aggressive driving or poor maintenance.
Cost: Purchase and Long-Term Ownership
Torque converters generally have a lower initial purchase cost compared to dual-clutch transmissions, making vehicles equipped with them more affordable upfront. Long-term ownership expenses for torque converters can increase due to potential fluid changes and wear on the hydraulic components, while dual-clutch systems may incur higher repair costs given their complex design and clutch replacements. Insurance premiums tend to be similar, but maintenance budgets for dual-clutch transmissions often exceed those for torque converter systems, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.
Best Applications: Which Vehicles Use Each System
Torque converters are commonly used in traditional automatic transmissions found in SUVs, trucks, and luxury cars, providing smooth power delivery and better performance in heavy-duty or off-road conditions. Dual-clutch transmissions (DCT) are favored in sports cars, performance vehicles, and some compact cars for their rapid gear shifts and enhanced fuel efficiency. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize comfort and durability with a torque converter or sportier, faster gear changes offered by a dual-clutch system.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Torque Converter and Dual Clutch
Choosing between a torque converter and a dual clutch transmission depends on driving preferences and performance needs. Torque converters offer smoother shifts and better durability for everyday driving, while dual clutch systems provide faster, more efficient gear changes suited for sporty or performance-oriented vehicles. Consider factors like fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and driving style to determine the optimal transmission choice.
Torque converter vs Dual clutch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com