OBD1 and OBD2 are diagnostic systems used to monitor vehicle emissions and engine performance, with OBD2 providing more comprehensive data and standardized trouble codes across all manufacturers. Understanding the differences between these two systems can help you effectively diagnose issues and maintain your vehicle; read on to learn more about their features and applications.
Table of Comparison
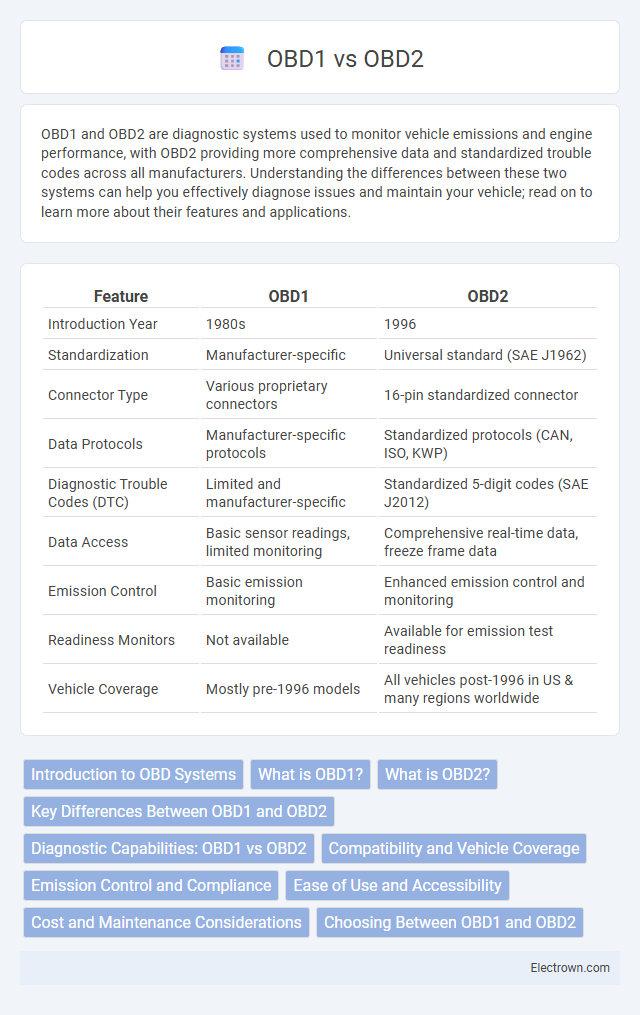
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction Year | 1980s | 1996 |
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Universal standard (SAE J1962) |
| Connector Type | Various proprietary connectors | 16-pin standardized connector |
| Data Protocols | Manufacturer-specific protocols | Standardized protocols (CAN, ISO, KWP) |
| Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) | Limited and manufacturer-specific | Standardized 5-digit codes (SAE J2012) |
| Data Access | Basic sensor readings, limited monitoring | Comprehensive real-time data, freeze frame data |
| Emission Control | Basic emission monitoring | Enhanced emission control and monitoring |
| Readiness Monitors | Not available | Available for emission test readiness |
| Vehicle Coverage | Mostly pre-1996 models | All vehicles post-1996 in US & many regions worldwide |
Introduction to OBD Systems
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) systems monitor vehicle performance and emissions by providing access to the engine control unit (ECU) data. OBD1, introduced in the early 1980s, offered basic diagnostics with limited standardized protocols and manufacturer-specific connectors. OBD2, mandated in 1996 for all vehicles in the United States, features a standardized 16-pin connector, advanced diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and enhanced real-time monitoring capabilities for improved emissions control and vehicle maintenance.
What is OBD1?
OBD1, or On-Board Diagnostics 1, is an early vehicle diagnostic system introduced in the 1980s primarily by American automakers to monitor engine performance and emissions. It uses proprietary protocols and connectors unique to each manufacturer, limiting compatibility and standardization compared to OBD2. This system provides basic fault codes through a flashing check engine light or a digital readout, requiring specialized tools for in-depth diagnostics.
What is OBD2?
OBD2, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system implemented in vehicles since 1996 to monitor engine performance and emissions. It provides comprehensive real-time data and diagnostic trouble codes via a universal 16-pin port, enabling more accurate vehicle diagnostics and repair. You can quickly access OBD2 data using a compatible scanner to identify issues and ensure compliance with emission standards.
Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
OBD1 and OBD2 differ primarily in their diagnostic capabilities and standardization, with OBD1 being an early, manufacturer-specific system and OBD2 offering a universal protocol supported by all vehicles sold in the U.S. since 1996. OBD2 features enhanced real-time data and comprehensive trouble codes, enabling more accurate diagnostics and easier emissions testing compared to the limited data of OBD1. Your ability to efficiently monitor vehicle health and troubleshoot issues improves significantly by using OBD2 scanners over the older OBD1 systems.
Diagnostic Capabilities: OBD1 vs OBD2
OBD1 diagnostic systems offered limited data with manufacturer-specific codes primarily focused on emission-related faults, lacking standardized protocols and comprehensive real-time sensor monitoring. OBD2 significantly expanded diagnostic capabilities by providing standardized trouble codes, extensive live data streams, and enhanced emission control monitoring across all vehicle makes and models post-1996. This evolution enables more precise fault detection, deeper engine performance insights, and streamlined vehicle maintenance processes.
Compatibility and Vehicle Coverage
OBD1 systems, introduced in the early 1980s, offer limited compatibility and are primarily found in vehicles manufactured before 1996, often specific to certain manufacturers such as General Motors or Ford. OBD2, standardized in 1996, provides broad compatibility across all makes and models sold in the United States and many other countries, supporting a universal diagnostic connector and standardized trouble codes. This expanded vehicle coverage allows OBD2 to efficiently interface with a wide range of domestic and imported vehicles, facilitating more comprehensive diagnostics and emissions monitoring.
Emission Control and Compliance
OBD1 systems provided basic emission control by monitoring essential engine functions and triggering limited diagnostic trouble codes; however, their data access and standardization were minimal, leading to inconsistent compliance across vehicles. OBD2 introduced enhanced emission control capabilities with standardized communication protocols, comprehensive sensor networks, and real-time monitoring of critical components like catalytic converters and oxygen sensors, ensuring stricter adherence to EPA regulations. The transition from OBD1 to OBD2 significantly improved vehicle emission diagnostics, enabling more effective detection and reduction of pollutants to meet evolving environmental standards.
Ease of Use and Accessibility
OBD2 offers superior ease of use and accessibility compared to OBD1 due to its standardized connector and universal communication protocols, allowing any OBD2-compatible scanner to read data from most vehicles manufactured after 1996. The OBD1 system varies by manufacturer, often requiring specific adapters or proprietary tools, which complicates diagnostics for users without advanced technical knowledge. Furthermore, OBD2 supports real-time data streaming and standardized trouble codes, streamlining the troubleshooting process for both professional mechanics and car owners.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations
OBD1 systems generally have lower initial costs due to their simpler technology but often require more frequent manual diagnostics and maintenance, which can increase long-term expenses. OBD2 systems, while initially more expensive, provide advanced self-diagnostic capabilities that enable quicker and more accurate detection of issues, reducing labor costs and maintenance time. Choosing between OBD1 and OBD2 impacts your overall vehicle maintenance budget depending on the complexity and efficiency of onboard diagnostic features.
Choosing Between OBD1 and OBD2
Choosing between OBD1 and OBD2 depends on your vehicle's model year and diagnostic needs. OBD1 systems, found in cars before 1996, offer basic diagnostics with manufacturer-specific protocols, while OBD2, mandatory for vehicles after 1996, provides standardized, comprehensive data access and enhanced compatibility with modern diagnostic tools. For accurate trouble code reading, emissions testing, and ease of use, your best choice is OBD2 if your vehicle supports it.
OBD1 vs OBD2 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com