Stepper motors offer precise position control and simplicity, making them ideal for micro-pumps requiring accurate, repeatable movements without complex feedback systems. Servo motors deliver higher torque and dynamic response through closed-loop control, benefiting micro-pumps that demand variable speed and load adaptability; explore the article to determine which motor suits your micro-pump application best.
Table of Comparison
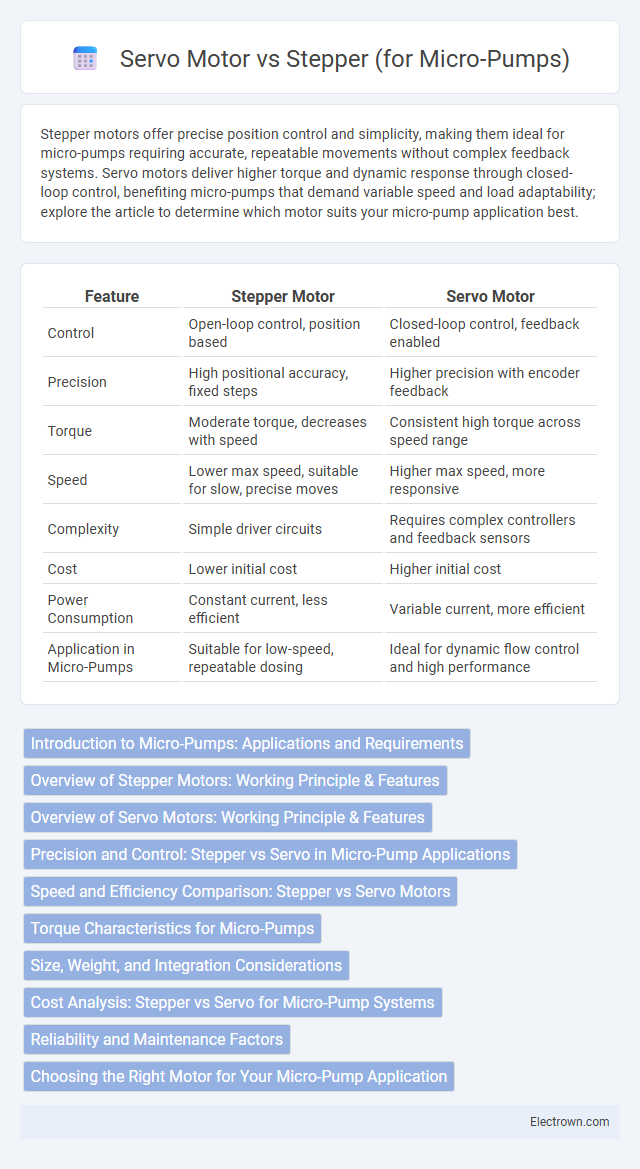
| Feature | Stepper Motor | Servo Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Open-loop control, position based | Closed-loop control, feedback enabled |
| Precision | High positional accuracy, fixed steps | Higher precision with encoder feedback |
| Torque | Moderate torque, decreases with speed | Consistent high torque across speed range |
| Speed | Lower max speed, suitable for slow, precise moves | Higher max speed, more responsive |
| Complexity | Simple driver circuits | Requires complex controllers and feedback sensors |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Power Consumption | Constant current, less efficient | Variable current, more efficient |
| Application in Micro-Pumps | Suitable for low-speed, repeatable dosing | Ideal for dynamic flow control and high performance |
Introduction to Micro-Pumps: Applications and Requirements
Micro-pumps are crucial in medical devices, chemical analysis, and microfluidic systems where precise fluid control and compact size are essential. Stepper motors enable accurate positioning with strong holding torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent flow rates and stable micro-pump operation. Servo motors offer high efficiency, faster response times, and closed-loop control, ideal for dynamic micro-pump applications demanding variable flow rates and precise feedback.
Overview of Stepper Motors: Working Principle & Features
Stepper motors operate by dividing a full rotation into equal steps, controlled via precise electrical pulses that enable accurate positioning without feedback sensors. These motors excel in applications like micro-pumps where consistent, repeatable motion and torque at low speeds are crucial. Your choice of a stepper motor ensures reliable control in micro-pump mechanisms, offering simplicity, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness compared to servo alternatives.
Overview of Servo Motors: Working Principle & Features
Servo motors operate using a closed-loop control system that continuously monitors position, speed, and torque through feedback sensors, ensuring precise movement ideal for micro-pumps requiring accurate flow control. Their working principle involves receiving control signals, which adjust the rotor's position by modulating the current in the motor windings, enabling smooth and high-torque operation at varying speeds. Key features of servo motors include high efficiency, rapid response, precise positioning, and the ability to maintain torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications demanding consistent and reliable micro-pump performance.
Precision and Control: Stepper vs Servo in Micro-Pump Applications
Stepper motors provide precise position control by moving in fixed increments, making them ideal for micro-pumps requiring consistent, repeatable flow rates. Servo motors offer superior dynamic response and torque control through closed-loop feedback, enhancing accuracy in applications where variable pressure and flow adjustments are critical. Your choice depends on whether micro-pump precision relies primarily on fixed-step accuracy or adaptive, real-time control.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison: Stepper vs Servo Motors
Stepper motors offer precise position control with consistent speed at low to moderate ranges, making them suitable for micro-pump applications requiring accurate dosing. Servo motors deliver higher speed capabilities and improved efficiency due to closed-loop feedback systems, which optimize power consumption and torque output in real-time. While steppers are simpler and cost-effective for fixed-speed tasks, servos excel in dynamic environments demanding rapid speed changes and higher overall efficiency.
Torque Characteristics for Micro-Pumps
Stepper motors provide high holding torque at low speeds, making them suitable for precise micro-pump flow control where consistent incremental positioning is essential. Servo motors deliver higher continuous torque over a wider speed range, enabling efficient operation under varying load conditions and faster response times in micro-pump applications. Torque stability and accuracy in micro-pumps are critical, with stepper motors favoring precise, stepwise control and servo motors excelling in dynamic, high-torque environments.
Size, Weight, and Integration Considerations
Stepper motors for micro-pumps typically feature a compact size and moderate weight, making them suitable for applications where space constraints are critical. Servo motors, while generally larger and heavier due to integrated feedback systems, offer precise control and smooth operation, which may justify their size for high-performance micro-pump integration. Integration considerations include the complexity of control electronics and power requirements, with stepper motors favoring simpler drives and servo motors requiring more sophisticated controllers for optimal performance.
Cost Analysis: Stepper vs Servo for Micro-Pump Systems
Stepper motors generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to servo motors, making them a budget-friendly option for micro-pump systems with moderate precision requirements. Servo motors typically incur higher initial expenses due to advanced feedback mechanisms and superior control accuracy, but they can reduce long-term costs by enhancing efficiency and minimizing maintenance needs. Your choice between stepper and servo motors should weigh immediate budget constraints against the potential for improved performance and durability in micro-pump applications.
Reliability and Maintenance Factors
Stepper motors offer high reliability for micro-pumps due to their simple construction and fewer moving parts, reducing the frequency of maintenance. Servo motors, while more complex with feedback systems, provide precise control and self-correcting capabilities that can reduce wear over time and extend operational lifespan. Maintenance of stepper motors primarily involves checking for mechanical wear, whereas servo systems require regular calibration and possible sensor diagnostics to ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Motor for Your Micro-Pump Application
Choosing the right motor for your micro-pump application hinges on precision control and torque requirements; stepper motors offer excellent positional accuracy and cost-effectiveness for low to medium torque needs, while servo motors deliver higher efficiency, smoother motion, and superior torque for demanding applications. Stepper motors operate well in open-loop systems, making them simpler and less expensive, whereas servo motors require feedback systems, providing precise speed and position control essential for micro-pumps handling variable flow rates. Your decision should consider factors such as required responsiveness, power consumption, and system complexity to optimize micro-pump performance and reliability.
Stepper vs Servo Motor (for micro-pumps) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com