Endocavity ultrasound probes offer superior imaging for internal organs and structures by providing close proximity and higher resolution compared to surface probes, which are better suited for general external examinations. Explore the article to understand how choosing the right ultrasound probe can enhance your diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
Table of Comparison
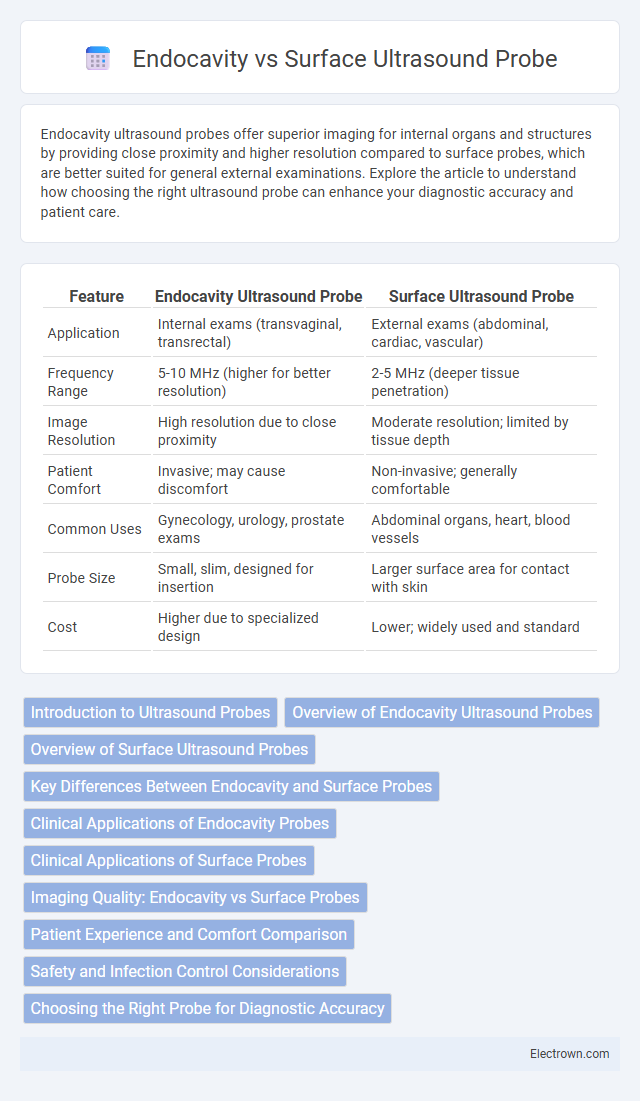
| Feature | Endocavity Ultrasound Probe | Surface Ultrasound Probe |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Internal exams (transvaginal, transrectal) | External exams (abdominal, cardiac, vascular) |
| Frequency Range | 5-10 MHz (higher for better resolution) | 2-5 MHz (deeper tissue penetration) |
| Image Resolution | High resolution due to close proximity | Moderate resolution; limited by tissue depth |
| Patient Comfort | Invasive; may cause discomfort | Non-invasive; generally comfortable |
| Common Uses | Gynecology, urology, prostate exams | Abdominal organs, heart, blood vessels |
| Probe Size | Small, slim, designed for insertion | Larger surface area for contact with skin |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized design | Lower; widely used and standard |
Introduction to Ultrasound Probes
Ultrasound probes are specialized devices that emit sound waves to create images of internal body structures, with two main types being endocavity and surface probes. Endocavity ultrasound probes, designed for internal examinations such as transvaginal or transrectal imaging, provide high-resolution images of organs close to the probe. Surface ultrasound probes, used externally on the skin, are ideal for general diagnostic imaging like abdominal or vascular assessments, helping you obtain clear, non-invasive visualization of tissues and blood flow.
Overview of Endocavity Ultrasound Probes
Endocavity ultrasound probes provide high-resolution imaging by being inserted directly into body cavities such as the vagina, rectum, or esophagus, enabling close proximity to target organs like the uterus, prostate, or heart. These probes use high-frequency sound waves to deliver detailed images essential for gynecological, urological, and cardiac diagnostics. Their specialized design allows for improved visualization of internal structures compared to surface ultrasound probes, which operate externally on the skin.
Overview of Surface Ultrasound Probes
Surface ultrasound probes, also known as external or transcutaneous probes, are designed for imaging superficial structures by emitting high-frequency sound waves through the skin. These probes provide detailed visualization of muscles, tendons, blood vessels, and organs near the body surface, making them ideal for examinations like abdominal scans, vascular assessments, and musculoskeletal imaging. Their ergonomic design and range of frequencies enable versatile use across various clinical applications, ensuring effective diagnostic outcomes in non-invasive procedures.
Key Differences Between Endocavity and Surface Probes
Endocavity ultrasound probes are designed for internal examinations, providing high-resolution images of organs such as the prostate, uterus, and ovaries by being inserted into body cavities, while surface probes are used externally for imaging superficial structures like abdominal organs and blood vessels. Endocavity probes offer closer proximity to target tissues, resulting in better image clarity and detail, whereas surface probes cover larger areas but with less resolution due to the distance from the tissue. Understanding these key differences helps you select the appropriate probe to optimize diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort.
Clinical Applications of Endocavity Probes
Endocavity ultrasound probes are essential for detailed imaging of internal pelvic structures, offering superior visualization for gynecological assessments, early pregnancy evaluations, and prostate examinations. Their design allows close proximity to organs such as the uterus, ovaries, and bladder, enhancing diagnostic accuracy in conditions like ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancies, and prostate enlargement. Your clinical practice can benefit from their ability to provide high-resolution images that surface probes may not capture effectively in these specialized applications.
Clinical Applications of Surface Probes
Surface ultrasound probes are primarily used for imaging superficial structures such as muscles, tendons, and blood vessels, offering high-resolution detail for musculoskeletal assessments and vascular studies. They excel in evaluating skin lesions, thyroid nodules, and breast tissue, making them indispensable in dermatology and oncology clinics. Your choice of a surface probe enables accurate monitoring of soft tissue abnormalities and guides interventions like biopsies and injections with precision.
Imaging Quality: Endocavity vs Surface Probes
Endocavity ultrasound probes provide superior imaging quality for internal organs by offering higher resolution and closer proximity to the target tissue, resulting in more detailed visualization of structures such as the uterus, ovaries, and prostate. Surface ultrasound probes, while less detailed for internal imaging, are ideal for evaluating superficial tissues and organs like the thyroid, breast, and musculoskeletal system due to their broader field of view and ease of access. Your choice between endocavity and surface probes should consider the specific anatomical area and diagnostic requirements to ensure optimal image clarity.
Patient Experience and Comfort Comparison
Endocavity ultrasound probes often provide higher-resolution images of internal organs but may cause discomfort or anxiety due to their invasive nature, especially during transvaginal or transrectal examinations. Surface ultrasound probes are non-invasive, offering a more comfortable patient experience with minimal discomfort, making them preferable for initial assessments or routine screenings. Patient preference typically favors surface probes when possible, though endocavity probes are essential for detailed diagnostics despite potential discomfort.
Safety and Infection Control Considerations
Endocavity ultrasound probes present higher infection control challenges due to their direct contact with mucous membranes, necessitating strict adherence to high-level disinfection protocols and the use of protective probe covers to prevent cross-contamination. Surface ultrasound probes, typically used on intact skin, require standard cleaning with low-level disinfectants, posing a lower risk of transmitting infections. Proper handling, thorough cleaning, and routine maintenance of both probe types are critical to ensure patient safety and minimize the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
Choosing the Right Probe for Diagnostic Accuracy
Endocavity ultrasound probes provide superior imaging of internal organs like the prostate or ovaries due to their closer proximity, enhancing diagnostic accuracy for conditions such as pelvic abnormalities. Surface ultrasound probes excel in evaluating superficial structures like the thyroid or breast, offering high-resolution images of tissues near the skin's surface. Your choice of probe directly impacts diagnostic precision, making it essential to select based on the target anatomy and clinical indications.
Endocavity vs Surface Ultrasound Probe Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com