Suction electrodes provide a secure and temporary attachment to the skin using negative pressure, making them ideal for short-term monitoring, while chest electrodes are designed for longer-term, stable placement during ECG or cardiac monitoring. Explore the differences in functionality and best use cases to determine which electrode suits your specific medical needs.
Table of Comparison
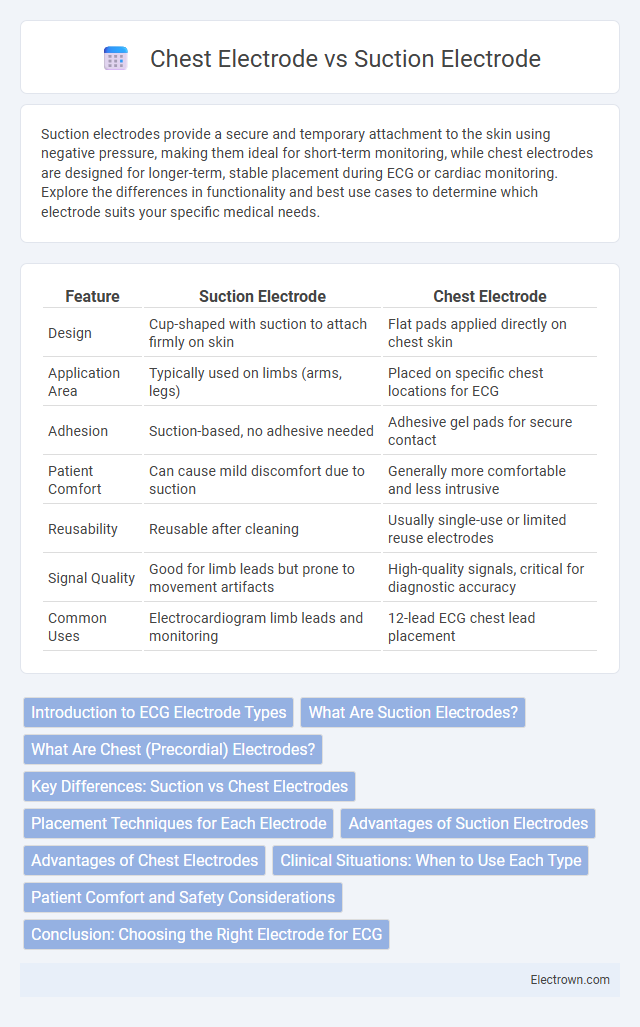
| Feature | Suction Electrode | Chest Electrode |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Cup-shaped with suction to attach firmly on skin | Flat pads applied directly on chest skin |
| Application Area | Typically used on limbs (arms, legs) | Placed on specific chest locations for ECG |
| Adhesion | Suction-based, no adhesive needed | Adhesive gel pads for secure contact |
| Patient Comfort | Can cause mild discomfort due to suction | Generally more comfortable and less intrusive |
| Reusability | Reusable after cleaning | Usually single-use or limited reuse electrodes |
| Signal Quality | Good for limb leads but prone to movement artifacts | High-quality signals, critical for diagnostic accuracy |
| Common Uses | Electrocardiogram limb leads and monitoring | 12-lead ECG chest lead placement |
Introduction to ECG Electrode Types
Suction electrodes and chest electrodes are two common types used in electrocardiography (ECG) to monitor heart activity. Suction electrodes adhere to the skin using vacuum pressure, typically placed on the limbs, while chest electrodes are adhesive pads positioned on the chest to capture precise cardiac electrical signals. Your choice between these electrodes depends on the required signal quality and patient comfort during ECG testing.
What Are Suction Electrodes?
Suction electrodes are specialized sensors designed to adhere securely to the skin using gentle vacuum pressure, ensuring stable electrical contact during medical monitoring or diagnostic procedures. They provide consistent signal quality by minimizing movement artifacts and are commonly used in electrocardiography (ECG) and other bioelectrical measurements. Understanding how suction electrodes function can help optimize your choice of electrode type for accurate and reliable patient monitoring.
What Are Chest (Precordial) Electrodes?
Chest (precordial) electrodes are specialized ECG electrodes placed on specific locations on the chest to detect the heart's electrical activity from multiple angles, providing detailed information about the anterior and lateral walls of the heart. Unlike suction electrodes, which create a vacuum seal to adhere to the skin, chest electrodes typically use adhesive pads for stable contact and accurate signal acquisition. Accurate placement of precordial electrodes is crucial for diagnosing conditions like myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, and other cardiac abnormalities.
Key Differences: Suction vs Chest Electrodes
Suction electrodes adhere to the skin using negative pressure, providing stable contact especially on irregular or moist surfaces, while chest electrodes use adhesive pads designed for direct application on the chest area to ensure strong, consistent electrical signal transmission. Suction electrodes are often preferred in clinical settings requiring rapid placement and removal, whereas chest electrodes are commonly utilized for prolonged cardiac monitoring during ECG procedures. Your choice depends on the specific medical context, skin condition, and duration of monitoring needed for accurate and reliable readings.
Placement Techniques for Each Electrode
Suction electrodes attach securely to the skin using negative pressure, allowing for easy placement on curved or irregular surfaces without the need for adhesive pads, making them ideal for short-term monitoring. Chest electrodes require precise placement on specific anatomical landmarks, such as the intercostal spaces on the sternum or lateral chest wall, to ensure accurate cardiac signal acquisition. Proper placement technique for chest electrodes involves skin preparation to reduce impedance and correct alignment to optimize electrocardiogram (ECG) signal quality.
Advantages of Suction Electrodes
Suction electrodes provide superior skin contact and stability, reducing motion artifacts for more accurate cardiac monitoring. They are easy to apply and reposition without causing patient discomfort, making them ideal for continuous or long-term ECG recording. You benefit from enhanced signal quality and reliable readings, especially during dynamic or ambulatory monitoring conditions.
Advantages of Chest Electrodes
Chest electrodes provide superior stability and contact quality compared to suction electrodes, ensuring more accurate and consistent ECG readings. Their adhesive design reduces motion artifacts and enhances patient comfort during extended monitoring sessions. Chest electrodes are also less prone to detachment, making them ideal for continuous cardiac monitoring in clinical and home settings.
Clinical Situations: When to Use Each Type
Suction electrodes are ideal for short-term monitoring in emergency or operating room settings due to their quick application and firm attachment on wet or oily skin. Chest electrodes provide more stable, long-term recordings in ambulatory or intensive care environments where continuous cardiac monitoring is essential. Your choice depends on the need for rapid placement versus prolonged signal accuracy in clinical cardiac monitoring.
Patient Comfort and Safety Considerations
Suction electrodes offer enhanced patient comfort by securely attaching without adhesives, reducing skin irritation and making them ideal for sensitive or prolonged monitoring. Chest electrodes, typically using adhesive pads, may cause discomfort or skin damage, especially in patients with fragile skin or allergies. Your choice between suction and chest electrodes should prioritize patient safety by considering skin sensitivity, duration of use, and the need for stable signal acquisition during cardiac monitoring.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Electrode for ECG
Suction electrodes provide stable adhesion for short-term ECG monitoring, especially on hairy or uneven skin, while chest electrodes offer superior signal quality and durability for long-term or stress-test applications. Selecting the appropriate electrode depends on the patient's skin type, duration of monitoring, and required signal fidelity. Optimal ECG results are achieved by matching electrode type to clinical need, balancing adhesion reliability with signal clarity.
Suction Electrode vs Chest Electrode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com