Non-contact thermometers measure temperature from a distance using infrared technology, offering quick and hygienic readings without physical contact. Contact thermometers require direct skin or object contact for accurate temperature measurement, making them suitable for continuous monitoring; explore the differences and choose the best option for your needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
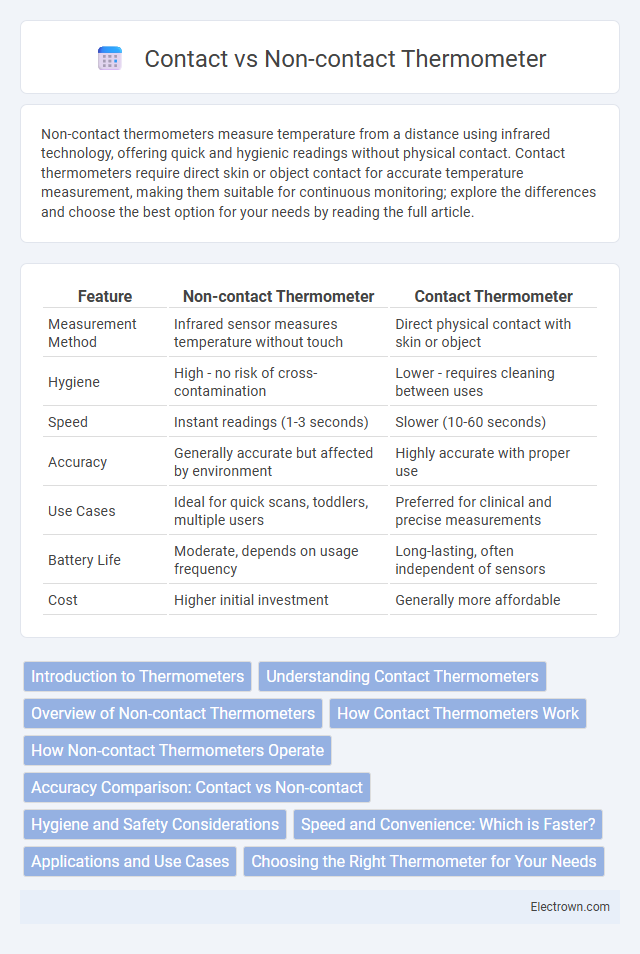
| Feature | Non-contact Thermometer | Contact Thermometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Method | Infrared sensor measures temperature without touch | Direct physical contact with skin or object |
| Hygiene | High - no risk of cross-contamination | Lower - requires cleaning between uses |
| Speed | Instant readings (1-3 seconds) | Slower (10-60 seconds) |
| Accuracy | Generally accurate but affected by environment | Highly accurate with proper use |
| Use Cases | Ideal for quick scans, toddlers, multiple users | Preferred for clinical and precise measurements |
| Battery Life | Moderate, depends on usage frequency | Long-lasting, often independent of sensors |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally more affordable |
Introduction to Thermometers
Thermometers measure temperature by detecting heat or infrared radiation emitted from objects or skin. Contact thermometers require physical touch, offering accurate internal body temperature readings through oral, rectal, or axillary methods. Non-contact thermometers use infrared sensors to quickly gauge surface temperature without touching, ideal for hygienic and rapid assessments of your body or environment.
Understanding Contact Thermometers
Contact thermometers measure temperature through direct physical touch with the object's surface, ensuring precise and reliable readings. Common types include thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and digital probe thermometers, which are widely used in medical, industrial, and culinary applications. Their accuracy depends on proper sensor placement and thermal equilibrium between the probe and the measured surface.
Overview of Non-contact Thermometers
Non-contact thermometers use infrared technology to measure temperature from a distance, providing a quick and hygienic way to check body heat without physical contact. These devices are especially useful in medical settings and during infectious disease outbreaks, as they reduce the risk of cross-contamination. Your choice of a non-contact thermometer ensures fast readings while maintaining safety and convenience.
How Contact Thermometers Work
Contact thermometers measure temperature through direct physical contact with an object or surface, using sensors such as thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), or thermistors to detect heat transfer. These devices rely on the principle that the sensor's electrical properties change in response to temperature variations, providing precise and accurate readings. Your choice of a contact thermometer is ideal for applications requiring exact temperature measurements on solid surfaces or in liquids.
How Non-contact Thermometers Operate
Non-contact thermometers operate by detecting infrared radiation emitted from the surface of an object or body without requiring physical contact. These devices use a sensor to capture the heat energy and convert it into an electronic signal, providing a quick and hygienic temperature reading. Your choice of a non-contact thermometer ensures safe, real-time measurement, especially useful in medical and industrial settings.
Accuracy Comparison: Contact vs Non-contact
Contact thermometers generally provide more accurate and consistent temperature readings by directly measuring the object's surface temperature through physical contact. Non-contact thermometers rely on infrared sensors to detect thermal radiation, offering quick readings but sometimes affected by environmental factors such as distance, surface emissivity, or ambient temperature. Your choice between these two types should balance the need for precision with convenience and hygiene considerations in various settings.
Hygiene and Safety Considerations
Non-contact thermometers reduce the risk of cross-contamination by measuring temperature from a distance without skin contact, making them ideal for maintaining hygiene in clinical and public settings. Contact thermometers require direct skin contact, necessitating thorough cleaning and sterilization between uses to prevent the spread of infections. Your choice should prioritize safety protocols, especially in environments where multiple users are involved or during infectious outbreaks.
Speed and Convenience: Which is Faster?
Non-contact thermometers provide rapid temperature readings within seconds without physical contact, making them ideal for quick screening in busy environments. Contact thermometers, such as digital or mercury types, require placement on the skin or under the tongue, resulting in longer measurement times of up to several minutes. The non-contact design enhances convenience and hygiene, especially in high-traffic or clinical settings where speed and minimizing cross-contamination are crucial.
Applications and Use Cases
Non-contact thermometers are ideal for measuring body temperature in healthcare settings, especially for screening infectious diseases due to their quick and hygienic operation. Contact thermometers excel in clinical environments requiring precise, continuous measurements such as oral, rectal, or underarm temperature monitoring. Industrial applications favor non-contact infrared thermometers for surface temperature checks on machinery without interrupting processes, while contact probes are preferred for food safety inspections and laboratory experiments needing direct temperature readings.
Choosing the Right Thermometer for Your Needs
Selecting the right thermometer depends on your specific needs and usage context. Non-contact thermometers offer quick, hygienic temperature readings without physical contact, ideal for screening multiple people or measuring temperature in infants and sensitive environments. Contact thermometers provide more precise core temperature measurements, suitable for clinical assessments or when consistent accuracy is essential for your health monitoring.
Non-contact vs Contact Thermometer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com