Impedance plethysmography measures blood flow and volume changes non-invasively by detecting electrical impedance variations, while dye dilution involves tracking a dye's concentration changes in blood to assess cardiac output and blood volume. Explore the rest of this article to understand which method suits your medical needs best.
Table of Comparison
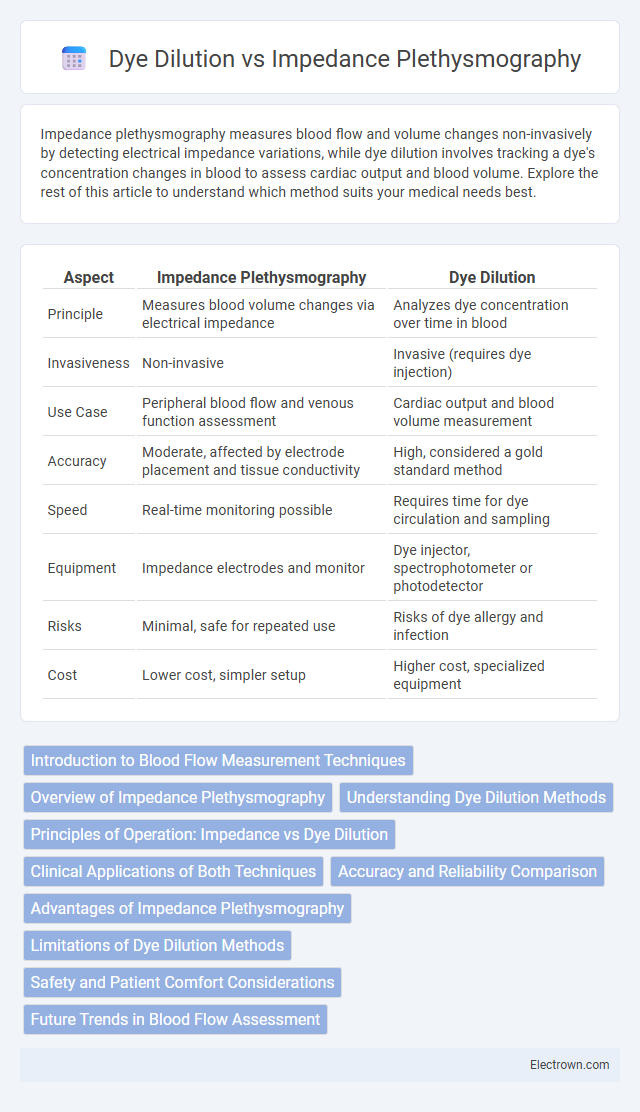
| Aspect | Impedance Plethysmography | Dye Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Measures blood volume changes via electrical impedance | Analyzes dye concentration over time in blood |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Invasive (requires dye injection) |
| Use Case | Peripheral blood flow and venous function assessment | Cardiac output and blood volume measurement |
| Accuracy | Moderate, affected by electrode placement and tissue conductivity | High, considered a gold standard method |
| Speed | Real-time monitoring possible | Requires time for dye circulation and sampling |
| Equipment | Impedance electrodes and monitor | Dye injector, spectrophotometer or photodetector |
| Risks | Minimal, safe for repeated use | Risks of dye allergy and infection |
| Cost | Lower cost, simpler setup | Higher cost, specialized equipment |
Introduction to Blood Flow Measurement Techniques
Impedance plethysmography and dye dilution are key blood flow measurement techniques used in clinical diagnostics and research to assess cardiovascular health. Impedance plethysmography relies on electrical impedance changes in limb tissues to estimate blood volume and flow, offering a non-invasive and continuous monitoring option. Dye dilution involves injecting a tracer dye and measuring its concentration downstream to calculate cardiac output and regional blood flow, providing precise quantitative data for your cardiovascular assessment.
Overview of Impedance Plethysmography
Impedance plethysmography measures blood flow by detecting changes in electrical impedance caused by volume fluctuations within limb segments, offering a noninvasive and continuous assessment of peripheral circulation. It utilizes electrodes placed on the skin to record impedance variations correlating with arterial blood volume during the cardiac cycle. This technique is particularly valuable for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis and evaluating vascular compliance, presenting an alternative to dye dilution methods that require invasive dye injection and blood sampling.
Understanding Dye Dilution Methods
Dye dilution methods measure blood flow and cardiac output by injecting a tracer dye and tracking its concentration changes in the bloodstream using photometric detectors. The technique provides precise quantification of volumetric blood flow and cardiac function, with accuracy relying on homogeneous mixing and minimal dye loss. Compared to impedance plethysmography, dye dilution offers direct visualization of blood passage and is considered a gold standard for validating other flow measurement methods.
Principles of Operation: Impedance vs Dye Dilution
Impedance plethysmography operates by measuring changes in electrical resistance as blood volume fluctuates within a limb, providing real-time data on blood flow and vascular resistance. Dye dilution measures cardiac output and blood flow by tracking the concentration changes of an injected dye over time, using optical sensors to determine the rate at which the dye disperses through the bloodstream. Your choice between these methods depends on the need for non-invasive monitoring with impedance plethysmography or the precise quantification offered by dye dilution techniques.
Clinical Applications of Both Techniques
Impedance Plethysmography is primarily utilized in clinical settings to assess peripheral vascular diseases, including deep vein thrombosis and venous insufficiency, due to its noninvasive measurement of blood volume changes in limbs. Dye Dilution technique serves as a gold standard for determining cardiac output and blood flow by analyzing the concentration of injected indicator dyes in the bloodstream, making it essential in cardiology and hemodynamic monitoring. Both methods offer critical diagnostic information, with Impedance Plethysmography favoring vascular assessments and Dye Dilution providing precise quantitative evaluation of cardiac function.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Impedance plethysmography offers non-invasive monitoring with moderate accuracy for detecting blood flow changes, while dye dilution provides higher precision through direct measurement of cardiac output using indicator dyes. Dye dilution is considered more reliable in clinical settings requiring exact quantitative data due to its established validation and reproducibility. Variability in impedance plethysmography results can occur from electrode placement and patient movement, influencing its consistency compared to the more robust dye dilution method.
Advantages of Impedance Plethysmography
Impedance plethysmography offers non-invasive and continuous monitoring of blood flow and volume changes, making it more patient-friendly compared to the invasive dye dilution method. It provides real-time results without the need for contrast agents or radiation exposure, reducing risk and discomfort during cardiovascular assessments. You benefit from quicker, safer diagnostics ideal for detecting peripheral vascular diseases and evaluating venous function with high sensitivity.
Limitations of Dye Dilution Methods
Dye dilution methods for measuring cardiac output are limited by potential inaccuracies due to dye recirculation and the requirement for precise timing during indicator injection and blood sampling. These methods also involve invasive procedures and reliance on chemical tracers, which can introduce errors related to dye mixing and distribution inconsistencies. Compared to impedance plethysmography, dye dilution suffers from longer processing times and increased complexity in dynamic physiological conditions.
Safety and Patient Comfort Considerations
Impedance plethysmography offers enhanced safety by being non-invasive, eliminating risks associated with dye injection such as allergic reactions or nephrotoxicity in dye dilution methods. Patient comfort is significantly improved with impedance plethysmography due to its painless electrodes placement compared to the dye dilution technique, which requires venous access and may cause discomfort or anxiety. These factors make impedance plethysmography a preferable option for repeated cardiovascular assessments, especially in vulnerable patient populations.
Future Trends in Blood Flow Assessment
Impedance plethysmography is advancing with wearable sensor integration and real-time data analytics, improving non-invasive blood flow monitoring accuracy and patient comfort. Dye dilution techniques, while highly precise, are likely to see reduced clinical use due to invasive nature and emerging alternatives offering faster, cost-effective results. Future trends emphasize combining impedance plethysmography with artificial intelligence for enhanced diagnostic capabilities and personalized vascular health assessments.
Impedance Plethysmography vs Dye Dilution Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com