A photoplethysmogram (PPG) is a non-invasive optical technique that measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, while a pulse oximeter uses PPG technology specifically to estimate blood oxygen saturation levels and heart rate. Discover how understanding the differences between these two devices can enhance Your ability to monitor vital health parameters effectively by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
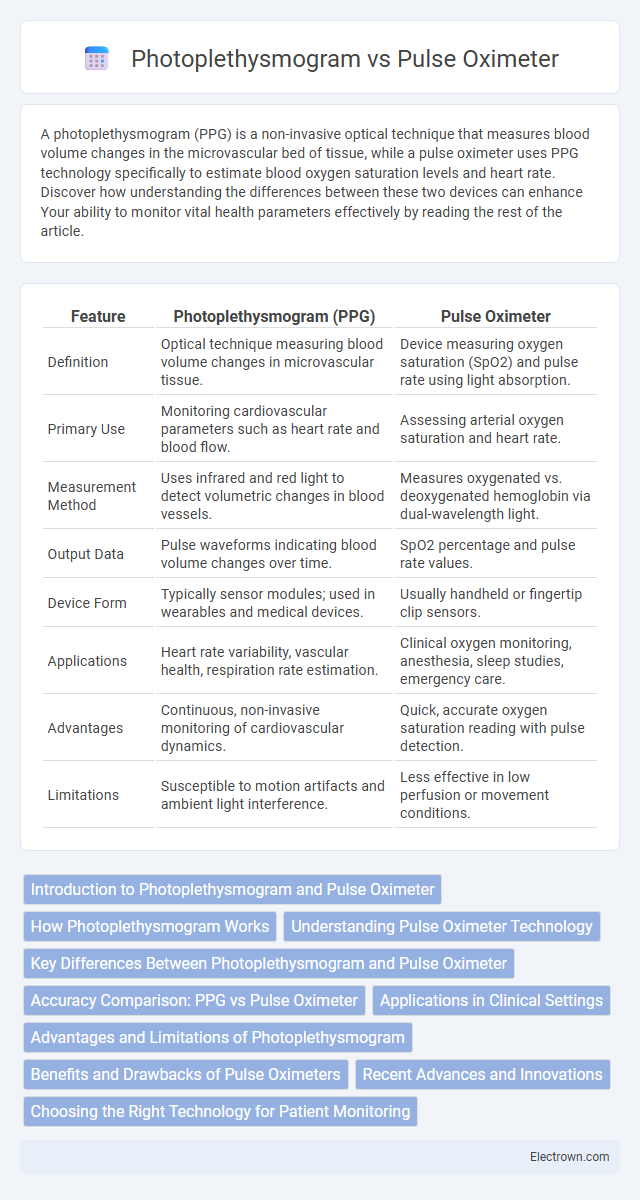
| Feature | Photoplethysmogram (PPG) | Pulse Oximeter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optical technique measuring blood volume changes in microvascular tissue. | Device measuring oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rate using light absorption. |
| Primary Use | Monitoring cardiovascular parameters such as heart rate and blood flow. | Assessing arterial oxygen saturation and heart rate. |
| Measurement Method | Uses infrared and red light to detect volumetric changes in blood vessels. | Measures oxygenated vs. deoxygenated hemoglobin via dual-wavelength light. |
| Output Data | Pulse waveforms indicating blood volume changes over time. | SpO2 percentage and pulse rate values. |
| Device Form | Typically sensor modules; used in wearables and medical devices. | Usually handheld or fingertip clip sensors. |
| Applications | Heart rate variability, vascular health, respiration rate estimation. | Clinical oxygen monitoring, anesthesia, sleep studies, emergency care. |
| Advantages | Continuous, non-invasive monitoring of cardiovascular dynamics. | Quick, accurate oxygen saturation reading with pulse detection. |
| Limitations | Susceptible to motion artifacts and ambient light interference. | Less effective in low perfusion or movement conditions. |
Introduction to Photoplethysmogram and Pulse Oximeter
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) is a non-invasive optical technique that measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, primarily used to monitor heart rate and blood flow dynamics. Pulse oximeter, a medical device employing PPG technology, estimates oxygen saturation levels (SpO2) in arterial blood by analyzing the variations in light absorption during pulsatile blood flow. Both tools are vital in clinical settings for cardiovascular and respiratory monitoring due to their real-time data acquisition and ease of use.
How Photoplethysmogram Works
A Photoplethysmogram (PPG) measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue using a light source and photodetector. The device emits infrared or red light waves that penetrate the skin, detecting variations in light absorption caused by pulsatile blood flow. This data allows for non-invasive monitoring of heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, and vascular health.
Understanding Pulse Oximeter Technology
Pulse oximeter technology relies on photoplethysmogram (PPG) signals to measure blood oxygen saturation non-invasively. The device emits light wavelengths through the skin, detecting blood volume changes in the microvascular bed to calculate oxygen levels and pulse rate accurately. Your understanding of this technology highlights how PPG forms the foundational principle behind the pulse oximeter's ability to provide real-time oxygen monitoring.
Key Differences Between Photoplethysmogram and Pulse Oximeter
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) measures blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue using a light-based technology, primarily capturing cardiovascular dynamics. Pulse oximeter utilizes PPG principles but specifically assesses oxygen saturation (SpO2) in the blood by analyzing the absorption of red and infrared light wavelengths. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right device for monitoring either vascular health or blood oxygen levels accurately.
Accuracy Comparison: PPG vs Pulse Oximeter
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensors detect blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, providing accurate and continuous heart rate data, but their accuracy can be affected by motion artifacts and ambient light interference. Pulse oximeters combine PPG technology with red and infrared light absorption measurements to offer more precise oxygen saturation levels (SpO2) along with pulse rate, making them more reliable for clinical use. Your choice between PPG alone or a pulse oximeter should consider the need for oxygen saturation accuracy alongside heart rate monitoring.
Applications in Clinical Settings
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) technology is widely used in clinical settings for monitoring blood volume changes in microvascular beds, aiding in cardiovascular assessments, and detecting peripheral circulation abnormalities. Pulse oximeters utilize PPG signals to non-invasively measure arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rate, proving essential in anesthesia, critical care, and respiratory disease management. The integration of PPG-based pulse oximetry supports continuous patient monitoring and early detection of hypoxemia in various medical environments.
Advantages and Limitations of Photoplethysmogram
The photoplethysmogram (PPG) offers advantages such as non-invasive measurement, cost-effectiveness, and portability, allowing continuous monitoring of blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. However, PPG signals are susceptible to motion artifacts, ambient light interference, and limited accuracy in patients with poor peripheral perfusion or darker skin tones. Unlike pulse oximeters that combine PPG with red and infrared light absorption for oxygen saturation, PPG alone primarily provides heart rate and blood flow information without direct oxygen level assessment.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Pulse Oximeters
Pulse oximeters offer non-invasive, continuous monitoring of blood oxygen saturation and pulse rate, providing quick and accurate readings essential in clinical and home settings. Their portability and ease of use make them beneficial for managing respiratory conditions, but drawbacks include potential inaccuracies caused by motion artifacts, poor circulation, or skin pigmentation. Understanding these limitations helps you rely on pulse oximeters effectively while considering supplementary diagnostic tools when necessary.
Recent Advances and Innovations
Recent advances in Photoplethysmogram (PPG) technology have enhanced signal processing algorithms, enabling more accurate and continuous cardiovascular monitoring. Pulse oximeters now integrate multi-wavelength sensors and AI-driven analytics to improve oxygen saturation measurement precision under motion and low perfusion conditions. Innovations in wearable devices combine PPG and pulse oximetry to provide real-time health insights through non-invasive, compact form factors.
Choosing the Right Technology for Patient Monitoring
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) provides real-time monitoring of blood volume changes within the microvascular bed, making it essential for assessing cardiovascular health, while pulse oximeters specifically measure oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rate using PPG technology. Selecting the right device depends on clinical needs: PPG offers detailed vascular information beneficial for blood flow analysis, whereas pulse oximeters prioritize oxygenation levels critical in respiratory care. Accurate patient monitoring relies on understanding these technological distinctions to enhance diagnostic precision and treatment efficacy.
Photoplethysmogram vs Pulse Oximeter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com