Star ground configurations centralize electrical connections to reduce noise and interference, while daisy chain grounds link components in series, which can introduce signal degradation and ground loops. Discover how choosing the right grounding method can enhance your circuit's performance and reliability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
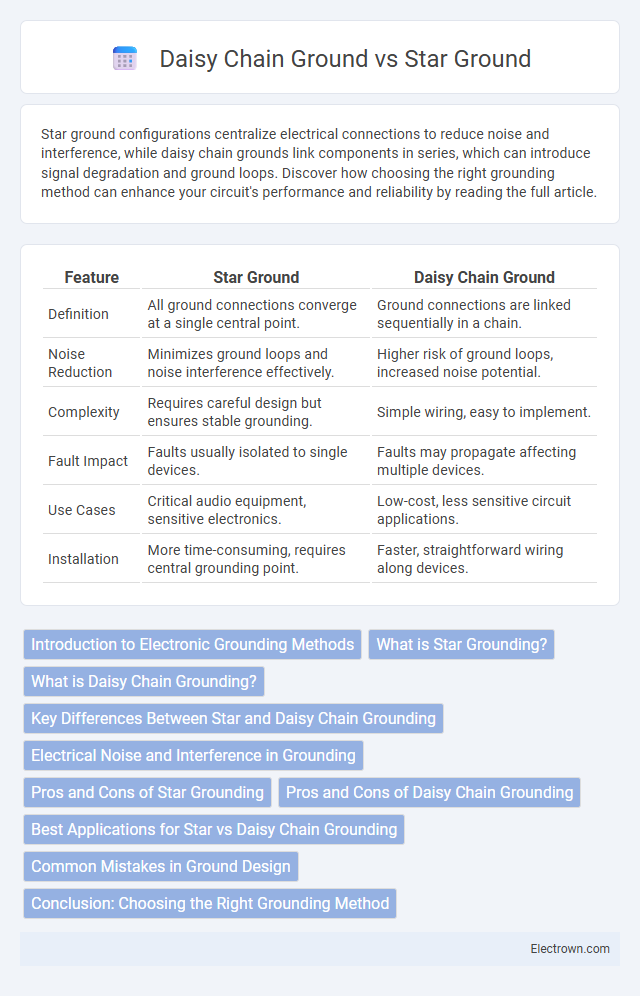
| Feature | Star Ground | Daisy Chain Ground |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All ground connections converge at a single central point. | Ground connections are linked sequentially in a chain. |
| Noise Reduction | Minimizes ground loops and noise interference effectively. | Higher risk of ground loops, increased noise potential. |
| Complexity | Requires careful design but ensures stable grounding. | Simple wiring, easy to implement. |
| Fault Impact | Faults usually isolated to single devices. | Faults may propagate affecting multiple devices. |
| Use Cases | Critical audio equipment, sensitive electronics. | Low-cost, less sensitive circuit applications. |
| Installation | More time-consuming, requires central grounding point. | Faster, straightforward wiring along devices. |
Introduction to Electronic Grounding Methods
Star ground and daisy chain ground are two common electronic grounding methods used to reduce noise and interference in circuits. Star grounding connects all ground points to a single central node, minimizing ground loops and voltage drops, which improves signal integrity in sensitive analog and mixed-signal designs. Daisy chain grounding links ground points sequentially, offering simplicity but increasing the risk of noise coupling and reduced performance in high-frequency or high-precision applications.
What is Star Grounding?
Star grounding is an electrical grounding method where all ground connections originate from a single central point, minimizing ground loops and reducing electromagnetic interference. This technique ensures that each device or circuit has its own dedicated ground path, improving signal integrity and noise performance. Star grounding is commonly used in sensitive audio, RF, and precision measurement systems to maintain a stable reference potential.
What is Daisy Chain Grounding?
Daisy chain grounding is a wiring method where multiple devices share a single continuous ground path, connecting from one device to the next in series. This approach can introduce noise and interference due to shared ground impedance, making it less effective for sensitive electronics compared to star grounding. Star grounding uses a central ground point to minimize ground loops and ensure stable, low-noise grounding connections across all components.
Key Differences Between Star and Daisy Chain Grounding
Star grounding features a single central grounding point where all ground wires converge, reducing electrical noise and interference by providing a low-impedance return path. Daisy chain grounding connects multiple ground points in series, which can introduce noise due to voltage drops along the chain, potentially affecting signal integrity. For your sensitive electronic setups, star grounding ensures cleaner signals by minimizing ground loops and maintaining consistent reference potential throughout the system.
Electrical Noise and Interference in Grounding
Star ground systems reduce electrical noise and interference by connecting all ground points to a single common node, minimizing ground loop currents and voltage differentials. Daisy chain grounding can increase susceptibility to noise due to the sequential connection of ground points, which may create unintentional ground loops and voltage drops along the chain. Proper star grounding is critical in sensitive electronic systems to ensure signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference.
Pros and Cons of Star Grounding
Star grounding offers superior noise reduction by connecting all ground points to a single central node, minimizing ground loops and electrical interference in complex circuits. Its main drawback lies in the increased complexity of layout design and potential signal integrity issues if the central ground node becomes overloaded. Despite these challenges, star grounding is preferred in high-precision applications such as audio equipment and sensitive measurement instruments for its effective isolation of noise pathways.
Pros and Cons of Daisy Chain Grounding
Daisy Chain Grounding simplifies wiring by connecting multiple devices in series to a single ground path, reducing cable bulk and installation time. However, it risks ground loops and increased noise interference, which can degrade signal integrity and affect sensitive equipment performance. For your setup, careful consideration is needed to balance ease of installation against potential grounding issues.
Best Applications for Star vs Daisy Chain Grounding
Star grounding is best suited for sensitive electronic equipment and audio systems where minimizing ground loops and electrical noise is critical, ensuring a single reference point for all ground connections. Daisy chain grounding is ideal for simpler, low-noise environments or where equipment is arranged sequentially, such as in lighting installations or basic control circuits, allowing a streamlined and cost-effective grounding path. Choosing star grounding enhances signal integrity in complex systems, while daisy chain grounding simplifies wiring in less demanding applications.
Common Mistakes in Ground Design
Common mistakes in ground design often arise from improper implementation of star ground and daisy chain ground techniques, leading to noise interference and signal integrity issues. Star ground systems typically suffer when multiple ground paths are inadvertently connected, causing ground loops and increased electromagnetic interference. Daisy chain grounds, if not carefully managed, can introduce voltage drops and ground potential differences, compromising your circuit's performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Grounding Method
Star ground grounding minimizes interference by connecting all ground points to a single node, ideal for sensitive audio and precision electronics where noise reduction is critical. Daisy chain grounding links components sequentially, suitable for simpler circuits with lower sensitivity to ground noise but risks ground loops in complex setups. Selecting the appropriate grounding method depends on circuit complexity and noise sensitivity, with star grounding favored for high-fidelity applications and daisy chaining acceptable for less demanding environments.
Star Ground vs Daisy Chain Ground Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com