FET amplifiers offer high input impedance and low noise, making them ideal for sensitive signal applications, while BJT amplifiers provide higher gain and faster response suitable for high-frequency circuits. Explore the full article to determine which amplifier best fits Your electronic design needs.
Table of Comparison
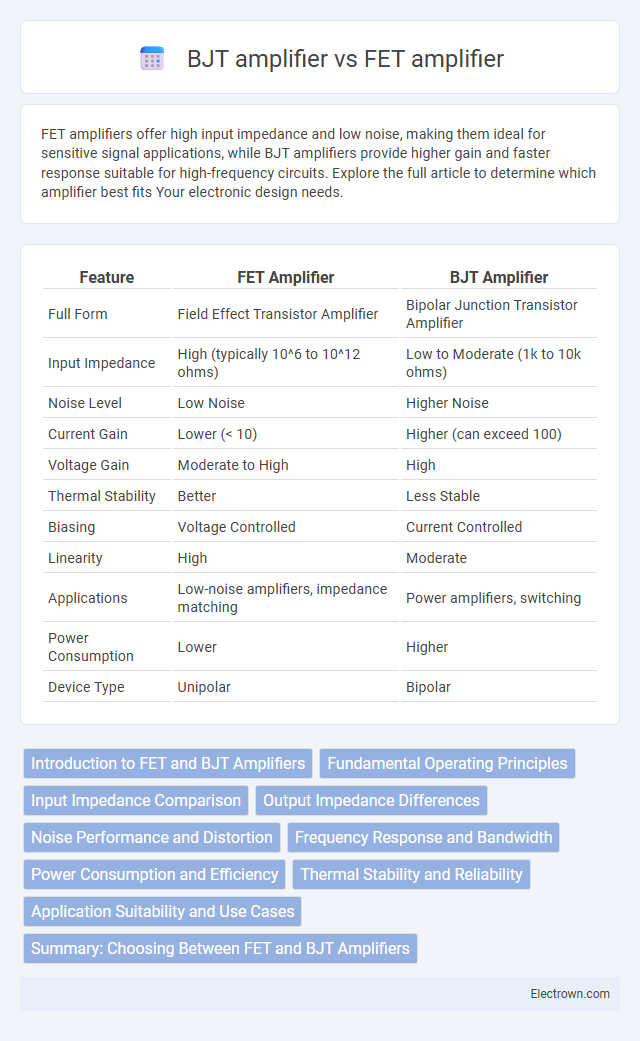
| Feature | FET Amplifier | BJT Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Field Effect Transistor Amplifier | Bipolar Junction Transistor Amplifier |
| Input Impedance | High (typically 10^6 to 10^12 ohms) | Low to Moderate (1k to 10k ohms) |
| Noise Level | Low Noise | Higher Noise |
| Current Gain | Lower (< 10) | Higher (can exceed 100) |
| Voltage Gain | Moderate to High | High |
| Thermal Stability | Better | Less Stable |
| Biasing | Voltage Controlled | Current Controlled |
| Linearity | High | Moderate |
| Applications | Low-noise amplifiers, impedance matching | Power amplifiers, switching |
| Power Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Device Type | Unipolar | Bipolar |
Introduction to FET and BJT Amplifiers
FET amplifiers utilize field-effect transistors, which control output current via an electric field, offering high input impedance and low noise characteristics ideal for sensitive signal amplification. BJT amplifiers employ bipolar junction transistors that operate through current injection, providing higher gain and faster switching speeds but with lower input impedance and increased noise levels. Choosing between FET and BJT amplifiers depends on application-specific requirements like input impedance, gain, noise performance, and frequency response.
Fundamental Operating Principles
FET amplifiers operate based on voltage-controlled current flow through a semiconductor channel, relying on the electric field to modulate conductivity, while BJT amplifiers function via current-controlled current flow between emitter and collector regions. The high input impedance of FETs stems from their insulated gate structure, contrasting with BJTs' lower input impedance due to base current requirements. Your choice between FET and BJT amplifiers depends on factors such as input impedance, noise performance, and linearity, all dictated by these fundamental operating principles.
Input Impedance Comparison
FET amplifiers typically offer much higher input impedance, often in the megaohm range, compared to BJT amplifiers which generally have input impedance in the kiloohm range. This high input impedance of FET amplifiers minimizes the loading effect on the preceding circuit, preserving signal integrity. Understanding this key difference can help you choose the right amplifier for applications requiring minimal signal distortion and maximum sensitivity.
Output Impedance Differences
FET amplifiers exhibit a higher output impedance due to the transistor's field-effect control, typically ranging from tens of kilo-ohms to mega-ohms, which benefits voltage amplification with minimal loading on subsequent stages. BJT amplifiers have lower output impedance, often in the range of a few hundred ohms to a few kilo-ohms, making them more suitable for driving low-impedance loads and providing higher current gain. These fundamental output impedance differences influence the selection of amplifier types in circuit design based on desired load driving capabilities and signal integrity.
Noise Performance and Distortion
FET amplifiers exhibit lower noise levels due to their high input impedance and reduced flicker noise, making them ideal for low-noise applications. BJT amplifiers often generate higher distortion but can provide better linearity at high gain, benefiting audio amplification tasks. Noise performance in FET amplifiers surpasses that of BJTs, while BJT amplifiers deliver superior gain linearity with potential distortion trade-offs.
Frequency Response and Bandwidth
FET amplifiers typically exhibit higher input impedance and lower noise, resulting in better high-frequency response and wider bandwidth compared to BJT amplifiers. BJT amplifiers often have faster switching speeds but suffer from higher input capacitance, limiting their performance at very high frequencies. Hence, FET amplifiers are preferred in RF and microwave applications where extended frequency response and broader bandwidth are critical.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
FET amplifiers exhibit lower power consumption due to their high input impedance and minimal gate current, making them highly efficient for low-power applications. BJT amplifiers consume more power because of continuous base current, resulting in reduced efficiency but offering higher gain and linearity. Efficiency in FET amplifiers typically exceeds that of BJTs in battery-operated or integrated circuit environments, optimizing energy use in modern electronics.
Thermal Stability and Reliability
FET amplifiers exhibit superior thermal stability compared to BJT amplifiers because their operation relies on voltage-controlled channels, reducing thermal runaway risks and maintaining consistent gain over temperature variations. BJT amplifiers are more susceptible to thermal instability due to the exponential increase in collector current with temperature, necessitating additional bias stabilization techniques to ensure reliability. Consequently, FET amplifiers often offer enhanced reliability in high-temperature environments, making them preferable for applications requiring stable performance under thermal stress.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
FET amplifiers excel in high-frequency applications and low-noise environments due to their high input impedance and low thermal noise, making them suitable for RF circuits and sensitive sensor interfaces. BJT amplifiers offer high gain and better linearity, which makes them ideal for audio amplification and power stages requiring robust current driving capabilities. Your choice between FET and BJT amplifiers largely depends on whether you prioritize noise performance and input sensitivity or voltage gain and current handling.
Summary: Choosing Between FET and BJT Amplifiers
FET amplifiers offer high input impedance and low noise, making them ideal for sensitive signal applications, while BJT amplifiers provide higher gain and better linearity, suitable for driving heavier loads. Your choice between FET and BJT amplifiers depends on whether input impedance, noise performance, or gain and robustness are more critical for your circuit. Evaluating these key parameters ensures optimal amplifier selection tailored to your electronic design needs.
FET amplifier vs BJT amplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com